Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Context - Annual review meeting on the Implementation of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
Details
- The Annual Meeting of the National Scheme Sanctioning Committee (NSSC) under Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen (SBM-G) Phase II to review the Implementation Plans of all the States and Union Territories was held recently.
- It was suggested to ensure ODF Sustainability while prioritising those households that are yet to have access, focusing on behaviour change communication, and swachhata activities to bring about visual cleanliness to all villages.
- It highlighted the importance and need to accelerate activities for Biodegradable Waste Management, Grey Water Management; GOBARdhan, Plastic Waste Management, and Faecal Sludge Management.
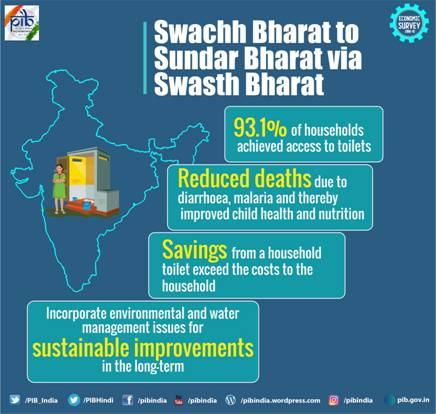
Swachh Bharat Mission
- Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) is a country-wide campaign initiated by the Government of India in 2014 to eliminate open defecation and improve solid waste management.
- It is a restructured version of the Nirmal Bharat Abhiyan launched in 2009.
- Phase 1 of the Swachh Bharat Mission lasted till October 2019.
- Phase 2 is being implemented between 2020–21 and 2024–25.
- The mission aimed to achieve an "open-defecation free" (ODF) India by 2 October 2019, the 150th anniversary of the birth of Mahatma Gandhi through the construction of toilets.
- The objectives of the first phase of the mission:
- Eradication of manual scavenging.
- Generating awareness and bringing about behaviour change regarding sanitation practices.
- Building capacity at the local level.
- The second phase of the mission aims to sustain the open defecation free status and improve the management of solid and liquid waste, while also working to improve the lives of sanitation workers.
- Under the scheme, the Government provides subsidies for constructing toilets, waste management structures, and awareness campaigns to bring behaviour change.
- The campaign is financed by the Government of India and state governments.
- The mission is split into two: Rural and Urban.
- In rural areas "SBM - Gramin" is financed and monitored through the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- In Urban areas "SBM - urban" is overseen by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
Present Status
- According to the dashboards maintained by ministries, more than 100 million individual household level toilets have been constructed in rural areas and 6 million household toilets in urban areas.
- Nearly 6 million community and public toilets have also been constructed in the urban areas.
- Nearly 11 crores of online Integrated Management Information systems (IMIS) have been constructed in the country.
- Nearly 2 lakh Community Sanitary Complexes (CSCs) have been constructed under the programme.
- More than 4,200 cities and more than 600,000 villages across the country have declared themselves open defecation free (ODF).
- More than 87 thousand wards in urban areas now have 100% door to door collection of solid waste and nearly 65 thousand words practice 100% segregation of waste at source.
- According to UNICEF, the number of people without a toilet has been reduced from 550 million to 50 million.
- The World Bank reports that 96% of Indians who have a toilet use it.
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1825069














