Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: economictimes.indiatimes.com
Context: The Indian telecom industry urges the government for Budget 2024-25 to eliminate the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) and reduce customs duties on telecom equipment. These measures are seen as vital for industry growth and improving accessibility to advanced communication technologies across the nation.
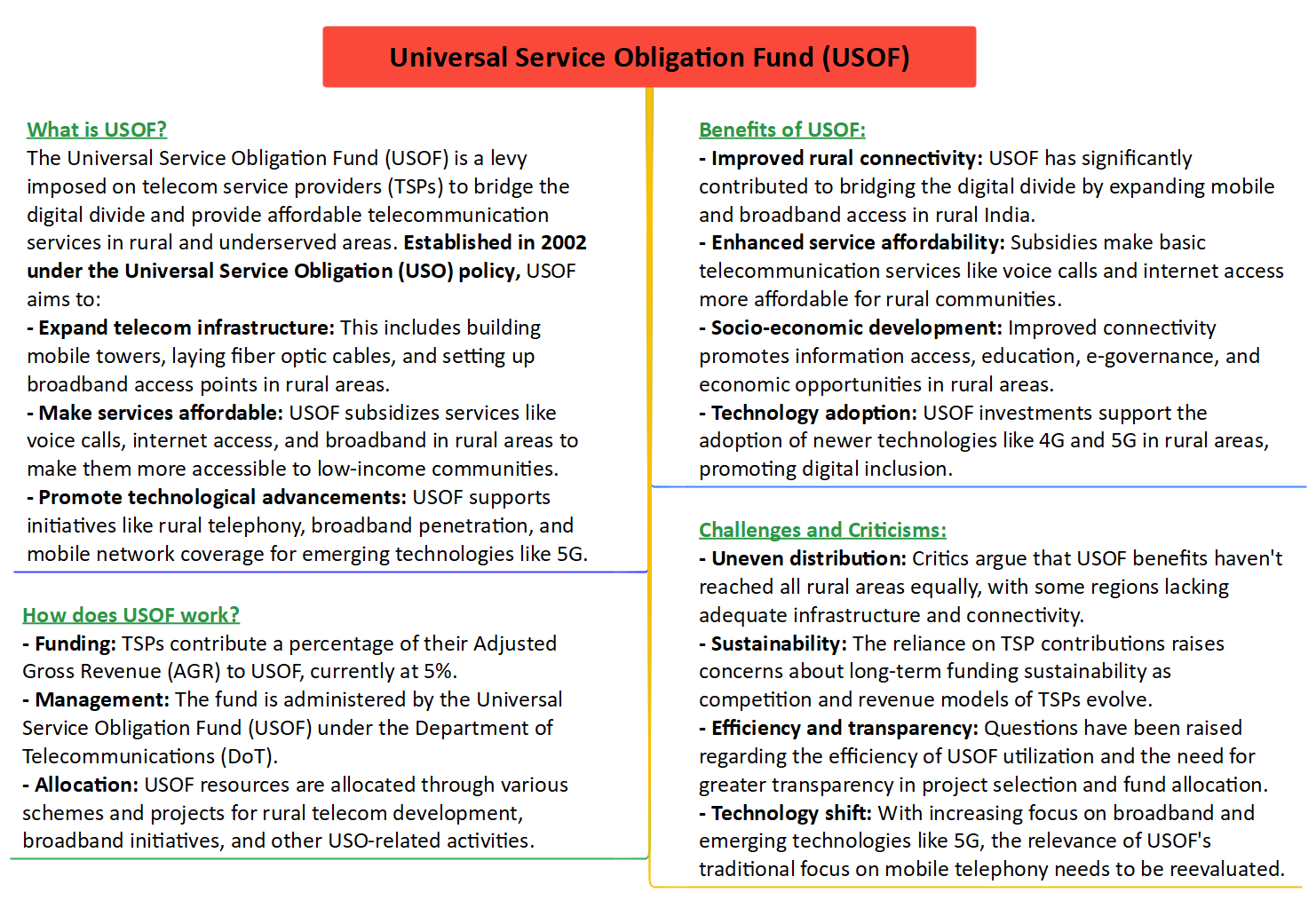
What is USOF?
- The Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) was established in 2002 as a financial mechanism to support the expansion of telecommunication services, especially in rural and remote areas.
- The fund is generated through levies imposed on telecom service providers (TSPs) based on their revenue.
Why demand to scrap it?
- Improved Rural Connectivity: The telecom industry argues that there has been significant progress in rural telephony and broadband penetration. As a result, the original purpose of the USOF, which was to bridge the digital divide in rural areas, has become less relevant.
- Technological Progress: The industry claims that the levy imposed by the USOF burdens TSPs, diverting resources that could be invested in newer technologies such as 5G and network upgrades.
- Competition Distortion: Different telecom operators contribute to the USOF unevenly, creating an unfair playing field. The industry suggests that scrapping the fund would level the competitive landscape.

Government's Perspective
- Rural Connectivity Needs: The government may argue that rural areas still lack adequate broadband and telecom access, and the USOF remains crucial for bridging this gap.
- Balancing Development: While progress has been made, there might be areas where connectivity is still lacking, and the government needs to balance the development across urban and rural regions.
- Alternative Solutions: Instead of abolishing the USOF, the government might consider reforming it by revising contributions based on the actual needs and advancements in technology.
Potential Outcomes
- Partial USOF Reform: Complete abolition of the USOF might be unlikely, but the government could consider revising the fund's structure and contributions to better align with current needs and technological advancements.
- Strategic Investments: The government could explore strategic investments in rural infrastructure, ensuring that connectivity reaches underserved areas without entirely relying on the USOF.
Reducing Customs Duties
- Current Scenario: High import duties on telecom equipment are currently a significant challenge, making network expansion and modernization expensive for telecom operators.
- Desired Change: The industry is seeking a significant reduction in customs duties, potentially down to zero, to make telecom equipment more affordable. This move is expected to have several positive outcomes:
- Faster 5G Rollout: Cheaper equipment can expedite the deployment of 5G infrastructure, promoting nationwide coverage.
- Improved Network Quality: Investments in better equipment can enhance call quality, data speeds, and network reliability.
- Enhanced Affordability: Lower costs could lead to increased competition, potentially translating into more affordable data plans for consumers.
Government's Perspective
- Domestic Manufacturing Impact: Reducing import duties could harm domestic telecom equipment manufacturers. The government might be concerned about the impact on the "Make in India" initiative.
- Fiscal Implications: Lowering revenue from customs duties may affect government finances, and the government needs to find a balance between reducing costs for the industry and maintaining revenue streams.
Potential Outcomes
- Phased Duty Reduction: The government might consider a gradual reduction in customs duties to balance the interests of the industry with the protection of domestic manufacturing.
- Support for Domestic Manufacturers: The government could introduce policies to support domestic manufacturing, ensuring that the reduction in import duties does not adversely affect local businesses.
Additional Requests
- Exemption from Service Tax: The industry is seeking an exemption from service tax on the "assignment of right to use natural resources," aiming to reduce operational costs for TSPs and improve profitability.
- Lowering License Fees: Currently set at 3% of revenue, the industry is requesting a reduction in license fees to cover only administrative costs, which could boost investment and innovation.
Government's Perspective
- Balancing Fiscal Concerns: The government needs to balance the industry's demands with fiscal considerations. Reducing taxes and fees may impact government revenue, affecting its ability to fund other essential services and projects.
Potential Outcomes
- Negotiations on Taxation: There could be negotiations between the government and the industry to find a middle ground on taxation, ensuring that the industry remains competitive while the government continues to collect necessary revenue.
- Alternative Revenue Streams: The government might explore alternative revenue streams or financing models to compensate for potential reductions in taxes and fees.
Impact on Consumers
- Improved Network Quality: Increased investment in infrastructure and technology could lead to better call quality, faster data speeds, and wider network coverage, ultimately benefiting consumers.
- Faster 5G Adoption: Quicker access to 5G could unlock its potential for enhanced connectivity, internet speed, and new applications, providing consumers with more advanced services.
- Potentially Lower Tariffs: If competition increases due to reduced costs, consumers could benefit from more affordable data plans, leading to increased accessibility and usage of telecom services.

Conclusion
- The telecom industry's budget wishlist reflects its desire to foster growth, enhance technology adoption, and improve access to advanced services. The government's challenge lies in finding a balance between industry needs, affordability for consumers, and national development goals. The final budget decision will significantly impact the future trajectory of India's telecom landscape and its potential to empower consumers across the nation.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How has the implementation of digital technology and connectivity infrastructure, such as high-speed internet and mobile networks, contributed to improving governance and socio-economic development in rural areas of India, and what challenges still exist in ensuring comprehensive ruler connectivity across the country?
|














