Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended
Context
- India’s 5G leap is about powering tomorrow.
About
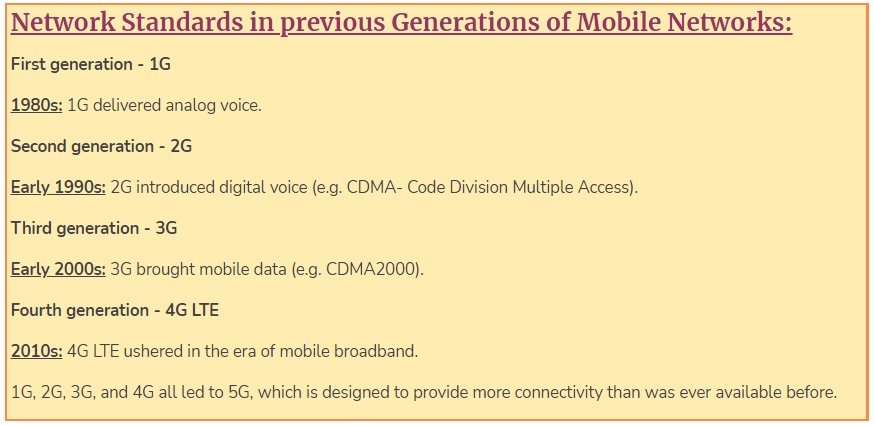
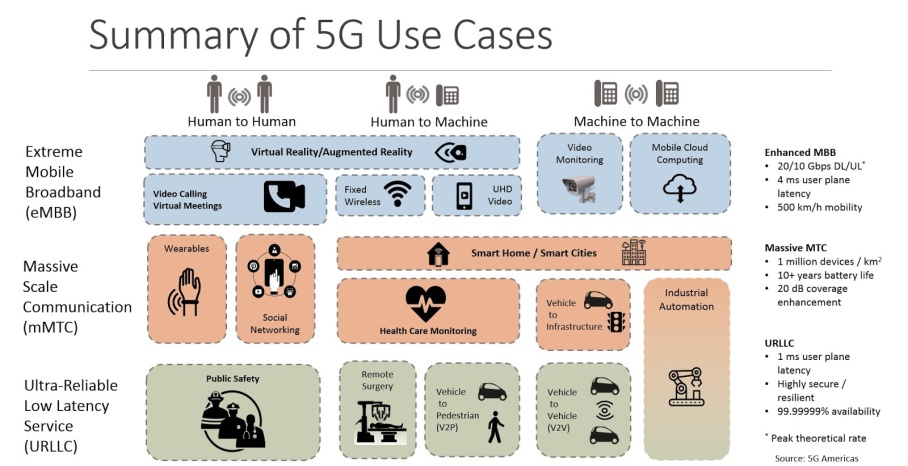
- 5G is the fifth generation of cellular technology. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks.
- 5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
- 5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience to more users.
- Network Standard: MIMO
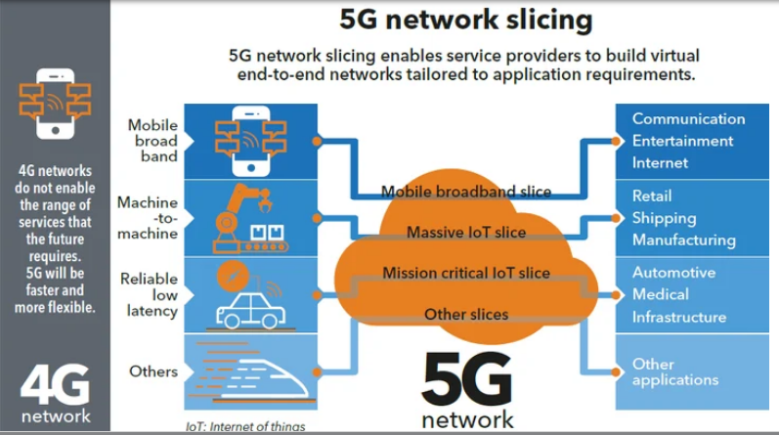
Network Slicing
- 5G network slicing is the use of network virtualization to divide single network connections into multiple distinct virtual connections that provide different amounts of resources to different types of traffic.
MIMO (5G)
- MIMO or ‘multiple-input, multiple-output’ is a wireless technology/ radio antenna technology that, when deployed, uses multiple antennas at both the source (transmitter) and the destination (receiver).
- This allows for more data to be sent and received at the same time, unlike in conventional wireless communications where only a single antenna is used.
- MIMO utilises a natural radio-wave phenomenon known as ‘multipath’ or ‘multipath wave propagation’.
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GGH95EQ83.1&imageview=0
Array
(
[0] => daily-current-affairs/the-technology-behind-5-g
[1] => the-technology-behind-5-g
)