Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Researchers have discovered the amino acid tryptophan in interstellar space.
|
INTERSTELLAR SPACE
Interstellar space is the area between the stars, but it is far from empty. It contains vast quantities of neutrinos, charged particles, atoms, molecules, dark matter and photons ranging from the highest-energy radiation to the sluggish light of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) albeit rather sparsely spread out.
|
Details
- Tryptophan, has been discovered in a stellar system designated as IC 348 with the Perseus molecular cloud.
- It is a region of space in the constellation of Perseus, where low-mass stars are formed.
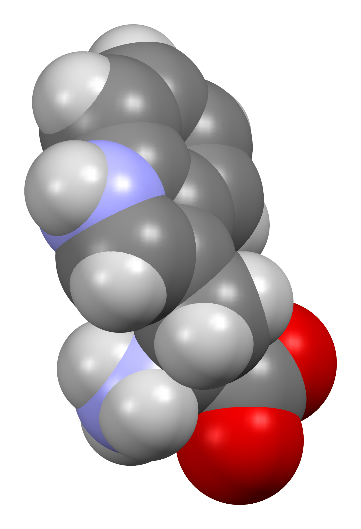
Tryptophan
About
- Tryptophan is an essential amino acid used to make proteins and proteins are required to sustain life.
- Tryptophan is an α-amino acid.
Source
- Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid.
- Foods that contain tryptophan include animal products like chicken and fish and plant foods like nuts or soy.
Function
- The body uses tryptophan to help make melatonin and serotonin.
- Melatonin helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle, and serotonin is thought to help regulate appetite, sleep, mood, and pain.
- The liver can also use tryptophan to produce niacin (vitamin B3), which is needed for energy metabolism and DNA production.
Decoding Amino Acids
- Essential and nonessential amino acids are the building blocks of life. These small organic compounds play a vital role in several biological process, particularly when it comes to building and rebuilding muscle tissue, in the form of growth and creating new proteins.
What Are Amino Acids?
- Often referred to as the building blocks of protein, when protein is metabolized, it’s broken down into its simplest form amino acids.
- There are 20 common amino acids that play numerous roles within your human biology.
- Amino acids are composed of an amino group and a carboxyl group which is acidic, hence the name amino acid.
- Between these groups are alpha carbons which are shared through a covalent bond to both the amino group, carboxyl group, and a carbon atom, thus making the general molecular structure of an amino acid.
- Amino acids are needed for several integral biological processes, such as muscle growth, muscle repair, and converting food into energy.
Types of Amino Acids
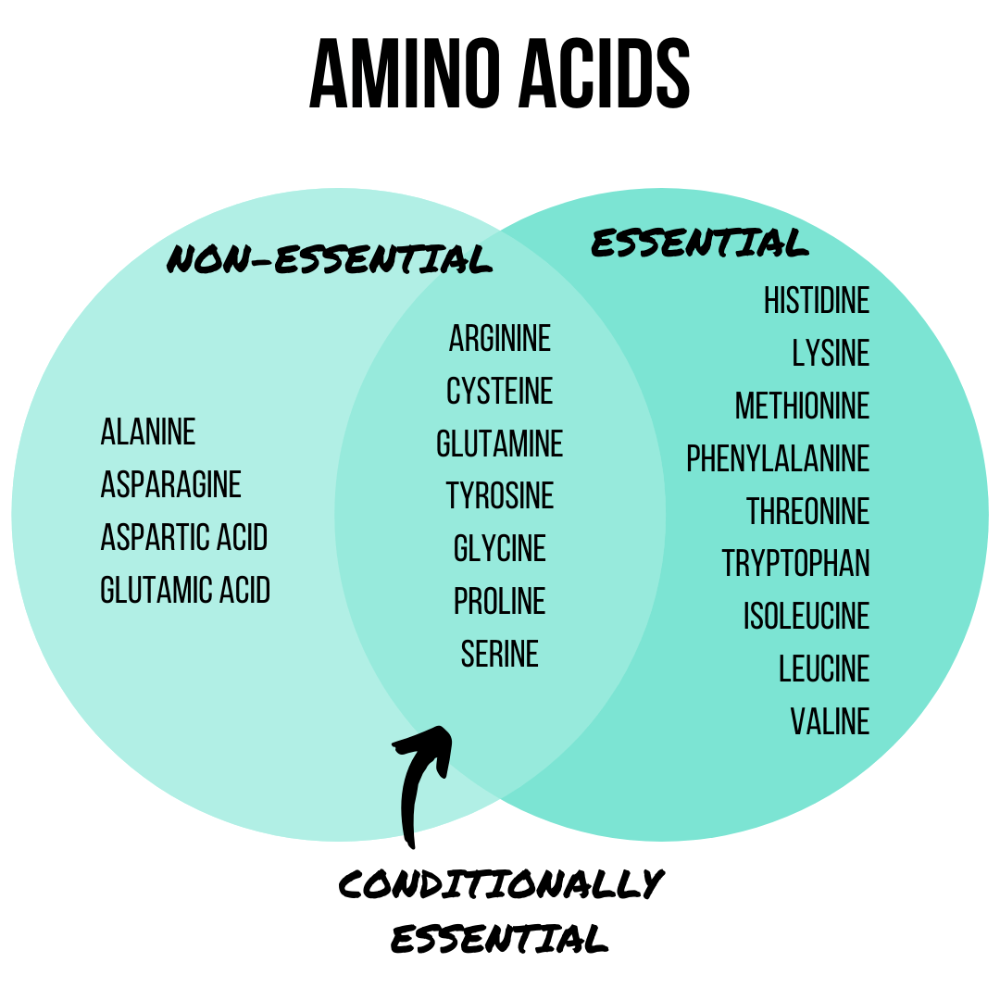
- Amino acids are broken down into three different groups, essential, non-essential, and conditional.
Essential Amino Acids
- Essential amino acids cannot be produced by our body, therefore it is essential to obtain them from our diet and the foods we eat or from supplements.
- Nine of the twenty amino acids are categorized as essential, which include leucine, isoleucine, valine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, histidine and tryptophan.
- Each amino acid, is separately, or in combination responsible for various functions in our body.
- Tryptophan, for example, is used to make niacin, melatonin, and serotonin, which promote healthy sleep and a positive mood state, while leucine is part of the branched chain amino acids, which helps stimulate muscle protein synthesis.
Nonessential Amino Acids
- The remaining eleven amino acids are considered nonessential.
- Nonessential amino acids are those that our body naturally produces and therefore not essential to acquire through dietary sources.
- Alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, arginine, cysteine, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, tyrosine are all considered nonessential amino acids.
- Additionally, there is a sub-group of amino acids, called conditionally essential amino acids.
Conditionally Essential Amino Acids
- Six of the eleven remaining nonessential amino acids are considered conditionally essential amino acids.
- Conditionally essential amino acids are amino acids that are produced by the body, yet in times of severe physical stress, growth, or trauma, may become depleted.
- At times our body requires additional stores of certain amino acids which can exceed the amount we naturally produce.
- For example, L-Glutamine is one of the most versatile conditionally amino acids. Glutamine is depleted quickly through physical exercise and severe physical stress, and is one of the very few amino acids, that can cross the blood-brain barrier while supporting healthy intestinal lining and immune function. Studies have shown that glutamine can reduce exercise induce muscle soreness, and muscle mass breakdown, making glutamine one of the best supplements for exercise recovery. A growing body of evidence also supports the use of glutamine for digestive health, specifically in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Inflammatory bowel disease states such as chrons, ulcerative colitis, leaky gut, and IBS, are characterized by gut hyperpermeability. Glutamine rebuilds and repairs the gut lining by feeding the epithelial cells, which line our digestive tract.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements:
1. Conditionally essential amino acids are amino acids that are produced by the body and therefore not essential to acquire through dietary sources.
2. Tryptophan is a conditionally essential amino acid used to make proteins.
3. Foods that contain tryptophan include animal products like chicken and fish and plant foods like nuts or soy.
4. Tryptophan is used to make niacin, melatonin, and serotonin, which promote healthy sleep and a positive mood state.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3, and 4 only
(d) All of the above.
Correct Answer: (c) 3, and 4 only
|

https://www.news9live.com/science/astronomers-spot-amino-acid-essential-for-life-in-stellar-nursery-ic-348-2186543


















