Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.firstpost.com/india/china-builds-xiaokang-border-defence-village-in-arunachal-implications-for-indias-security-10124821.html
Context: China has recently occupied newly constructed "Xiaokang" border villages along India's northeastern border, raising concerns due to their dual-use infrastructure near the Line of Actual Control in Arunachal Pradesh and Lohit Valley.
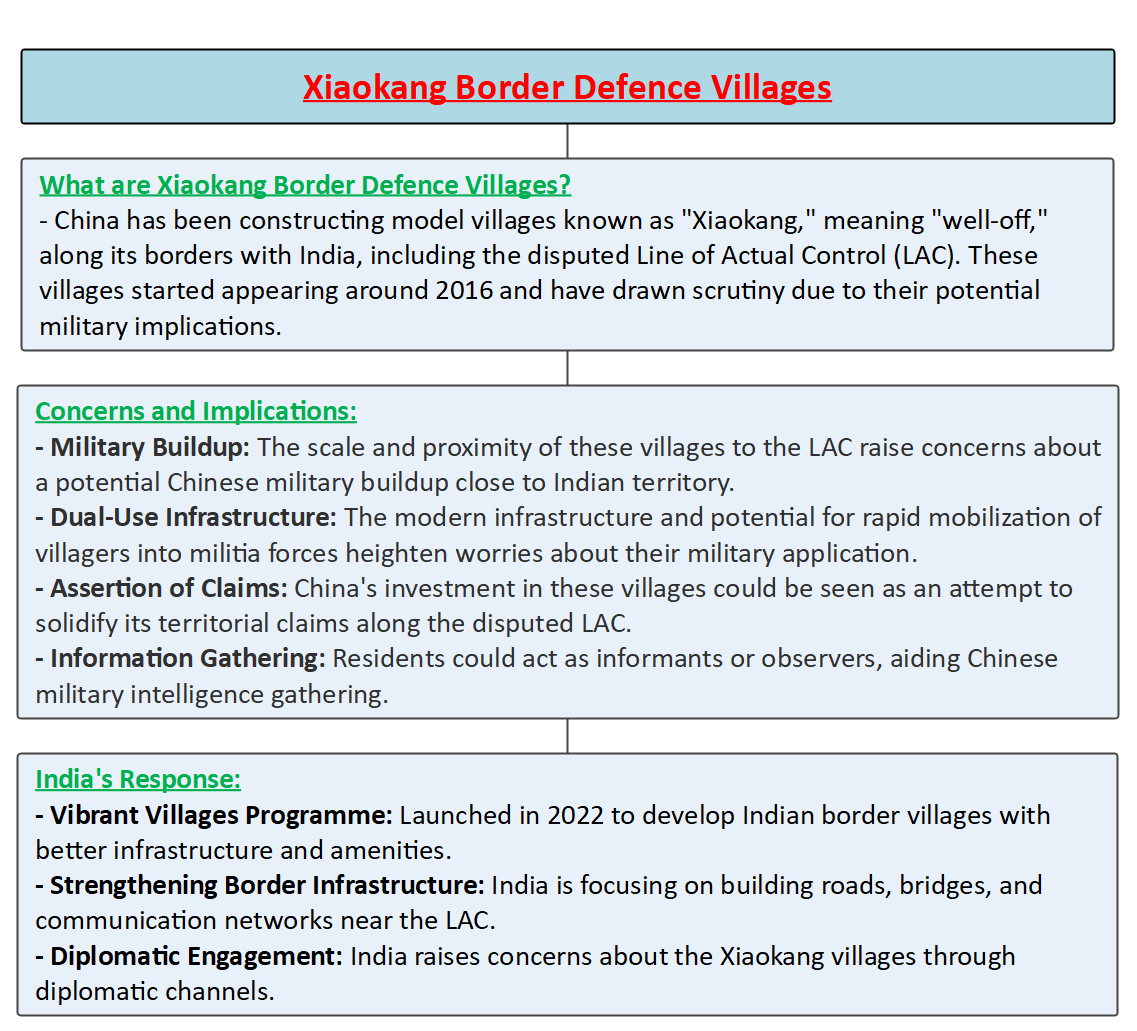
Xiaokang Border Defence Villages
- The Xiaokang Border Defence Villages are part of China's broader strategy to assert its presence and influence along its borders, particularly with neighbouring countries like India.
- These villages have been constructed along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), which separates India and China. The term "Xiaokang" translates to "well-off" or "moderately prosperous" in English.
Features
- Construction and Structure: The Xiaokang villages consist of more than 600 well-constructed, double-storey, and spacious buildings, located strategically along the borders.
- Dual-Use Nature: While the exact purposes of these villages remain unclear, they are considered dual-use infrastructure, capable of serving both civilian and military functions. This dual-use nature raises concerns from a defence perspective, as it can be seen as an attempt to consolidate territorial claims along the LAC.
- Strategic Significance: The Xiaokang villages are strategically placed to enhance China's presence in border areas, potentially providing logistical support to military operations and asserting influence in disputed territories.
Steps Taken by India
- Vibrant Villages Programme: In response to China's Xiaokang villages, India introduced the Vibrant Villages Programme in 2022. This initiative aims to develop border villages into modern settlements with amenities and tourist attractions.
- Border Area Development Programme (BADP): Building on the existing BADP under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, India plans to develop 663 border villages in the first phase, including 17 along the borders with China in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Focus on Infrastructure: India is concentrating on strengthening its border infrastructure and constructing new roads, bridges, and helipads to improve accessibility and connectivity in the northeastern region.

Challenges
- The dual-use nature of Xiaokang villages raises security concerns for India, as these structures may have implications for military activities along the LAC.
- The Xiaokang villages are located in disputed border regions, adding complexity to already contentious territorial disputes between India and China.
- The ongoing construction of infrastructure by both India and China along the LAC can lead to a potential arms race, escalating tensions in the region.
Way Forward
- Continued diplomatic efforts and dialogue between India and China are essential to address border issues, including the concerns arising from the Xiaokang villages.
- Engaging with international bodies and neighbouring countries to garner support and understanding regarding the implications of such developments can contribute to a more stable and cooperative regional environment.
- Exploring multilateral agreements or frameworks for border management and dispute resolution can provide a structured approach to handling conflicts.
- Implementing confidence-building measures between India and China to foster trust and transparency in border-related activities.
- Exploring avenues for economic cooperation and mutually beneficial projects in border regions can create incentives for peaceful coexistence.
Conclusion
- The Xiaokang border defence villages represent a significant development along the India-China border with potential implications for both countries' security and economic interests. While the exact purpose remains unclear, the dual-use nature and strategic location of these villages raise concerns for India and necessitate a measured response focusing on infrastructure development, alternative routes, and improved border preparedness.
Must Read Articles:
India-China Border Dispute: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/india-china-border-dispute-42
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. In the context of the broader global landscape, including the rise of new power dynamics and the US-China rivalry, how does the India-China border dispute fit into the larger strategic picture, and what are the potential implications for global security and stability?
Answer Structure:
●Provide some background information on the India-China border dispute, such as the historical origins, the main areas of contention, and the recent developments.
●Analyze the broader global landscape, including the rise of new power dynamics and the US-China rivalry, and how they affect the interests and motivations of both India and China in the border dispute.
●Discuss the potential implications for global security and stability, such as the risks of escalation, the impact on regional cooperation, and the role of other actors and institutions.
●Conclude with some recommendations or suggestions for resolving or managing the border dispute peacefully and constructively.
|