Description
Copyright infringement is not intended
In News
- Recently the Chief Ministers of Haryana and Punjab discussed the Sutlej Yamuna Link (SYL) canal dispute in New Delhi in the Presence of the Union Jal Shakti Minister.
- The meeting remained inconclusive as no consensus was arrived at surrounding the construction of the SYL.
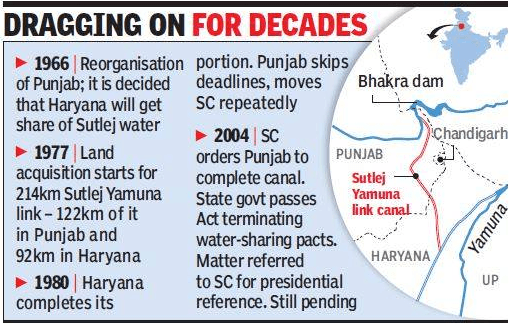
Sutlej Yamuna Link (SYL) Canal :
- The canal will resolve the water dispute between the rivers Ravi and Beas between Punjab and Haryana.
- The water dispute emerged in 1966 at the time of the reorganization of Punjab and the formation of Haryana.
- The Punjab assembly has opposed the proposal of Water sharing of the two rivers with Haryana.
- In 1982, the Prime Minister initiated the construction of the SYL Canal, but the political parties in Punjab were against the construction of the canal.
- Incidence of Violence pressured the government to stop the construction of the Canal.
- Arguments of Punjab
- Many areas in Punjab may go dry after 2029.
- The groundwater level is declining.
- Punjab needs water for irrigation purposes and for ensuring food security
- As per the study, water in about 79% of the state’s area is over-exploited.
- Arguments of Haryana
- The Haryana government stated that providing water for irrigation is getting tough for the state.
- Declining groundwater level.
- The problem of drinking water.
Sutlej River :
- Sutlej River is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River.
- It rises in the Kailash Mountain near Mansarover Lake from Rakas lake in Tibet.
- The Bhakra Nangal Dam is built on the river Sutlej.
- It provides irrigation and other facilities to Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana states.
- The Sutlej water is allocated to India under the Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan.
- The drainage basin in India includes the states and union territories of Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Ladakh and Haryana.
.jpeg)
Yamuna River :
- The Yamuna is the 2nd-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India.
- Yamuna river originates from the Yamunotri Glacier at the Bandarpunch peaks of the Lower Himalaya in Uttrakhand.
- It merges with the Ganges at Triveni Sangam, Prayagraj, which is also a site of the Kumbh Mela.
- It flows through several states: Haryana and Uttar Pradesh, passing by Uttarakhand and later Delhi.
- The important tributaries of the Yamuna River are Tons, Chambal, Hindon, Betwa and Ken.
Constitutional Provisions and Water :
- Entry 17 of the State List deals with water; water supply, irrigation, canal, drainage, dams, water storage and water power.
- Entry 56 of the Union List empowers the Union Government for the regulation and development of inter-state rivers and river valleys.
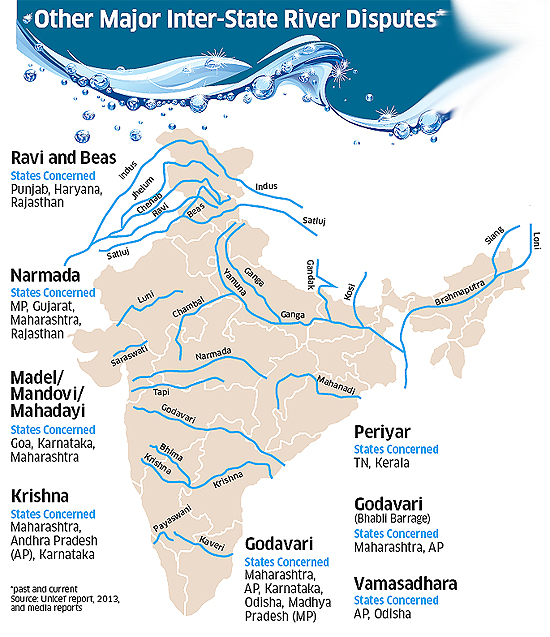
Inter-State Water Dispute in India:
- Article 262 of the Indian Constitution provides for the adjudication of interstate water disputes.
- Parliament may by law provide for the adjudication of any dispute concerning the use, distribution and control of waters of any inter-state river and river valley.
- Parliament may also provide that neither the Supreme Court nor any other court is to exercise jurisdiction in respect of any inter-state water dispute.
- The Parliament has enacted two laws;
- The River Boards Act (1956).
- The Inter-State Water Disputes Act (1956).
- Under the River Boards Act, a river board is established by the Central government for the regulation and development of Inter-state Rivers and river valleys.
- The Inter-State Water Disputes Act of 1956 authorizes the Central government to set up an ad hoc tribunal for the adjudication of a dispute between two or more states about inter-state water disputes.
- The judgment of the tribunal would be final and binding on the parties to the dispute.
.jpeg)
https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/20496/OPS/GN4ANCQ36.1.png?rev=2023-01-05T00:24:00+05:30&cropFromPage=true














