Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context: In light of the recent reports of fatalities in several countries allegedly associated with the use of India-made drugs that were found to be "adulterated", the Union Government has issued a directive for the compulsory implementation of the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) by a stipulated date. The GMP standards were updated in 2018 to align them with the World Health Organisation (WHO) norms.
Details
- The Indian government has taken a vital measure to address the recent reports of fatalities allegedly caused by "contaminated" drugs made in India. It has set a deadline for all pharmaceutical companies in the country to comply with the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) that were updated in 2018 to match the World Health Organization (WHO) standards. The revised GMP aims to ensure that the quality and safety of the drugs produced in India are consistent with global norms and expectations.
- The government has announced different deadlines for different categories of companies to implement the revised GMP, depending on their turnover:
- Companies with a turnover of more than Rs 250 crore have to implement the revised GMP within 6 months from the date of notification.
- Companies with a turnover of less than Rs 250 crore have to implement the revised GMP within 1 year from the date of notification.
- The revised GMP will apply to all companies manufacturing medicines for the domestic market. Companies exporting medicines to other countries must already be WHO-GMP certified. The revised GMP will help improve the quality and safety of medicines produced in India and enhances their competitiveness in the global market.
Present Status
- The revised GMP is based on the global WHO-GMP standards, which are followed by most countries in the world. Currently, only about 2,000 out of 10,500 manufacturing units in India are compliant with the WHO-GMP standards.
.jpg)
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
About
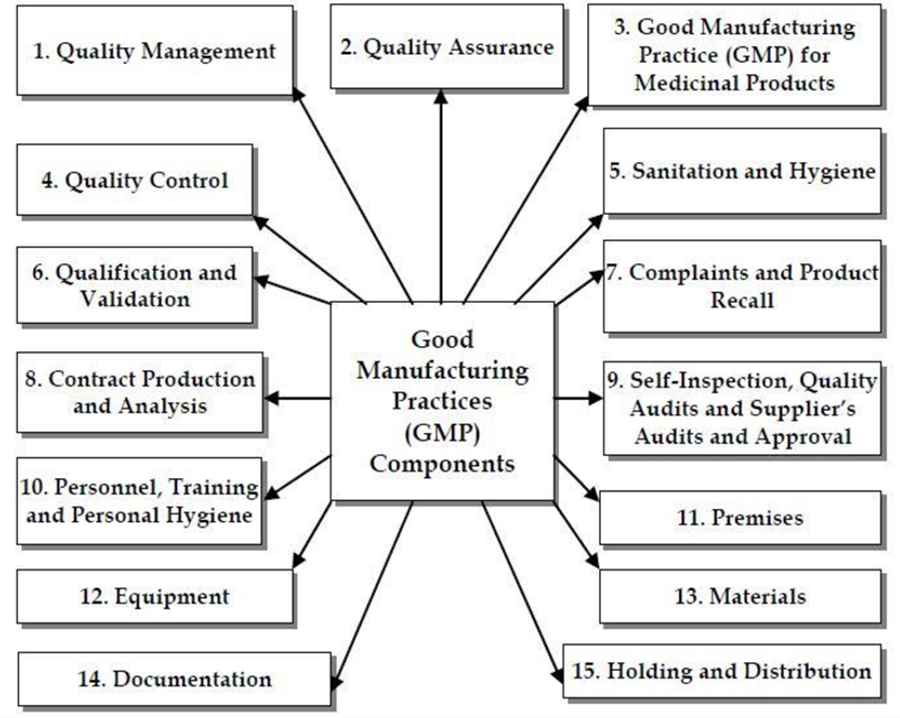
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is a set of guidelines and standards aimed at ensuring the quality, safety, and consistency of pharmaceutical, food, and other regulated products during their manufacturing process. GMP guidelines are established by regulatory authorities to protect the health of consumers and to ensure that the products are manufactured in a controlled and standardized manner.
Background of GMP
- The concept of GMP originated in the 1940s when the World Health Organization (WHO) introduced the first GMP for the production of biological products such as vaccines and sera. The need for GMP was further highlighted by several incidents of substandard and contaminated drugs that caused serious adverse effects and deaths among patients.
- In 1969, when the World Health Assembly recommended the first version of the WHO Certification Scheme on the quality of pharmaceutical products moving into the global market, it accepted the WHO GMP as an integral part of the Scheme. Since then, WHO has revised and updated its GMP guidelines several times to reflect the advances in science and technology and to harmonize with other international standards.
Features of GMP
- Quality Management System: This is the framework that defines the policies, objectives, responsibilities, and procedures for ensuring product quality. A quality management system ensures that products meet their intended specifications and quality standards.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: This is the process of creating, maintaining, and storing records of all manufacturing activities and operations. Documentation and record-keeping provide evidence of compliance with GMP and enable traceability and accountability.
- Personnel Training and Qualification: This is the process of providing adequate training and qualification to personnel who are involved in the manufacturing process. Personnel training and qualification ensure that personnel are competent to perform their assigned tasks and follow GMP requirements.
- Premises and Equipment: These are the physical facilities and devices that are used for manufacturing. Premises and equipment should be designed, constructed, maintained, and cleaned according to appropriate standards to prevent contamination and cross-contamination of products.
- Production Control: This is the process of controlling the production process according to written procedures that are approved by authorized personnel. Production control ensures that products are manufactured in a consistent and controlled manner. Any deviation from the approved procedures should be recorded and investigated.
- Quality Control: This is the process of verifying that products conform to their specifications at every stage of production. Quality control involves the testing of raw materials, intermediates, finished products, packaging materials, and stability samples. Quality control ensures that only products that meet the quality criteria are released for distribution.
- Validation: This is the process of demonstrating that critical processes and methods are capable of consistently producing products of the required quality. Validation involves collecting and analyzing data to confirm the performance and reliability of processes and methods.
- Change Control: This is the process of evaluating and approving any change in the manufacturing process or method that may affect product quality. Change control involves assessing the impact of the change, testing the modified product, and updating the documentation accordingly.
- Complaint Handling: This is the process of recording, investigating, and resolving any complaint received from customers or users regarding product quality or safety. Complaint handling involves identifying the root cause of the problem, taking corrective and preventive actions, and communicating with the complainant.
- Recall Procedure: This is the process of withdrawing defective or potentially harmful products from the market. The recall procedure involves notifying the relevant authorities, retrieving the affected products, investigating the cause of the defect, and preventing recurrence.
Significance of GMP
- GMP is significant for both manufacturers and consumers of pharmaceutical products.
For manufacturers
- Quality assurance: GMP helps to prevent errors, defects, wastage, and rework in the production process, which can compromise the quality of the products. By following GMP, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the specifications and expectations of their customers and regulators.
- Safety and efficacy: GMP helps to ensure that the products are safe and effective for their intended use. By following GMP, manufacturers can avoid contamination, cross-contamination, mix-ups, and deviations that can affect the safety and efficacy of the products. GMP also requires manufacturers to conduct testing and validation of their products and processes to verify their performance and suitability.
- Regulatory compliance: GMP helps to meet the regulatory requirements and standards of different countries and regions. By following GMP, manufacturers can avoid legal actions, fines, sanctions, recalls, and reputational damage that can result from non-compliance. GMP also enables manufacturers to access global markets and expand their customer base.
- Competitive edge: GMP helps to gain a competitive edge in the pharmaceutical industry. By following GMP, manufacturers can demonstrate their commitment to quality, safety, efficacy, and customer satisfaction. GMP also helps to enhance the reputation and credibility of the manufacturers and their products.
For consumers
- Health protection: GMP helps to protect the health and well-being of the consumers who use pharmaceutical products. By buying products from GMP-compliant manufacturers, consumers can avoid adverse reactions and complications that can arise from poor quality, unsafe, ineffective, or inconsistent products. GMP also ensures that the products have accurate labelling, packaging, storage, and distribution information to guide the consumers on how to use them properly.
- Effective treatment: GMP helps to provide effective treatment for various diseases and conditions. By buying products from GMP-compliant manufacturers, consumers can receive reliable and effective products that can help them achieve their desired health outcomes. GMP also ensures that the products have sufficient shelf life and stability to maintain their quality, safety, efficacy, and consistency until they are used.
- Cost saving: GMP helps to save money and time for consumers who use pharmaceutical products. By buying products from GMP-compliant manufacturers, consumers can avoid wasting money and time on substandard, unsafe, ineffective, or inconsistent products that can cause harm or fail to deliver results. GMP also reduces the risk of product recalls, shortages, or unavailability that can inconvenience or endanger consumers.
Steps Taken by India to Implement GMP
- India is one of the largest producers and exporters of pharmaceutical products in the world. The Indian pharmaceutical industry is estimated to be worth over $40 billion and employs more than 2.5 million people. India is also a major supplier of generic drugs and vaccines to many developing countries, especially in Africa and Asia.
- However, the Indian pharmaceutical industry has also faced several challenges and criticisms regarding its quality standards and regulatory oversight.
- In recent years, several countries have reported deaths allegedly linked to contaminated or substandard India-manufactured drugs. For example, Nigeria banned the import of cough syrup containing codeine that was manufactured by an Indian company after it was found to be responsible for an addiction epidemic among Nigerian youths. Uganda recalled a batch of paracetamol tablets that were manufactured by another Indian company after they were found to contain high levels of a carcinogenic impurity.
- These incidents have raised serious concerns about the quality and safety of Indian pharmaceutical products and have tarnished the reputation and credibility of the Indian pharmaceutical industry. To address these issues, the Indian government has taken several steps to improve its GMP standards and enforcement.
Revising Schedule M of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act
- Schedule M of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act is the main regulation that governs the GMP requirements for pharmaceutical products in India. The government revised Schedule M in 2018, bringing it on par with WHO-GMP standards. The revised Schedule M introduced several new provisions, such as pharmaceutical quality system, quality risk management, product quality review, and validation of equipment.
Setting a deadline for mandatory implementation of revised Schedule M
- The government has set a deadline for pharmaceutical MSMEs to adopt the revised Schedule M within six months or one year depending on their turnover. Those who fail to comply will face suspension of license or penalty.
Introducing GMP-related computerized system
- The government has mandated that all manufacturing units should introduce a GMP-related computerized system that will automatically record all the steps followed and checks done during the production process. This will ensure transparency and accountability.
Challenges Faced by India in Implementing GMP
- Lack of awareness and training: Many manufacturers, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs), are not fully aware of the benefits and importance of GMP. They also lack adequate training and skills to implement GMP properly.
- High cost and complexity: Implementing GMP involves high cost and complexity for many manufacturers. They have to invest in upgrading their infrastructure, equipment, technology, documentation, etc. They also have to comply with multiple regulations from different authorities at the central and state levels.
- Resistance to change: Some manufacturers are reluctant or resistant to change their existing practices and adopt GMP. They may perceive GMP as an unnecessary burden or interference in their business operations.
- Lack of enforcement and monitoring: The enforcement and monitoring of GMP compliance is weak and inconsistent in India. There is a shortage of qualified inspectors and auditors who can conduct regular and effective inspections and audits. There is also a lack of coordination and cooperation among different regulatory agencies at the central and state levels.
- Competition from other countries: India faces stiff competition from other countries such as China, Bangladesh, Vietnam, etc., who offer cheaper and faster production of pharmaceutical products. Some of these countries may not follow GMP standards or may have lower standards than India. This may create an unfair advantage for them in the global market.
Way Forward for India to Improve GMP Implementation
- Strengthening Regulatory Oversight: The regulatory authorities need to continuously enhance their capacity and monitoring capabilities to ensure GMP compliance. They need to conduct regular inspections, audits and investigations, and take strict actions against non-compliant manufacturers. They also need to harmonize their standards and guidelines with international norms and best practices.
- Capacity Building: The personnel involved in manufacturing and quality control need to undergo training and capacity-building programs to improve their knowledge, skills and competence in GMP. They need to be aware of the latest developments and innovations in the field and follow the standard operating procedures (SOPs) diligently. They also need to foster a culture of quality and ethics in their organizations.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: The industry needs to collaborate with international regulatory bodies, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and others, to learn from their experiences and expertise in GMP implementation. They also need to share information and data and adopt best practices and benchmarks.
- Technological Integration: The industry needs to embrace technology and automation to enhance data integrity and streamline manufacturing processes. They need to use advanced tools and systems, such as electronic batch records, barcodes, radio frequency identification (RFID), artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain, to ensure traceability, transparency and accountability in GMP.
- Consumer Awareness: Consumers need to be educated about the significance of GMP and their role in demanding quality products. They need to be informed about the risks and consequences of using substandard or counterfeit products, and how to identify them. They also need to report any adverse reactions or complaints to the authorities.

Conclusion
- The Indian government has set a deadline for pharmaceutical companies to adopt the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in line with World Health Organization (WHO) standards. This is a positive move that will benefit both the industry and public health. By following the revised GMP, Indian pharmaceutical companies can improve the quality, safety and efficacy of medicines, enhance their reputation and credibility in the global market, foster innovation and competitiveness in their sector, and contribute more to public health outcomes.
Must Read Articles:
COMMON DRUG STANDARDS: https://www.iasgyan.in/ias-gazette-magazine/perspectivecommon-drug-standards
SCHEDULE-M: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/schedule-m
Drug Recall Law in India: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/drug-recall-law-in-india
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What are the key challenges that pharmaceutical companies encounter when ensuring the production of quality medicines for both the domestic and international markets? Elaborate the significance and impact of maintaining high-quality standards in the pharmaceutical industry. Additionally, identify the major obstacles faced by companies in achieving and upholding these standards, and propose potential strategies or solutions to address these challenges effectively.
|
https://indianexpress.com/article/india/adopt-who-standard-good-manufacturing-practices-govt-sets-deadline-for-pharmas-8873888/














