Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The joint assessment by UNESCO and IUCN highlights the critical importance of UNESCO World Heritage sites in conserving biodiversity.
Details
Rich Biodiversity
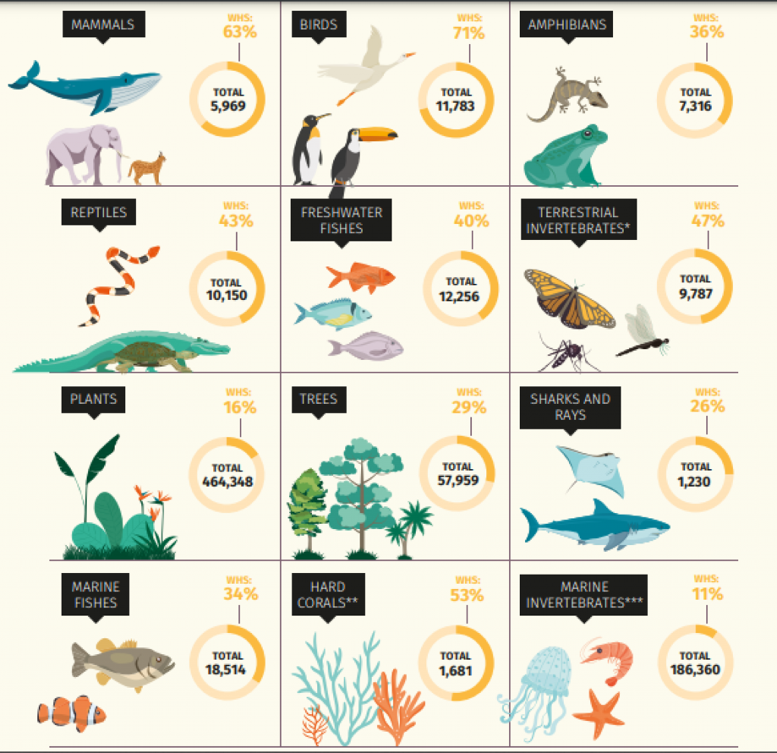
- UNESCO World Heritage sites are home to an astonishing array of biodiversity, including 75,000 species of plants and over 30,000 species of mammals, birds, fish, reptiles, and amphibians.
- These sites collectively harbor a fifth of all the species known globally.
Iconic Species
- Many iconic and endangered species find refuge in these sites.
- Up to one-third of the remaining populations of elephants, tigers, and pandas, and at least one in ten great apes, giraffes, lions, and rhinos inhabit these areas. For example, all remaining Javan rhinos and vaquitas are found within these sites.
Protection and Challenges
- While these sites provide a safe haven for many threatened species, they are not immune to challenges.
- Climate change and human activities such as agricultural expansion, infrastructure development, poaching, overexploitation of resources, and the introduction of invasive species threaten their biodiversity.
Climate Impact
- The report underscores the significance of protecting these sites in the context of climate change.
- A 1-degree Celsius increase in global temperature can double the number of species threatened by adverse climate conditions, making the preservation of these sites even more urgent.
Expansion of World Heritage Sites
- The report encourages countries to nominate additional biodiversity-rich areas for World Heritage status.
- This expansion would extend protections to more critical ecosystems and species.
Cultural Sites and Biodiversity
- Cultural World Heritage sites also play a vital role in biodiversity conservation, with approximately 20% of them located in Key Biodiversity Areas. This demonstrates the interconnectedness of culture and nature.
Ecosystem Services
- World Heritage sites not only conserve biodiversity but also provide essential ecosystem services.
- These sites help maintain water resources, support sustainable livelihoods, and foster a positive relationship between humans and nature.
Policy Recommendations
- The report calls for governments to prioritize World Heritage sites in their National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans, aligning conservation efforts with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
Climate Adaptation
- By 2025, all World Heritage site managers will receive training in climate change adaptation strategies.
- By 2029, climate adaptation plans will be in place for all sites. These measures highlight the commitment to address climate-related challenges.

Conclusion
UNESCO World Heritage sites are not only of cultural and historical significance but also serve as invaluable strongholds for biodiversity. Protecting these sites is essential for safeguarding iconic species, conserving biodiversity, and addressing the challenges posed by climate change and human activities. The report emphasizes the need for a holistic approach that recognizes the interdependence of nature and culture in conservation efforts.
MUST READ ARTICLES:
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/world-heritage-sites-47
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which statement is true regarding UNESCO World Heritage Sites?
1. All UNESCO World Heritage Sites are natural landscapes.
2. UNESCO World Heritage Sites are recognized for their cultural, historical, or natural significance.
3. UNESCO World Heritage Sites are primarily selected based on their economic value.
Options:
A) 1 only
B) 2 and 3
C) 2 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
|
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/wildlife-biodiversity/protect-world-heritage-sites-to-conserve-biodiversity-un-91481

















