Description
Context
- Indian stem cell and developmental biologist Prof. Maneesha S Inamdar has been part of the WHO Expert Advisory Committee on Developing Global Standards for Governance and Oversight of Human Genome Editing.
About
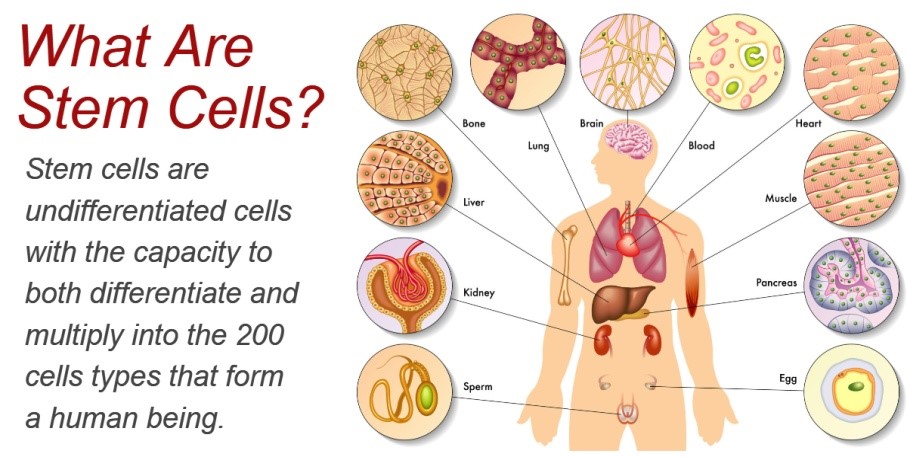
- Stem cells are the body's raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated.
- Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells.
- These daughter cells either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or become specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells.
- No other cell in the body has the natural ability to generate new cell types.
- They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms.
- They serve as a repair system for the body.
|
Embryonic stem cells
· Embryonic stem cells supply new cells for an embryo as it grows and develops into a baby.
· These stem cells are said to be pluripotent, which means they can change into any cell in the body.
Adult stem cells
· Adult stem cells supply new cells as an organism grows and to replace cells that get damaged.
· Adult stem cells are said to be multipotent, which means they can only change into some cells in the body, not any cell, for example:
· Blood (or 'haematopoietic') stem cells can only replace the various types of cells in the blood.
· Skin (or 'epithelial') stem cells provide the different types of cells that make up our skin and hair.
|
Why are stem cells useful?
- Helps us understand the basic biology of how living things work and what happens in different types of cell during disease.
- Therapy – to replace lost or damaged cells that our bodies can’t replace naturally.
- Grow new cells in a laboratory to replace damaged organs or tissues
- Correct parts of organs that don’t work properly
- Research causes of genetic defects in cells
- Research how diseases occur or why certain cells develop into cancer cells
- Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness
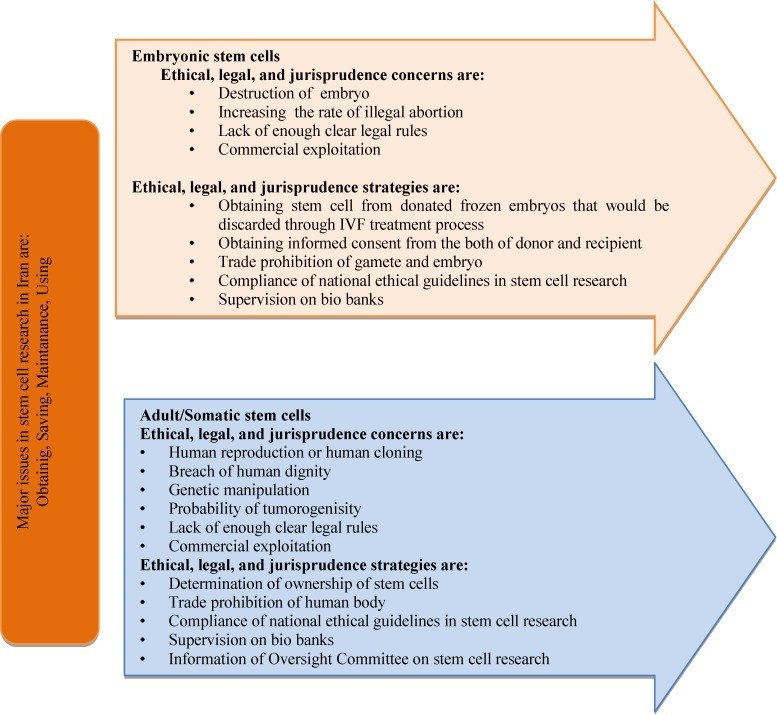
Issues in Stem Cell Research and Way Ahead
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1734868
















