




Copyright infringement not intended
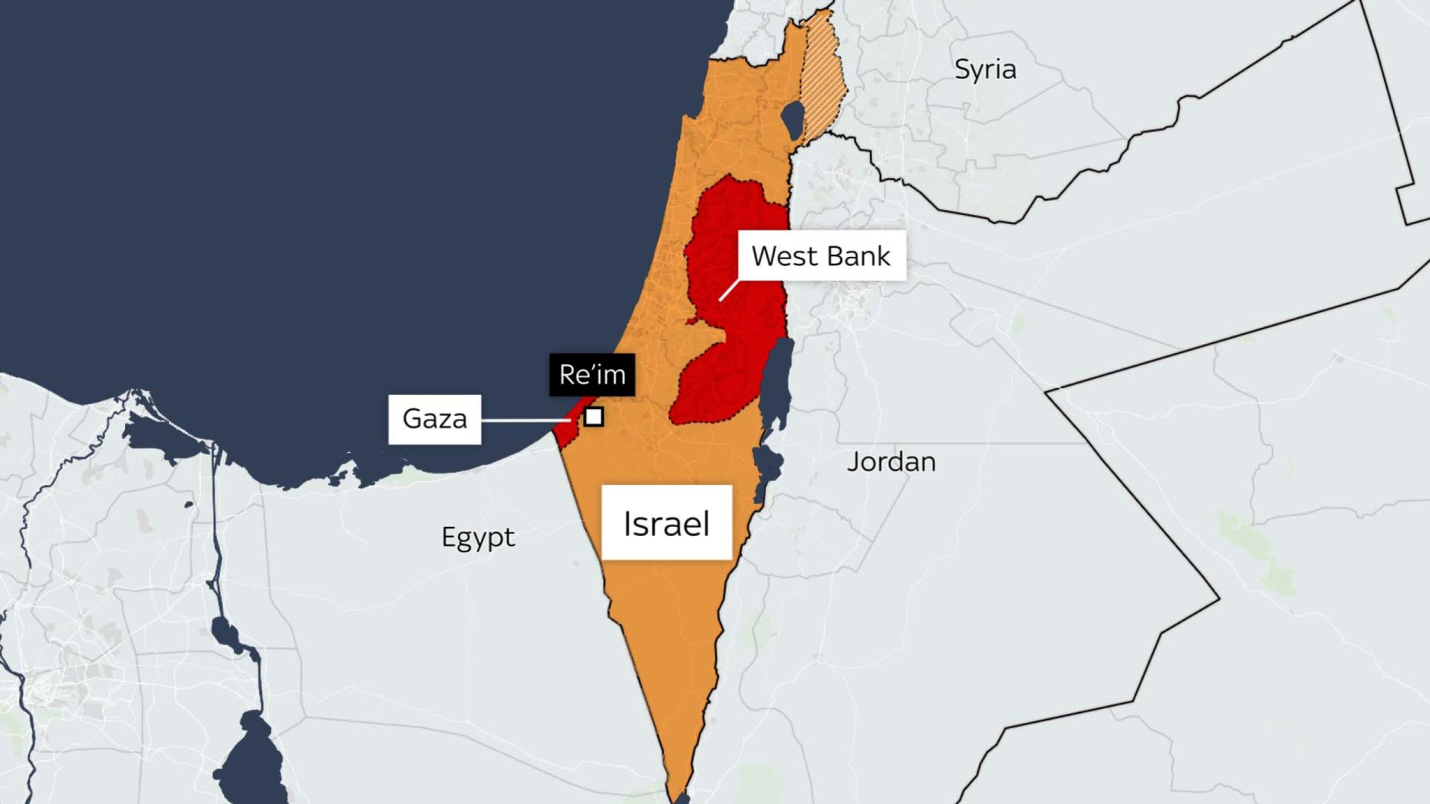
Picture Courtesy: https://news.sky.com/story/israel-hamas-war-the-latest-conflict-in-maps-12980904
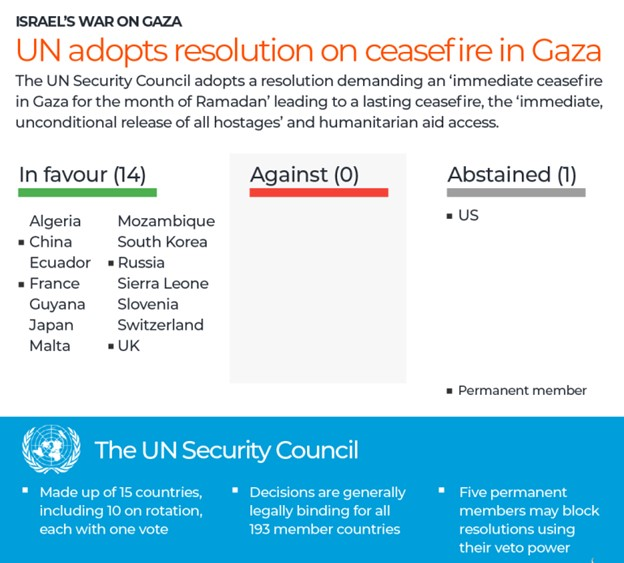
Context: The United States' absence from the recent UNSC resolution on Israel and Hamas represents a change from its previous solid backing for Israel at international forums.
Key Highlights
|
United Nations Security Council (UNSC) ●The UNSC was established after World War II to address the failures of the League of Nations in maintaining global peace and security. ●Its primary responsibilities include ensuring international peace and security, recommending new UN member admissions to the General Assembly, and approving changes to the UN Charter. ●The UNSC has significant powers outlined in the UN Charter, including the authority to establish peacekeeping operations, impose international sanctions, and authorize military action. ●Resolutions passed by the Security Council are binding on member states. ●The UN Security Council consists of 15 members, five of which are permanent: China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States. These five nations, known as the P5, have veto power over substantive resolutions. The other 10 members are elected on a regional basis for two-year terms. ●Permanent members of the Security Council can veto any substantive resolution, including those related to admitting new UN members or appointing the Secretary-General. However, this veto power does not extend to General Assembly matters. |
Must Read Articles:
ISRAEL HAMAS CONFLICT: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/israel-hamas-conflict
INDIA ISRAEL RELATIONS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/india-israel-relations-9
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. What are the challenges and opportunities for deepening and diversifying the India-Israel relationship in the context of shifting geopolitical dynamics in the Middle East and South Asia, as well as global trends in technology, trade, and security cooperation? |











© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved