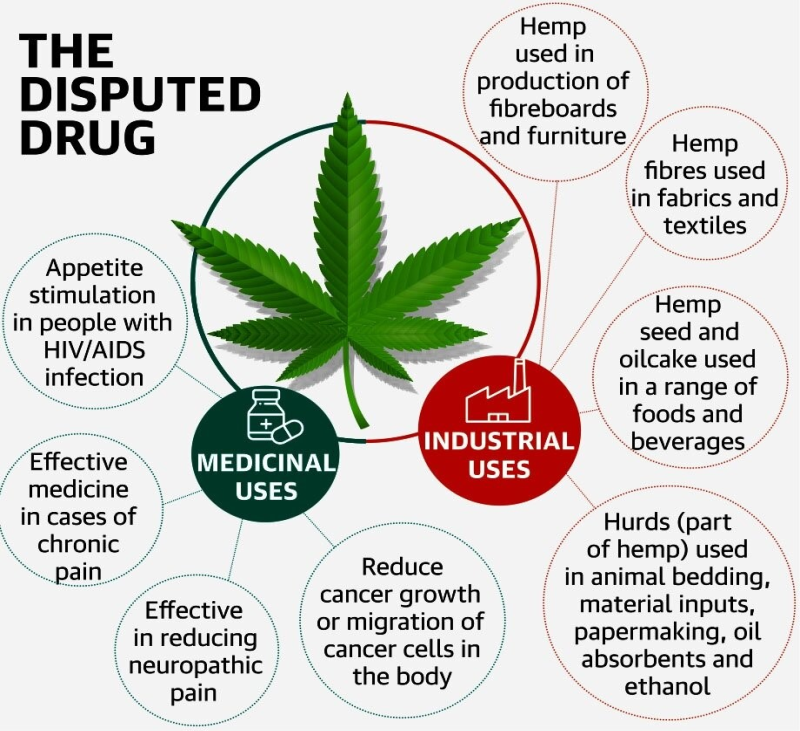
Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.medicalnewstoday.com
Context: Researchers at the CSIR-Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (IIIM) in Jammu, India, have identified a compound derived from cannabis that exhibits potent antibiotic properties against Staphylococcus aureus, a major cause of antibiotic-resistant infections.
Details
- Researchers at the CSIR-Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (IIIM), Jammu, have discovered that a compound called tetrahydrocannabidiol (THCBD) found in cannabis possesses antibiotic properties.
- This finding is significant in the context of the escalating threat of antibiotic resistance, a major global health concern.
- The study focused on the antibiotic effects of THCBD against Staphylococcus aureus, a bacterium responsible for a high number of deaths due to antimicrobial resistance (AMR).

Key Points
- Antibiotic Resistance (AMR) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites no longer respond to medications used to treat them, leading to increased risks of disease spread, severe illness, and death.
- CSIR-IIIM Jammu researchers focused on the antibiotic properties of THCBD, a phytocannabinoid found in the cannabis plant.
- THCBD demonstrated potent antibiotic effects against Staphylococcus aureus, specifically the methicillin-resistant strain (MRSA), which is resistant to the last line of antibiotics. The compound showed effectiveness against efflux pump overexpression and MRSA strains.
- THCBD was obtained through a process where cannabidiol extracted from a cannabis plant reacted with hydrogen, using palladium as a catalyst.
- THCBD was found to be effective in bacterial cultures in the lab. It significantly reduced the number of viable microbial cells of Staphylococcus aureus skin infections in mice.
- The study is seen as an exciting development in the fight against AMR and opens up possibilities for new therapeutics. Collaboration efforts and government authorization are being sought to expedite research progress.
Conclusion
- The discovery of THCBD in cannabis as a potential antibiotic offers a promising avenue for combating antibiotic resistance. The study emphasizes the need for further research, collaboration, and policy changes to harness the benefits of cannabis compounds in addressing global health challenges.
Must Read Articles:
CANNABIS AND AMR: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/cannabis-and-amr
ANTIBIOTICS RESISTANCE: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/antibiotics-resistance
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Considering the potential for bioterrorism involving weaponized antibiotic-resistant bacteria, how to effectively manage biosecurity risks while maintaining open scientific research and collaboration?
|

















