Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: saniprofessional.com
Context: A serious bacterial infection that can destroy skin and soft tissue is spreading in the US, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The agency warned that Vibrio vulnificus, also known as flesh-eating bacteria, can cause severe illness and death in people with certain health conditions.
Details
- The bacteria that causes flesh-eating disease has been spreading in some states of the US, especially during the summer season. According to the CDC, Connecticut, New York and North Carolina have reported many infections and deaths from this bacteria in July and August.
- The CDC advises people to seek medical attention immediately if they suspect they have been infected by the bacteria, as early treatment can increase the chances of survival.
- The bacterium has become more resistant to microbes, and many infections do not respond to antibiotics anymore. The fatality rate for wound infections is 25%, and if the infection reaches the bloodstream, it can be deadly.
Vibrio vulnificus
About
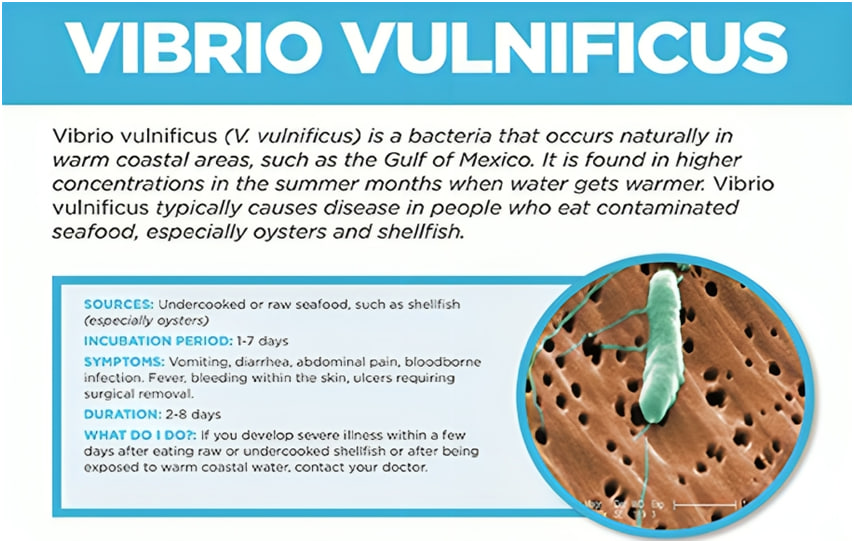
- Vibrio vulnificus is a species of bacteria belonging to the Vibrio genus. It is found in warm coastal waters and is known to cause severe infections in humans, particularly when they come into contact with contaminated water or consume raw or undercooked seafood.
Symptoms
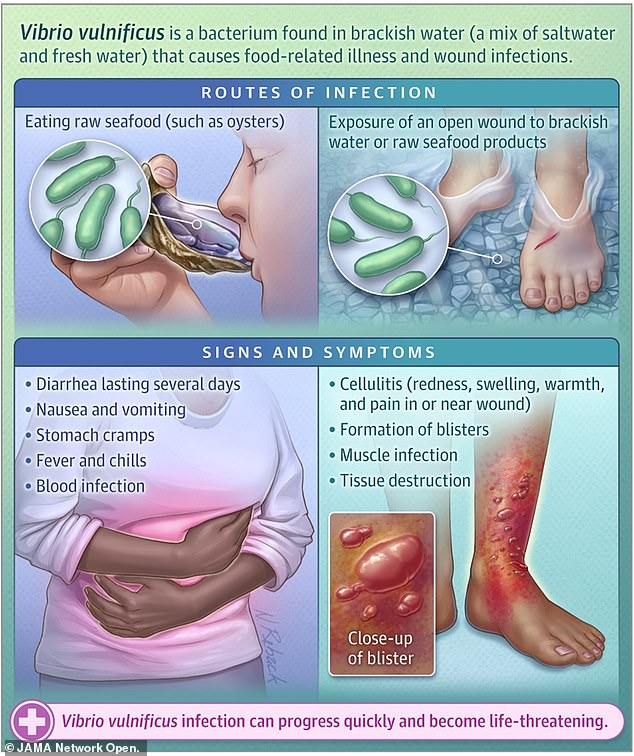
- Wound Infections: When Vibrio vulnificus enters the body through open wounds or cuts exposed to contaminated water, it can cause wound infections. Symptoms may include redness, swelling, pain, and the formation of blisters or ulcers at the site of infection.
- Gastrointestinal Infections: Infections acquired through the consumption of contaminated seafood can lead to symptoms such as diarrhoea, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Septicemia (Bloodstream Infection): In severe cases, the bacteria can enter the bloodstream, resulting in septicemia. Symptoms may include fever, chills, low blood pressure, confusion, and, in advanced stages, septic shock.
Picture Courtesy: www.dailymail.co.uk
Impact
- Septicemia: This is a bloodstream infection caused by Vibrio vulnificus. The bacteria can multiply in the bloodstream, spreading throughout the body, and can lead to a condition known as septicemia or bacteremia. Symptoms can include fever, chills, low blood pressure, and systemic inflammation.
- Septic Shock: If septicemia is left untreated, it can progress to septic shock. Septic shock is a medical emergency characterized by a severe drop in blood pressure, multiple organ failure, and a high risk of death. It requires immediate medical intervention.
- Sepsis: Vibrio vulnificus infections can trigger a systemic inflammatory response in the body, leading to sepsis. Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition where the body's immune system goes into overdrive in response to an infection. It can result in organ failure, including the heart, kidneys, lungs, and liver.
Challenges
Antibiotic Resistance
- Antibiotic resistance is a significant concern when it comes to treating Vibrio vulnificus infections. Approximately 50% of these infections are no longer responsive to commonly used antibiotics. This antibiotic resistance can complicate treatment and limit the effectiveness of traditional antibiotic therapies.
- Healthcare providers need to carefully select antibiotics based on susceptibility testing and, in some cases, use combination therapies to manage these infections effectively.
Seasonal Variation
- Vibrio vulnificus infections indeed exhibit seasonal variation, with a higher incidence during the warm summer months. This is because the bacteria thrive in warm coastal waters. The seasonal variation presents challenges for public health efforts and prevention strategies.
- During peak seasons, there may be a need for increased awareness and surveillance to detect cases early and provide prompt treatment. Additionally, public education campaigns about the risks associated with consuming raw seafood or swimming in warm coastal waters with open wounds can help reduce the number of infections.
Cure or Treatment
- There is no specific cure for Vibrio vulnificus infection. However, antibiotics can be used to treat the infection.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are a crucial component of treatment for Vibrio vulnificus infections. Healthcare providers will prescribe antibiotics that are effective against the bacteria, based on susceptibility testing. Antibiotic resistance can be a concern, so the choice of antibiotics may need to be adjusted accordingly.
- Wound Care: For localized infections, especially those caused by wound exposure to contaminated water, aggressive wound care is essential. This includes cleaning and debriding the wound to remove infected tissue. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove necrotic (dead) tissue.
- Septicemia and Septic Shock: In cases where Vibrio vulnificus infection progresses to septicemia or septic shock, immediate medical intervention is crucial. This involves hospitalization, intravenous antibiotics, and supportive care. Supportive care may include measures to stabilize blood pressure, provide oxygen, and manage organ dysfunction. In severe cases, patients may require admission to an intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring and advanced medical support.
Way Forward in dealing with Vibrio vulnificus infections
- Public Awareness: Increasing public awareness about the risks associated with Vibrio vulnificus infections is vital. Education campaigns can help individuals understand the dangers of exposure, especially during the warm summer months. Information about proper seafood handling and wound care is essential in reducing the risk of infection.
- Safe Seafood Handling: Emphasizing the importance of thoroughly cooking seafood is crucial for preventing foodborne Vibrio vulnificus infections. Educating consumers and food service establishments about safe food handling practices can reduce the incidence of these infections.
- Wound Care: Encouraging individuals with open wounds or cuts to take precautions when in coastal waters is essential. Covering wounds with waterproof bandages or avoiding swimming with open wounds can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
- Research and Surveillance: Continued research into antibiotic resistance mechanisms in Vibrio vulnificus and the development of more effective treatments are essential. Enhanced surveillance and reporting systems can help monitor infections and outbreaks, enabling rapid responses to contain the spread of the bacteria.
- Climate Change Considerations: Recognizing the link between rising sea temperatures and bacterial proliferation is crucial for long-term prevention efforts. Addressing climate change and its impact on coastal ecosystems can help mitigate the environmental factors that contribute to the growth of Vibrio vulnificus.

Conclusion
- Vibrio vulnificus is a serious bacterial pathogen that can lead to severe infections and life-threatening conditions. Public awareness, safe seafood handling, wound care, and research into effective treatments are essential components of the way forward in mitigating the impact of this bacteria on public health. Additionally, addressing the environmental factors contributing to its proliferation is a critical aspect of long-term prevention.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. The term “Vibrio vulnificus” is frequently seen in the news. What is Vibrio vulnificus?
A) A type of virus found in coastal waters.
B) A species of bacteria found in warm coastal waters.
C) A type of parasite commonly found in seafood.
D) A fungal infection associated with swimming in freshwater lakes.
Answer: B
Explanation: Vibrio vulnificus is a species of bacteria that belongs to the Vibrio genus. It is commonly found in warm coastal waters, particularly in the Gulf of Mexico and along the southeastern coast of the United States. Vibrio vulnificus can also be found in other warm-water regions around the world.
This bacterium is noteworthy for its ability to cause infections in humans, particularly when individuals come into contact with contaminated water or consume raw or undercooked seafood, such as oysters, clams, and shellfish.
|
https://www.hindustantimes.com/world-news/cdc-issues-national-health-alert-for-infections-caused-by-flesh-eating-bacteria-101693744869417.html

















