Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The government move to allow the use of surety insurance bonds as a substitute for bank guarantees is likely to take time for implementation by the insurance industry.
What purpose does a surety bond serve?
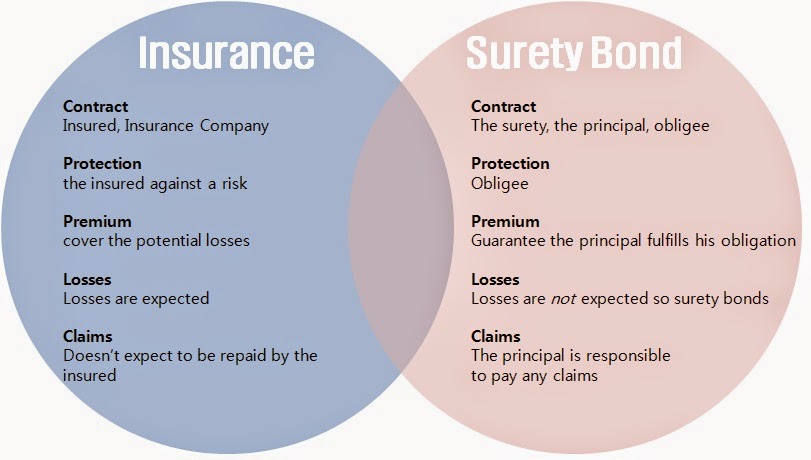
- A surety bond is a contract between the person who needs to be bonded and the bonding company. It guarantees that if an event such as negligence, fraud, or dishonesty takes place on behalf of this individual in their professional capacity, they will repay any damages caused. The most common use for these bonds is for contractors.
- A surety bond is provided by the insurance company on behalf of the contractor to the entity, which is awarding the project. When a principal breaks a bond’s terms, the harmed party can make a claim on the bond to recover losses.
What Does a Surety Bond Mean?
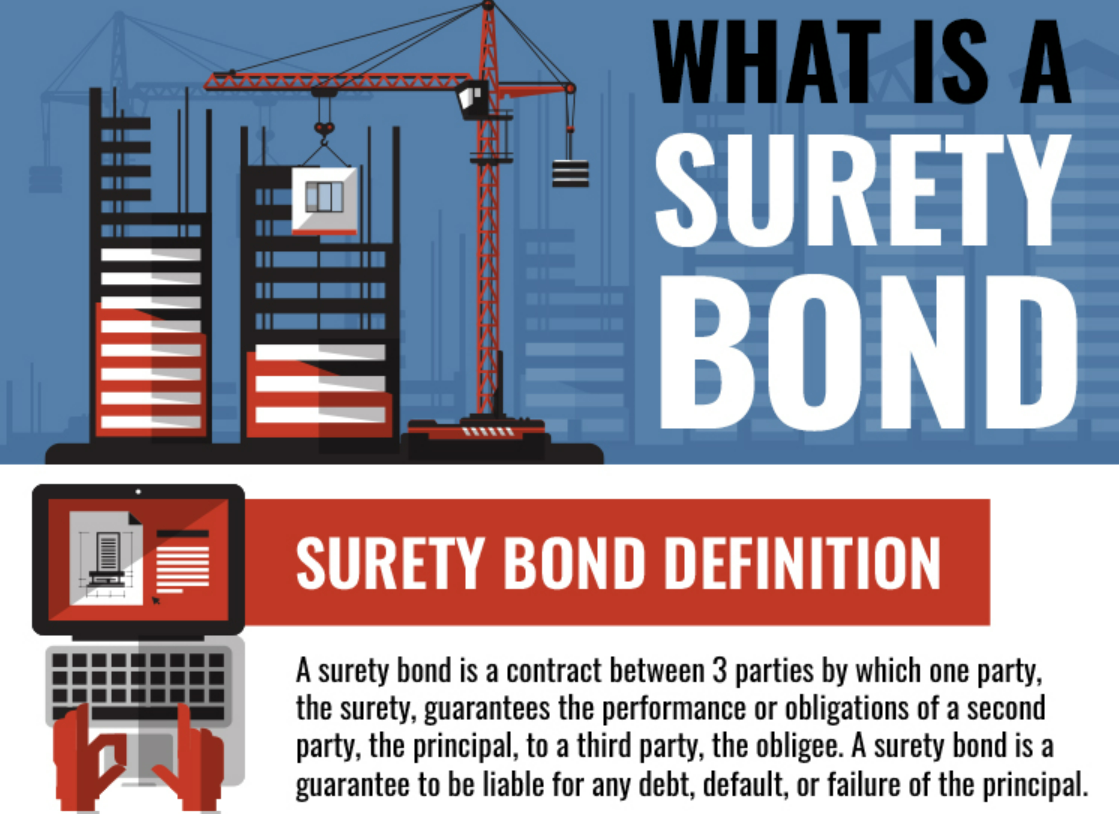
- A surety bond can be defined in its simplest form as a written agreement to guarantee compliance, payment, or performance of an act. Surety is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement. The three parties in a surety agreement are:
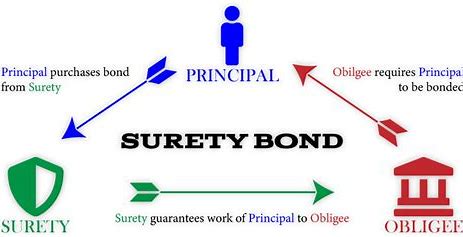
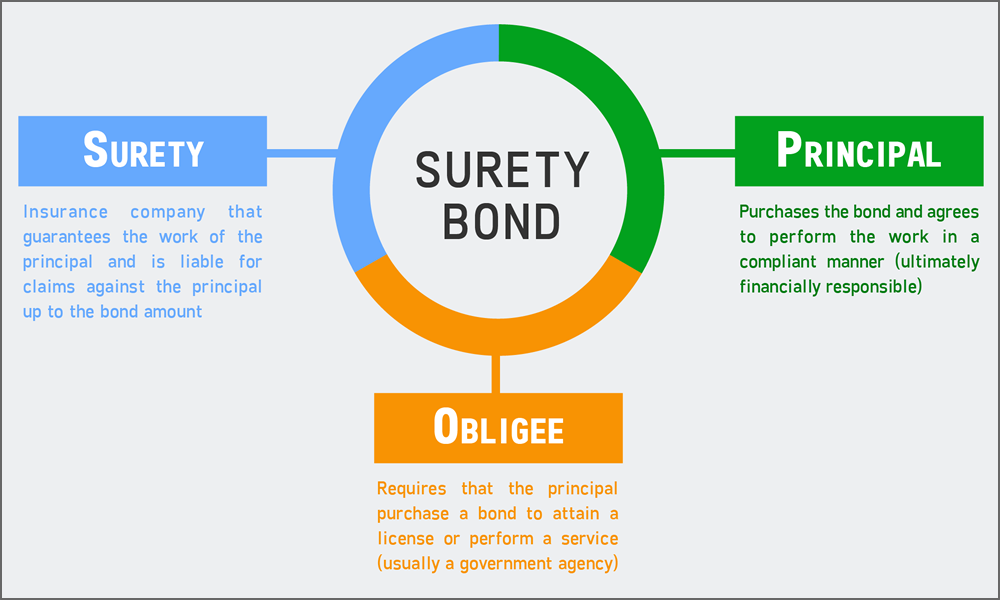
- Principal – the party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety – the insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee - the party who requires, and often receives the benefit of— the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organization.
- Surety bonds guarantee the performance of a variety of obligations, from construction or service contracts, to licensing and commercial undertakings.
Relevance of Surety Bonds in India
- Surety bonds help provide owners of construction projects with guarantees of success and enhanced reputations.
- According to Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) surety bonds are proven risk management mechanisms with a long history that help ensure public and private owners execute their construction projects in accordance with the plans and specifications and ensure subcontractors and suppliers are paid.
- Also, according to IRDAI the surety bonds should be accepted as an alternative form of guarantee by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and government departments and accordingly reflect in the appropriate contract documents.
- For surety market to develop in India and keeping in mind best practices observed in other markets, a robust legislation requiring surety bonds and other non-fund based guarantees would be a necessary condition.
- The Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises runs various schemes to aid the smaller businesses in development, such as, the credit guarantee scheme, where the businesses eligible for these schemes can approach approved banks and can get collateral-free loans. This can be extended for issuance of surety bonds also and in such cases, surety bonds and government guarantees can work more efficiently than banks to secure and promote the MSME sector within India.
- Further, the surety bonds business may be revived with offering of surety bonds to construction companies in India that covers road projects, housing/commercial buildings and other projects of government as well as private sector.
- A huge market is available for surety bonds in the country and now, the onus is on the insurance fraternity to come out with products quickly.
Surety bonds: Slow take-off likely as pricing, reinsurance concerns remain | Business News,The Indian Express
1.png)



















