Description
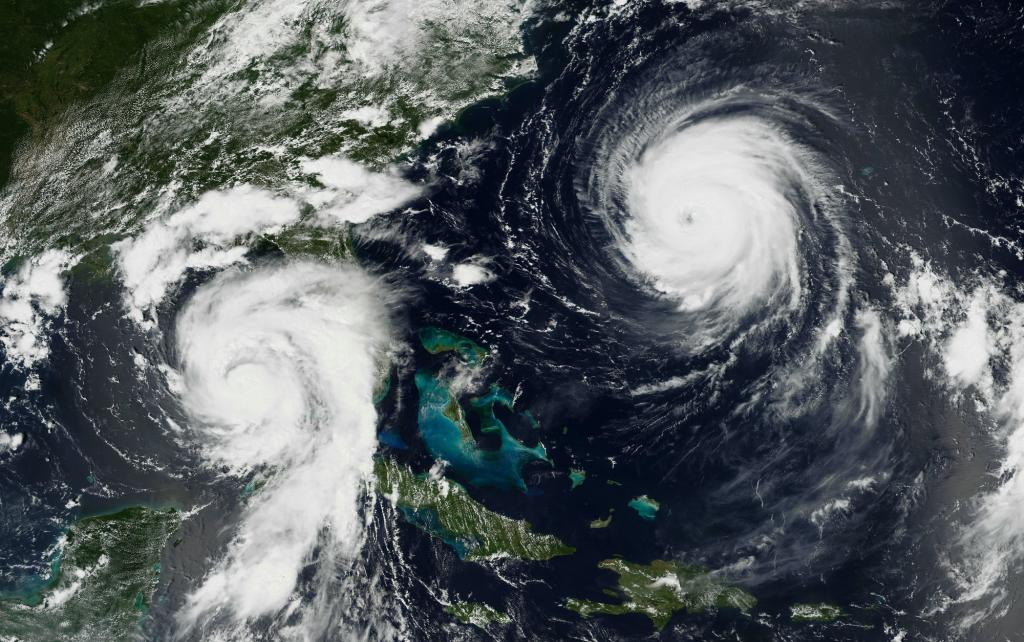

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/climate-change/what-is-wind-shear-an-atmospheric-scientist-explains-how-it-can-tear-down-hurricanes-96276
Context: Wind shear is a crucial force that can determine the severity of a storm, as it is a key factor in weather forecasting during the Atlantic hurricane season.
What is Wind Shear?
- Wind shear refers to the change in wind speed, wind direction, or both, over a certain distance in the atmosphere.
- It is a crucial atmospheric phenomenon that can have significant effects on weather patterns and the development of severe storms, including hurricanes.
Types of Wind Shear
- Vertical Wind Shear: Vertical wind shear involves changes in wind speed or direction with changes in altitude. It is commonly associated with atmospheric instability and can have profound effects on the development and organisation of thunderstorms, squall lines, and other convective weather systems.
- Horizontal Wind Shear: Horizontal wind shear refers to changes in wind speed with changes in lateral position for a given altitude. It is often observed near weather fronts, mountainous terrain, and other geographical features.
Role of Vertical Wind Shear in Hurricane Development
In the context of hurricanes, vertical wind shear plays a critical role in determining the strength and structure of these powerful storms.
- Symmetrical Structure: Hurricanes thrive in environments where their vertical structure is symmetrical. Symmetrical hurricanes are characterised by a well-defined eye surrounded by a circular arrangement of thunderstorms. This symmetrical structure allows for efficient heat and moisture transfer, which fuels the storm's intensification.
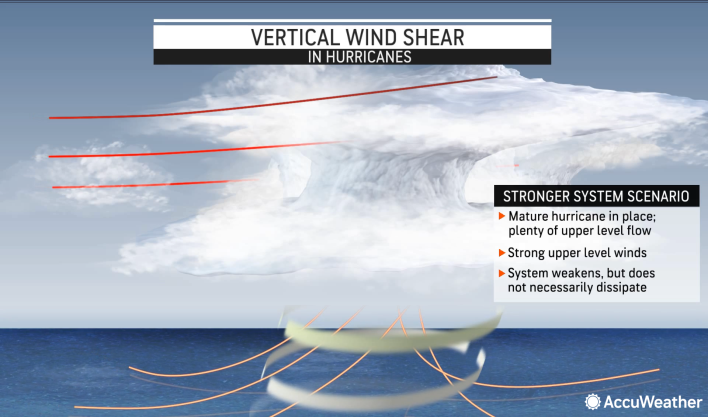
- Impact on Hurricane Intensity: Vertical wind shear can disrupt the symmetrical structure of hurricanes by tilting or displacing the storm's core. Strong vertical wind shear can weaken the storm's circulation and inhibit the development of deep convection near the centre of the hurricane. As a result, the storm's intensity may decrease, and it may struggle to maintain its organisation.
- Influence of Climate Patterns: Climate phenomena such as El Niño and La Niña can influence vertical wind shear patterns in the Atlantic basin. During El Niño events, stronger vertical wind shear is typically observed over the Atlantic, inhibiting tropical storm development. Conversely, La Niña conditions often lead to reduced wind shear, creating a more favourable environment for hurricane formation and intensification.
Implications of Wind Shear on Hurricane Forecasting
- Meteorologists closely monitor wind shear patterns during hurricane season to assess the potential for storm development and intensification. By analyzing vertical wind shear profiles, forecasters can better predict the behaviour of hurricanes and provide timely warnings to affected regions.
Causes and Associated Weather Features
- Thunderstorms: Wind shear is frequently observed near thunderstorms, particularly in the form of microbursts and downbursts. These phenomena can lead to sudden and localized changes in wind speed and direction, posing hazards to aviation.
- Fronts: Wind shear is commonly associated with the passage of weather fronts, such as cold fronts and warm fronts. The interaction between air masses of different temperatures and humidity levels can create significant wind shear along the frontal boundaries.
- Low-Level Jets: Areas of locally higher low-level winds, known as low-level jets, can also be associated with wind shear. These jets can enhance wind shear near the Earth's surface, affecting weather patterns and aviation operations.
- Mountainous Terrain: Wind shear is often observed near mountains, where the interaction between airflow and terrain features can lead to turbulent and variable wind conditions.
- Thermal Wind Concept: The thermal wind concept explains how differences in wind speed at different heights are dependent on horizontal temperature differences. This concept helps to explain the existence of phenomena such as the jet stream, which is influenced by temperature gradients in the atmosphere.
Impacts on Aviation and Weather
- Aircraft Control: Wind shear poses significant challenges to aircraft control, particularly during takeoff and landing. Sudden changes in wind speed and direction can affect aircraft performance and stability, requiring skilled piloting techniques to manage.
- Aviation Safety: Wind shear has been implicated in many aircraft accidents, either as the primary cause or a contributing factor. It is a critical consideration for aviation safety and is closely monitored by pilots and air traffic controllers.
- Weather Forecasting: Understanding wind shear patterns is essential for weather forecasting, as it can influence the development and intensity of various weather phenomena, including thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes.

Conclusion
- Wind shear is a fundamental atmospheric phenomenon that influences weather patterns and storm development. In the context of hurricanes, vertical wind shear plays a crucial role in shaping the intensity and structure of these powerful storms. Understanding the dynamics of wind shear is essential for improving hurricane forecasting and mitigating the impacts of severe weather events.
Source:
Down to Earth
Wikipedia
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which of the following best defines wind shear?
A) The change in temperature with altitude in the atmosphere.
B) The difference in air pressure between two points at sea level.
C) The variation in wind speed and direction over a certain distance in the atmosphere.
D) The movement of air masses from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas.
Answer: C
|

















