Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended.
Context:
- As per a study, Acidification may strip Indian soils of 3.3 billion tonnes of essential carbon, affecting crop growth, sequestration.
Details of the study:
- Acidification may lead to the loss of approximately 3.3 billion tonnes of essential carbon from Indian soils. This loss could have significant implications for crop growth and carbon sequestration.
- Research suggests that acidification could cause a decline in the carbon content of Indian soils, affecting their fertility and ability to support agricultural productivity.
- Acidification-induced loss of soil carbon could hinder efforts to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through soil-based carbon storage. This could impede climate change mitigation efforts and exacerbate environmental challenges.
Soil acidification status in India
- Soil acidification has affected about 48 million hectares (mha) out of 142 mha of arable land.
- Acidic soils in India are widespread in the humid southwestern, northeastern, and Himalayan regions. The northeastern region, in particular, has recorded acidity in approximately 95 percent of the soils.
Suggestions from the study:
- Need for Mitigation Strategies:
- The findings underscore the urgency of implementing mitigation strategies to address soil acidification and preserve soil carbon levels.
- Effective soil management practices
- Effective soil management practices, such as liming and organic matter addition, may help mitigate the impacts of acidification and maintain soil fertility.
- Policy Implications:
- Policymakers and agricultural stakeholders need to prioritize soil health and implement measures to prevent soil acidification.
- Integrated approaches
- Integrated approaches that combine soil conservation, sustainable land management, and agricultural practices are essential for mitigating the adverse effects of soil acidification on crop productivity and carbon sequestration.
|
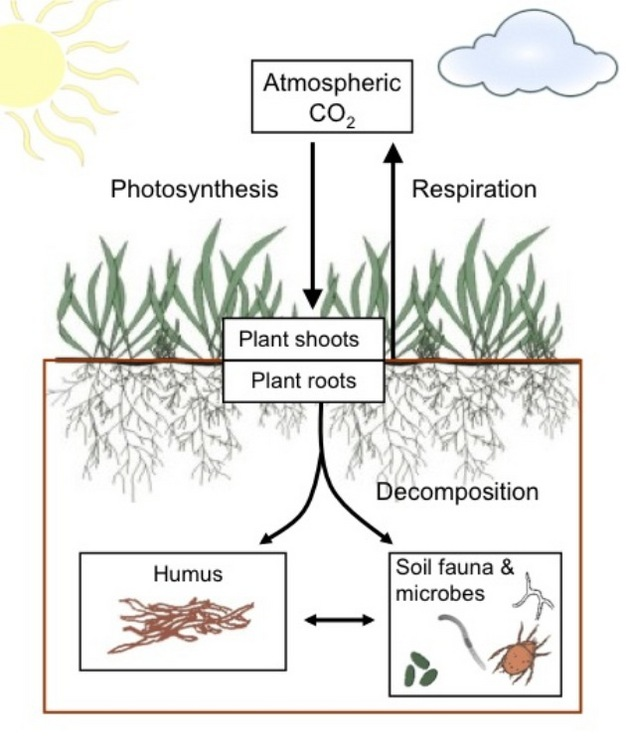
Soil carbon
●Soil carbon is the solid carbon stored in global soils. This includes both soil organic matter and inorganic carbon as carbonate minerals.
●Carbon in soil can be stored in the form of SIC or soil organic carbon (SOC). The former includes mineral forms of carbon like calcium carbonate produced by weathering parent material in soil or from the reaction of soil minerals with atmospheric carbon dioxide.
●Soil organic carbon (SOC) is the carbon that remains in the soil after partial decomposition of any material produced by living organisms. It constitutes a key element of the global carbon cycle through the atmosphere, vegetation, soil, rivers, and the ocean.
●Together, soils store more than thrice the quantity of carbon in vegetation or double the quantity of carbon in the atmosphere.
|
Source:
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/environment/acidification-may-strip-indian-soils-of-3-3-billion-tonnes-of-essential-carbon-affecting-crop-growth-sequestration-study-95561
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Discuss the implications of soil acidification on Indian agriculture and carbon sequestration, as highlighted by the study. Examine the extent of soil acidification in India and evaluate the suggested mitigation strategies. Assess the policy implications and propose integrated approaches to address soil acidification, ensuring soil health and sustainable agricultural practices. (250 Words)
|















