Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Iran attempts to seize two oil tankers near the Strait of Hormuz.
Details
- In the early hours of Wednesday, Iran made an attempt to seize two oil tankers near the strategically significant Strait of Hormuz.
- The US Navy reported that one of the tankers was fired upon by Iranian naval vessels but retreated after the US Navy's response.
- Tensions between Iran and the United States have been escalating since the US withdrawal from the 2015 nuclear agreement.
Incident Details
- Two oil tankers were targeted by Iranian naval vessels in the Gulf of Oman and off the coast of Muscat, Oman's capital.
- The first incident involved the TRF Moss, a Marshall Islands-flagged tanker, approached by an Iranian naval vessel.
- The second incident occurred three hours later with the Richmond Voyager, a Bahamian-flagged tanker, being ordered to stop by an Iranian naval vessel.
US Navy Response
- The US Navy promptly responded to both incidents.
- The USS McFaul, a guided-missile destroyer, along with an MQ-9 Reaper drone and a P-8 Poseidon patrol plane, were deployed in response.
- The destroyer approached the tankers at maximum speed to ensure their safety.
Iranian Naval Provocations
- Iran has a history of seizing and harassing commercial vessels in the region.
- At least five commercial vessels have been seized by Iran in the past two years, with over a dozen others harassed.
- Most incidents occur in and around the Strait of Hormuz, a critical passage for global crude oil transportation.
Motives behind Iranian Actions
- Iran has used the seizure of commercial vessels as a bargaining tool in negotiations with the West.
- Previous incidents, such as the seizure of a US-bound oil tanker in April, have been justified by Iran as responses to collisions or other claims without providing evidence.

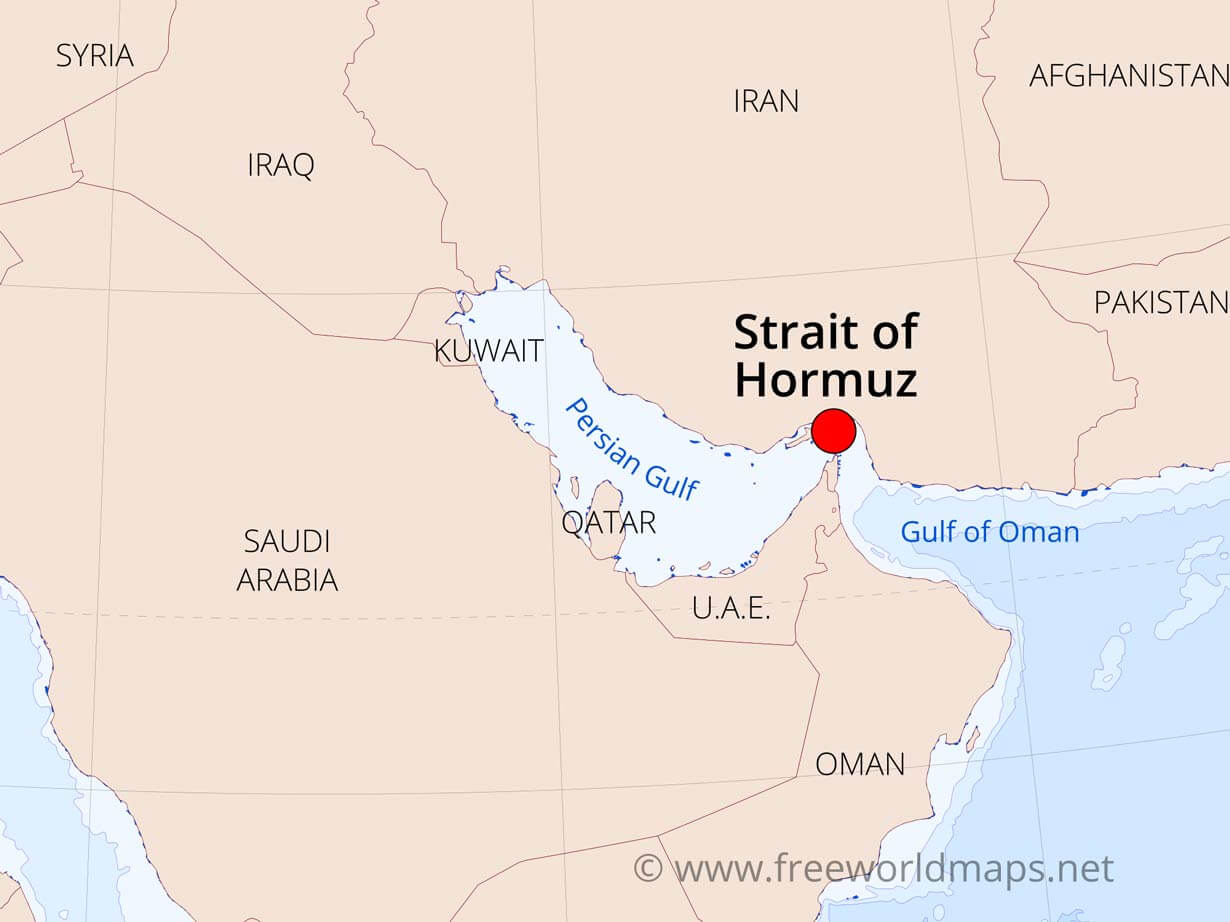
About Strait of Hormuz
- The Strait of Hormuz is a narrow waterway located between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman.
- It serves as a crucial maritime choke point, connecting the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea.
Geographic Location
- The strait is situated at the entrance of the Persian Gulf, bordered by Iran to the north and the United Arab Emirates and Oman to the south.
Strategic Importance
- Approximately 20% of the world's crude oil passes through the Strait of Hormuz, making it one of the most important shipping lanes globally.
- The strait is a key conduit for oil exports from major oil-producing countries in the Persian Gulf, including Iran, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq, and the UAE.
- Any disruption or closure of the strait could have a significant impact on global energy markets, leading to increased oil prices and potential supply shortages.
Width and Length
- The strait is approximately 33 nautical miles wide at its narrowest point.
- It stretches for about 96 nautical miles, extending from the Musandam Peninsula in Oman to the Iranian coast.
Traffic Volume
- The strait witnesses heavy maritime traffic with an estimated 17 million barrels of oil passing through it each day.
- Besides oil tankers, the strait accommodates various vessel types, including container ships, cargo vessels, and naval warships.
International Law and Jurisdiction
- The Strait of Hormuz is considered international waters, allowing vessels from different nations to navigate through it.
- Ownership and jurisdictional disputes between Iran and neighboring countries have occasionally emerged, leading to tensions in the region.
Security Concerns
- The strait has been a site of regional tensions, including naval confrontations and incidents between Iran and international forces.
- Piracy and armed robbery against vessels have been reported in the region, requiring international naval patrols and security measures.
Geopolitical Significance
- The strait's location influences geopolitical dynamics, as it provides leverage for regional powers and influences their relationships with international actors.
- Various countries maintain a military presence in the area to protect their interests and ensure the security of maritime traffic.
Environmental Considerations
- The strait is home to diverse marine life and delicate ecosystems, making it important to balance maritime activities with environmental preservation efforts.
- The high volume of oil tanker traffic raises concerns about potential oil spills, which could have severe environmental consequences.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Discuss the strategic importance of the Strait of Hormuz and its implications for global energy security. (150 words)
|

https://www.wionews.com/world/iran-attempts-to-seize-oil-tankers-in-strait-of-hormuz-prompts-us-navy-response-612454











