Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Every year on July 28, World Hepatitis Day is observed to raise awareness about viral hepatitis — which causes inflammation of the liver, leading to severe disease and also, liver cancer.
Hepatitis
- Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that is caused by a variety of infectious viruses and noninfectious agents leading to a range of health problems, some of which can be fatal.
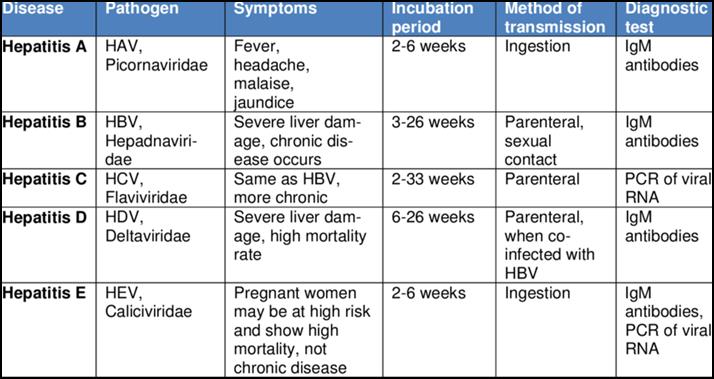
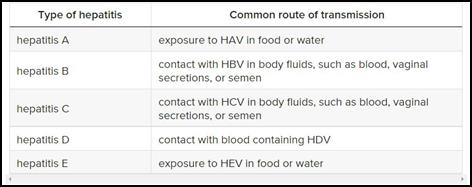
- There are five main strains of the hepatitis virus, referred to as types A, B, C, D and E. While they all cause liver disease, they differ in important ways including modes of transmission, severity of the illness, geographical distribution and prevention methods.
- In particular, types B and C lead to chronic disease in hundreds of millions of people and together are the most common cause of liver cirrhosis, liver cancer and viral hepatitis-related deaths.
Causes of Noninfectious Hepatitis
- Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
- Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
- The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue (cirrhosis) and liver failure.
- Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
- In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. It’s three times more common in women than in men.

Common symptoms of hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
- Fatigue
- Flu-like symptoms
- Dark urine
- Pale stool
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Yellow skin and eyes, which may be signs of jaundice
Treatment and Vaccines
- Safe and effective vaccines are available to prevent hepatitis B virus (HBV). This vaccine also prevents the development of hepatitis D virus (HDV) and given at birth strongly reduces transmission risk from mother to child.
- Chronic hepatitis B infection can be treated with antiviral agents. Treatment can slow the progression of cirrhosis, reduce incidence of liver cancer and improve long term survival.
- A vaccine also exists to prevent infections of hepatitis E (HEV), although it is not currently widely available.
- There are no specific treatments for HBV and HEV and hospitalization is not usually required.
- There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. Antiviral medicines can cure more than 95% of persons with hepatitis C infection, thereby reducing the risk of death from cirrhosis and liver cancer, but access to diagnosis and treatment remains low.
- Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is most common is low- and middle-income countries due to reduced access to clean and reliable water sources and the increased risk of contaminated food. A safe and effective vaccine is available to prevent hepatitis A. Most HAV infections are mild, with the majority of people recovering fully and developing immunity to further infection. However, these infections can also rarely be severe and life threatening due to the risk of liver failure.
https://indianexpress.com/article/lifestyle/health/world-hepatitis-day-2022-alcoholic-hepatitis-symptoms-causes-prevention-reversible-8056457/
1.png)