Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.globsec.org/what-we-do/publications/30-years-weimar-triangle-idea-yesterday-or-concept-tomorrow
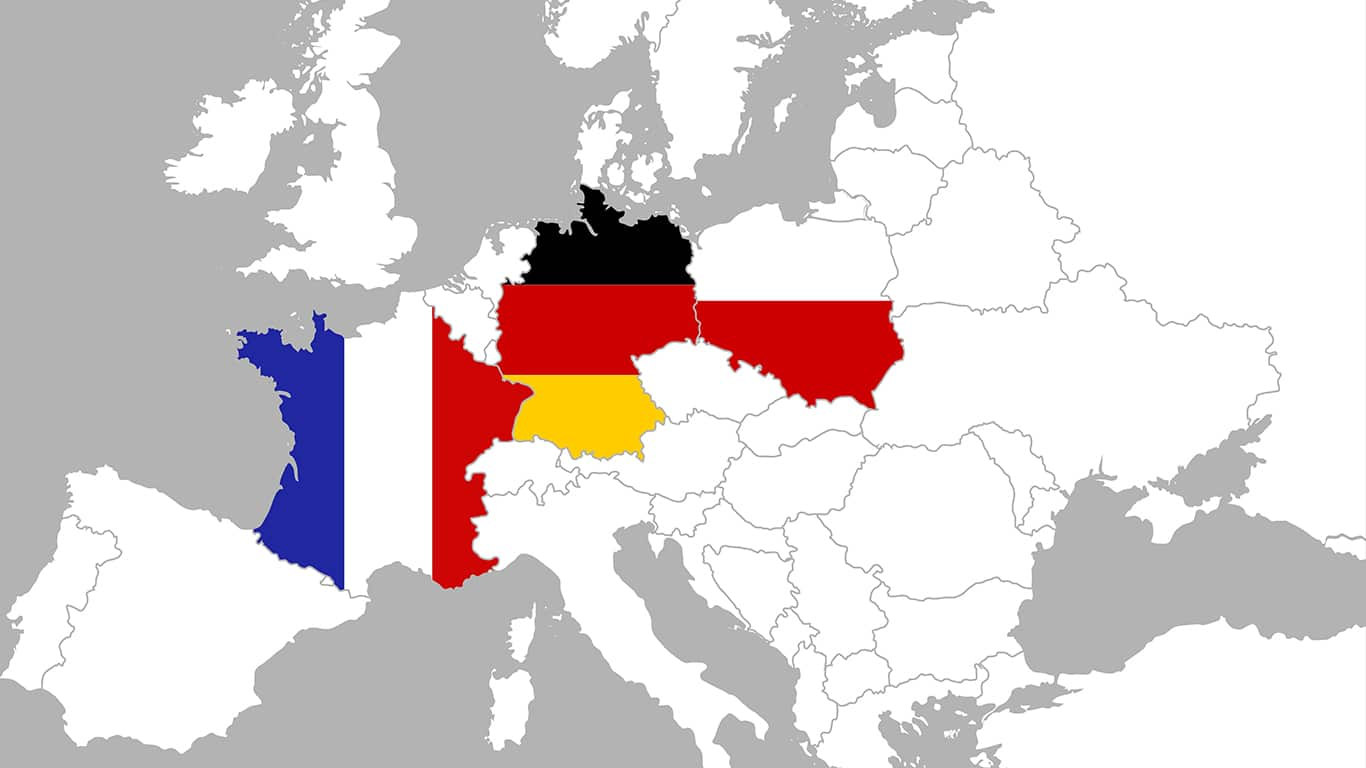
Context: The Weimar Triangle, a cooperation platform between Poland, France, and Germany, has announced a new initiative to strengthen cooperation and address common challenges.
Details
- The governments of Poland, France, and Germany expressed a commitment to enhancing Europe's security and defence capabilities.
- France, Germany, and Poland are expected to unveil a new cooperation agreement to combat foreign disinformation operations, particularly those originating from Russia. The three countries have reportedly been victims of destabilization strategies and information attacks.
The Origins of the Weimar Triangle
- The Weimar Triangle was established in 1991 in the German city of Weimar, where the foreign ministers of France, Germany, and Poland met for the first time to discuss the future of Europe after the end of the Cold War.
- The main goal of the Weimar Triangle was to support Poland's transition from communism to democracy and market economy and to facilitate its integration into the European Union and NATO.
- The group also aimed to promote cooperation between the three countries on cross-border and European issues, such as security, energy, climate, migration, and human rights.
- Since its inception, the Weimar Triangle has held regular summit meetings between the leaders and foreign ministers of the three countries, as well as inter-parliamentary contacts, and military, scientific, and cultural cooperation.

Key Areas of Cooperation
European Affairs
- Working together to influence the direction and policies of the European Union, promoting common values, and addressing challenges facing the EU.
- Fostering collaboration and solidarity among European nations to address common issues such as migration, economic disparities, and social challenges.
Security and Defense
- Collaborating on strategies and initiatives to ensure the stability and security of the region.
- Joint efforts to enhance military capabilities, share intelligence, and coordinate defence planning.
- Working together within the framework of NATO to address global security challenges and contribute to collective defence.
Economic Development
- Facilitating and promoting trade and investment between nations to boost economic growth.
- Collaborating on research and development, technology transfer, and innovation to drive economic progress.
- Developing joint strategies to address economic disparities and challenges specific to the region.
Climate Change and Energy
- Coordinating efforts to mitigate climate change, reduce carbon emissions, and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
- Collaborating on the development and implementation of sustainable energy solutions, including renewable energy sources.
- Ensuring the stability and security of energy supplies while transitioning to a more sustainable energy future.
Science and Technology
- Collaborating on joint research initiatives, sharing scientific knowledge, and working together on cutting-edge projects.
- Facilitating the exchange of technology and expertise to promote mutual advancement.
- Supporting innovation ecosystems and creating favourable conditions for the development of new technologies.
Culture and Education
- Promoting mutual understanding and appreciation of each other's cultures through cultural exchange programs.
- Facilitating dialogue and initiatives to enhance understanding and cooperation on cultural and social issues.
- Supporting joint educational programs, student exchanges, and academic collaborations to strengthen ties and knowledge sharing.
Challenges of the Weimar Triangle
- The different political orientations and interests of the three countries on some issues, such as EU enlargement, fiscal policy, defence spending, relations with Russia and Turkey, and Brexit.
- The rise of populism and nationalism in some parts of Europe has undermined the values and principles of democracy and multilateralism that underpin the Weimar Triangle.
- The lack of visibility and public awareness of the Weimar Triangle among the citizens of the three countries and beyond.
.jpg)
Way Forward
- The Weimar Triangle remains an important platform for dialogue and cooperation between three key European partners. As Europe faces new challenges and opportunities in a changing world order, the Weimar Triangle can play a constructive role in shaping a common vision and strategy for the future of Europe.
Must Read Articles:
India-France Bilateral Relations: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/india-france-bilateral-relations-34
Poland: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/poland-42
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How can India and Europe bridge their differences on global issues like climate change, trade regulations, and the role of international organizations? Can they find common solutions despite their differing geopolitical priorities and economic structures?
Answer Structure:
●Identify the main areas of convergence and divergence between India and Europe on global issues, such as their views on multilateralism, human rights, democracy, security, and development.
●Analyze the factors that shape their respective positions, such as their historical experiences, strategic interests, domestic politics, and regional dynamics.
●Evaluate the potential benefits and challenges of enhancing their cooperation, such as the opportunities for joint action, the trade-offs involved, and the risks of misunderstanding or conflict.
●Propose some concrete recommendations for strengthening their dialogue and partnership, such as the areas of mutual interest, the mechanisms of consultation and coordination, and the best practices for communication and trust-building.
|






.jpg)