Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
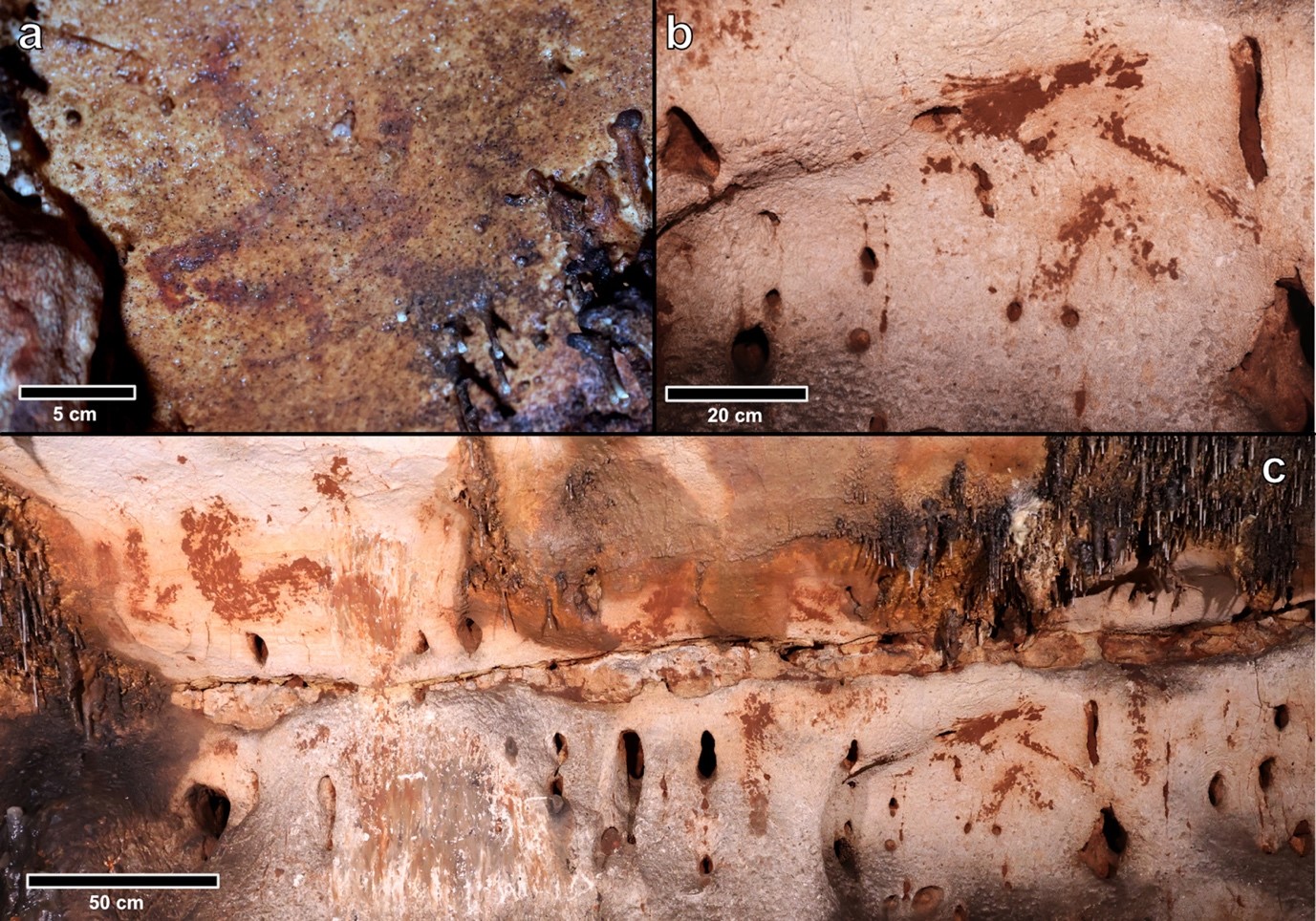
- A professor of ancient Indian history and his team of researchers have discovered two rock-cut Shaivite temple caves in a forested area near Rajapur, Ratnagiri, about 380km from Mumbai.
Details
Ratnagiri, Maharashtra
- Ratnagiri is a coastal district located on the western coast of Maharashtra, India, bordered by the Arabian Sea.
History and Cultural Heritage:
- The district has witnessed the influence of various dynasties, including the Mauryas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, and the Marathas.
- The cultural fabric of Ratnagiri is woven with vibrant traditions, folk arts, and cultural practices that reflect the influence of the Konkani culture, adding to the diversity and richness of the region's cultural heritage.
Natural Attractions:
- Ratnagiri is renowned for its pristine beaches, including Ganapatipule Beach, Mandvi Beach, and Bhatye Beach.
- The district is characterized by its lush green hills, verdant valleys, and scenic landscapes.
Historical Landmarks:
- Ratnagiri Fort: built during the Bahamani reign and later fortified by the Marathas.
- Thibaw Palace: Formerly known as the Bhor Palace, Thibaw Palace is a historical edifice that served as the exile residence of the last Burmese king, King Thibaw, and his family.
Horticultural Significance:
- Ratnagiri is famous for its Alphonso mangoes.
- The district is also known for its cashew plantations.
Cultural Festivals:
- Ganesh Chaturthi.
- Nariyal Purnima: Nariyal Purnima, also known as Coconut Day, is celebrated with rituals and festivities centered around the worship of the sea and coconut.

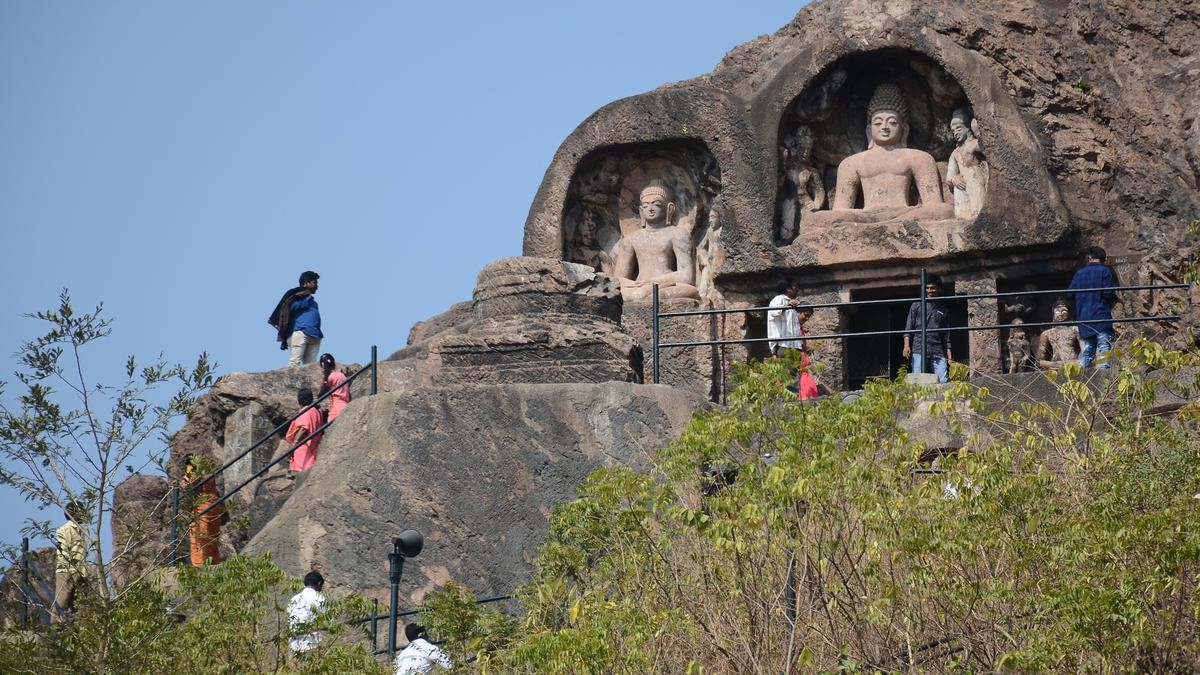
Elephanta Caves
- Elephanta Caves is a UNESCO World Heritage Site situated on Elephanta Island in Mumbai Harbour, Maharashtra.
- Believed to have been constructed between the 5th and 8th centuries AD, the caves represent an important era in Indian history, reflecting the rich cultural tapestry of ancient India.
History:
- While the exact origins remain debated, it is generally believed that the Elephanta Caves were built during the rule of various dynasties, including the Chalukyas and the Rashtrakutas.
Architecture:
- The caves exhibit exemplary rock-cut architecture.
- The caves are divided into main areas, including the main cave or the Great Cave, smaller caves, and various sculptural panels, each representing a unique aspect of Hindu religious and mythological beliefs.
- The layout and design of the caves reflect the principles of Hindu temple architecture, incorporating elements such as mandapas (halls), pillars, and intricate carvings depicting stories from Hindu mythology.
Sculptures and Artwork:
- The caves are adorned with numerous sculptures of Hindu gods and goddesses, with a primary focus on depictions of Lord Shiva in various forms, such as Nataraja, Ardhanarishvara, and Mahayogi.
- The sculptures are characterized by their expressive and dynamic forms, showcasing the mastery of ancient Indian sculptors in capturing subtle emotions and intricate details.
- The sculptures at Elephanta Caves symbolize various aspects of Hindu mythology, philosophy, and the cosmic cycle, reflecting the cyclical nature of life, death, and rebirth as depicted in Hindu religious texts.
Main Features:
- Shiva-Centric Themes and Depictions: The caves primarily emphasize the cult of Lord Shiva, with sculptures and reliefs depicting various aspects of his divine persona, including his role as the creator, preserver, and destroyer.
- Notable Sculptures such as the Trimurti and Ardhanarishvara: The Trimurti sculpture, depicting the three aspects of the divine - Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva - is one of the most iconic and revered sculptures in the caves. The Ardhanarishvara sculpture symbolizes the unity and balance of male and female energies in the universe.
.jpg)
Conclusion
The Elephanta Caves stand as a testament to the artistic brilliance and cultural richness of ancient India, showcasing the profound influence of Hindu mythology and philosophy on the artistic expressions of the time.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which of the following statements about the Elephanta Caves is/are correct?
Options:
A) Elephanta Caves are located in the state of Maharashtra, India.
B) The rock-cut architecture at Elephanta Caves primarily depicts stories from Hindu mythology.
C) Elephanta Caves were built during the 12th century AD.
D) Both A and B
Answer: D)
|