



Context
About
Composition
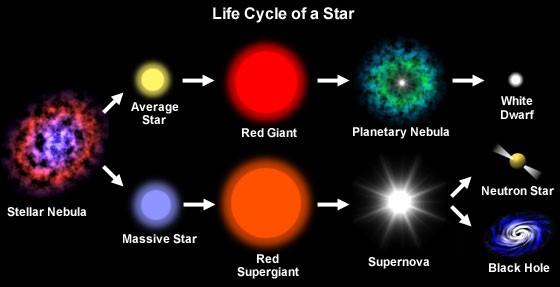
https://www.sciencenews.org/article/white-dwarf-star-smallest-ever-found-moon-size-most-massive











© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved