




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
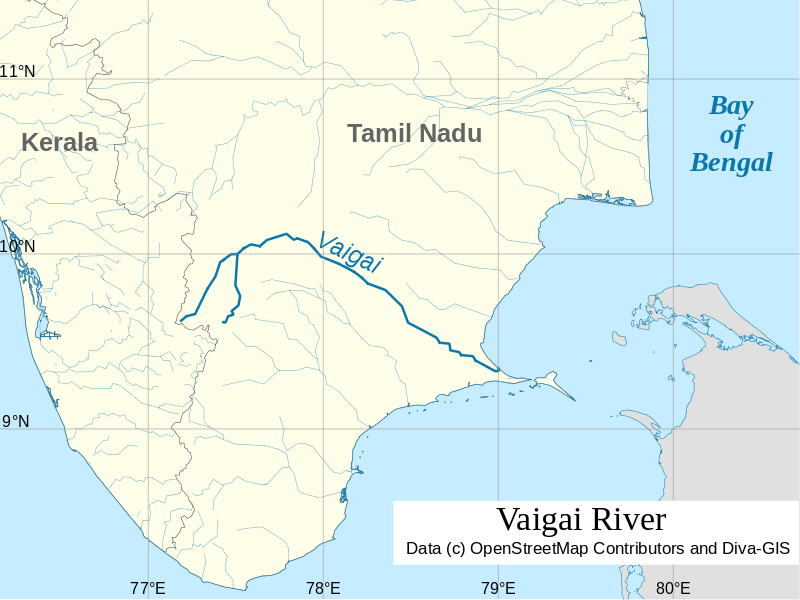
About
The following are some important facts regarding the Vaigai River
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Discuss the socio-environmental and economic implications of large-scale dam projects in India. Using a specific case study, analyze the challenges and benefits associated with such projects, and evaluate the measures needed for sustainable and inclusive development while addressing concerns about displacement, environmental degradation, and water management. |






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved