Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- In a landmark surgery in January, doctors replaced the heart of a 57-year-old patient with the heart of a genetically altered pig. However, the patient died two months after the operation.
About
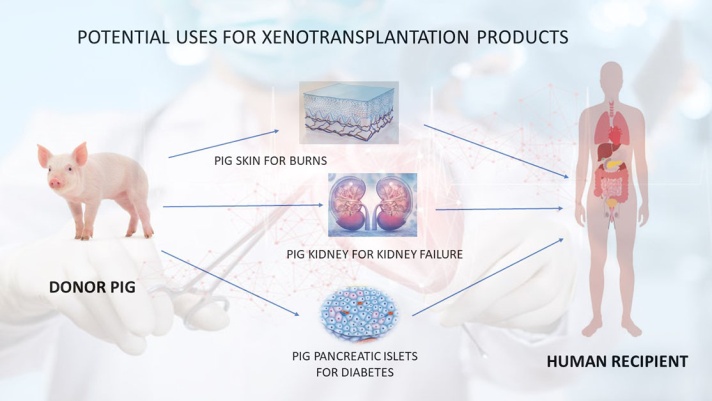
- Xenotransplantation is any procedure that involves the transplantation, implantation or infusion into a human recipient of either -
(a) live cells, tissues, or organs from a nonhuman animal source, or
(b) human body fluids, cells, tissues or organs that have had ex vivo contact with live nonhuman animal cells, tissues or organs.
- Such cells, tissues or organs are called xenografts or xenotransplants.
Need
- The development of xenotransplantation is, in part, driven by the fact that the demand for human organs for clinical transplantation far exceeds the supply.
Challenges pertaining to Xenotransplantation
Shorter life spans of animal organs.
- Typically, animals have much shorter life spans than humans. Even if the success rate improves for transplanting animal organs to humans, there would still be a risk of the organs wearing out or dying prematurely.
Xenozoonosis
- Disease transmission (xenozoonosis) and permanent alteration to the genetic code of animals are also causes for concern.
Animal Rights
- Similarly to objections to animal testing, animal rights activists have also objected to xenotransplantation on ethical grounds.
Moral issues
- Many oppose xenotransplantation because of their religious beliefs that uphold humans being a superior species to animals, thus making them stand their ground that mixing species is against God’s will.
Very high rejection rate
- Human body recognizes tissues and organs from animals as not being natural. Thus, strong anti-rejection drugs are needed when performing xenotransplantation to depress the entire immune system. Most organ transplant procedures were not able to prove very effective in the long run.
Prospects of Xenotransplantation
Potential treatment for end-stage organ failure
- Human xenotransplantation offers a potential treatment for end-stage organ failure, a significant health problem in parts of the industrialized world.
Increase Organ Availability
- Xenoplantation has the potential to increase organ availability.
Open New Research Areas
- This would open new research about treating illnesses meaning that different animals have individual ways of fighting infections and through xenoplantation humans might be able to cure deadly diseases.
End Transplant List
- If xenoplantation has a positive outcome when transferring pig organs to humans the availability of pig organs is much higher than human organs. This would help decrease the organ transplant list and cut waiting time for patients.
Life-saving benefits
- It can offer life-saving solutions to extend the life of a person who is on a human transplant list long enough.
Reduces opportunities on the black market for organ donations
- The sale of human organs on the black market has been a huge issue. Using organs from animals, instead of those donated by humans, can end this type of trade.
Satisfy the supply and demand of organs
- This method of organ transplantation has the potential to eliminate the huge deficit between high demand and minimal supply of organs.
Final thoughts
- Xenotransplantation has raised a lot of good questions that lean to both the positive and the negative sides.
- By weighing its pros and cons, the government and concerned stakeholders can decide whether this is a technology that we pursue as a society or not.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/everyday-explainers/what-is-xenotransplantation-7814612/















