Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
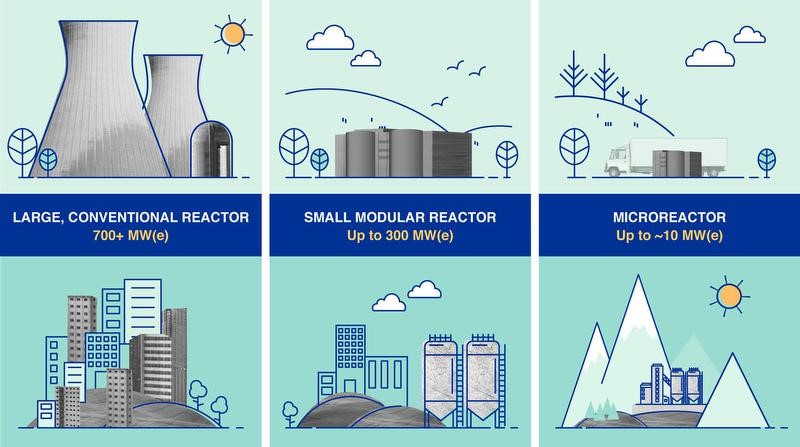
- Conventional nuclear power plants often suffer from time and cost overruns. As an alternative, several countries are developing small modular reactors (SMRs) — nuclear reactors with a maximum capacity of 300 MW — to complement conventional NPPs.
Details
Introduction
- The global pursuit of decarbonization, aligned with the UN Sustainable Development Goal 7, highlights the need for accessible, sustainable, and modern energy sources.
- As the world transitions away from fossil fuels, the power sector's decarbonization becomes crucial.
- To address this challenge, small modular reactors (SMRs), a type of nuclear reactor, have emerged as a potential solution to provide reliable low-carbon electricity.
- Studies have found that SMRs can be safely installed and operated at several brownfield sites that may not meet the more stringent zoning requirements for conventional NPPs.
- Most land-based SMR designs require low-enriched uranium, which can be supplied by all countries that possess uranium mines and facilities for such enrichment if the recipient facility is operating according to international standards.
- Since SMRs are mostly manufactured in a factory and assembled on site, the potential for time and cost overruns is also lower.
Understanding SMRs
- SMRs are compact nuclear reactors with a maximum capacity of 300 MW, designed to complement conventional nuclear power plants (NPPs).
- They feature enhanced safety measures, simpler designs, and passive safety features, reducing the potential for uncontrolled radioactive material release.
- SMRs can be installed in decommissioned thermal power plant sites, reducing the need for additional land acquisition.
Challenges of Decarbonization
- While renewable energy sources like solar and wind play a vital role, a firm power-generating technology is needed for grid stability and reliability.
- The transition to clean energy demands critical minerals like lithium and rare earth elements, posing challenges due to increased demand and geopolitical risks.
Advantages of SMRs
- SMRs offer lower core damage frequency and source term compared to conventional NPPs, enhancing safety.
- They can be installed at brownfield sites, simplifying regulatory approvals and reducing land requirements.
- SMRs are manufactured in factories, minimizing time and cost overruns, and their lower spent nuclear fuel storage reduces environmental impact.
- The term "modular" signifies their modular construction approach, allowing for factory assembly and simplified on-site installation.
Grid Integration and Energy Security
- Nuclear power plants generate 10% of global electricity, aiding in emissions reduction and providing stable power supply.
- Conventional NPPs have faced time and cost overruns, leading to the development of SMRs to complement existing plants.
- Integrating SMRs under international safeguards can help India move closer to net-zero, given uranium's wider distribution compared to critical minerals.

Applications and Use Cases
- Remote Communities: SMRs can provide clean and reliable energy to remote communities, replacing diesel generators and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Industrial Complexes: They can serve as a dependable energy source for energy-intensive industries such as mining, desalination, and manufacturing.
- Urban Areas: SMRs can supplement urban energy grids, enhancing reliability while minimizing emissions.
- Decarbonization: Their 24/7 power generation capability can complement renewable energy sources, aiding in the decarbonization of power generation.
Challenges and Considerations
- Regulatory Framework: Establishing efficient and harmonized regulatory frameworks for SMRs across different jurisdictions remains a challenge.
- Public Perception: Overcoming public concerns related to nuclear energy, safety, and waste management is crucial for widespread SMR acceptance.
- Capital Investment: While potential cost savings are anticipated, initial capital investment for SMR development and deployment may be significant.
- Fuel Supply: Ensuring a sustainable and reliable supply of fuel, such as enriched uranium, is essential for the continuous operation of SMRs.
Global Developments
- International Interest: Many countries, including the United States, Canada, Russia, and China, are investing in SMR research, development, and deployment.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Partnerships between governments, research institutions, and private companies are driving SMR innovation and technology advancement.
- Research and Demonstration: Some SMR designs are already in advanced stages of development, with prototypes being tested and evaluated for safety and efficiency.
Role in Energy Transition
- Carbon Mitigation: SMRs offer a low-carbon alternative to fossil fuel-based power generation, contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Energy Security: Their reliable and continuous power output can enhance energy security by reducing dependency on volatile fuel markets.
- Economic Growth: SMR deployment can stimulate economic growth through job creation, technological innovation, and infrastructure development.
India's Energy Landscape
- SMRs can aid India's ambitious target of becoming net-zero by 2070 by expanding nuclear power.
- Private sector investments are essential, requiring amendments to the Atomic Energy Act and enactment of laws for safety and regulatory oversight.
- Public perception of nuclear power can be improved through comprehensive dissemination of environmental and public health data.

Conclusion
SMRs offer promise in India's journey towards decarbonization and net-zero emissions. Their enhanced safety features, compatibility with existing infrastructure, and potential for private sector investments make them an attractive option. However, efficient regulatory frameworks, collaboration among nations, and public awareness are essential to harness SMRs' benefits and contribute to a sustainable energy future.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Discuss the concept of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and their potential role in addressing the challenges of decarbonization and providing clean, reliable energy. (250 Words)
|
https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/47118/OPS/G7BBJKJST.1+GERBJM7J5.1.html