Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Zimbabwe announced that it will construct its first utility-scale geothermal energy Independent Power Producer (IPP) and support the reduction of greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions in the country, of which the energy sector is the highest contributor.
Details
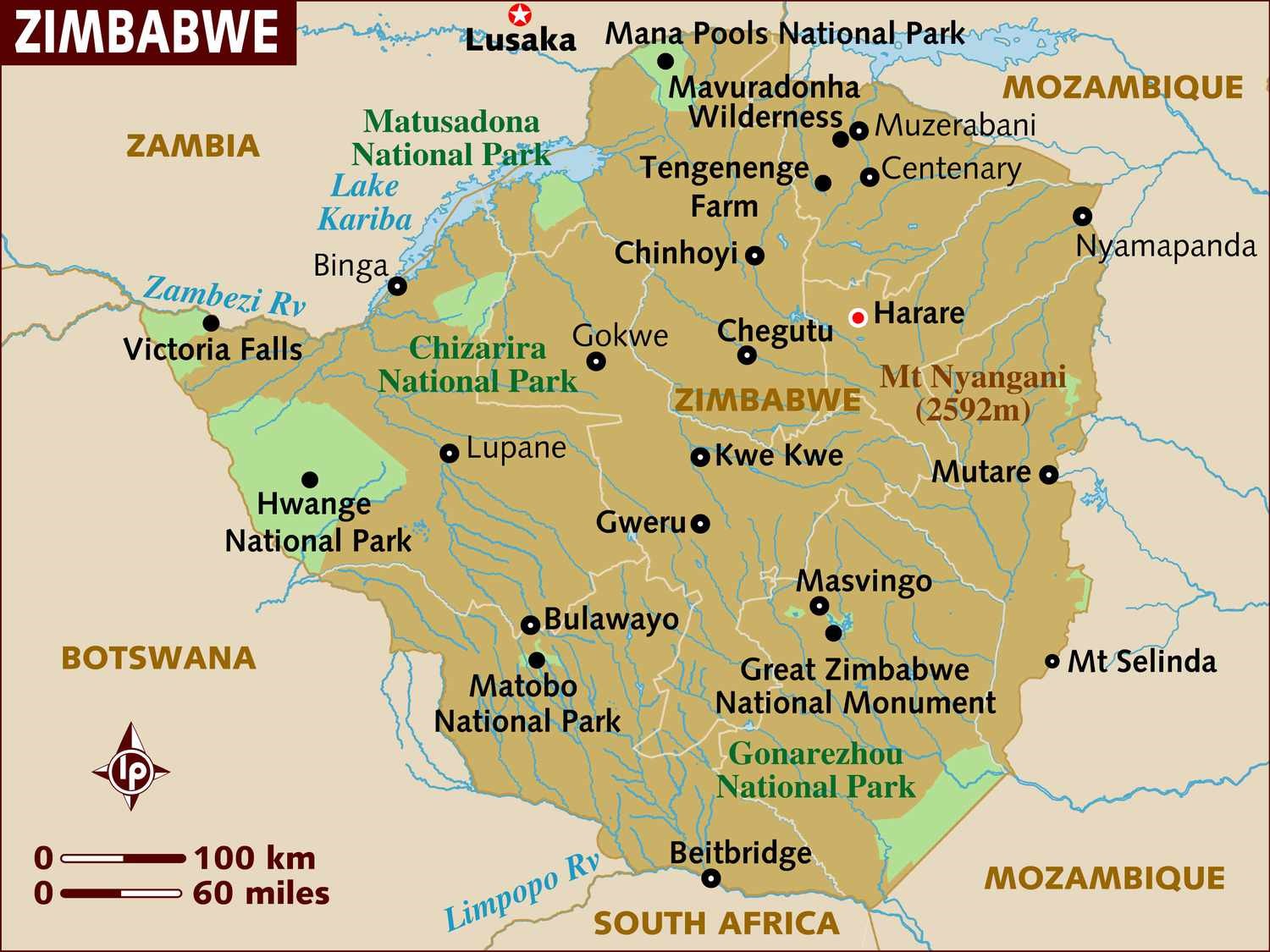
- Zimbabwe, a landlocked country located in southern Africa, has a rich history, diverse culture, and significant economic and natural resources.
Geography and Location
- Location: Situated in southern Africa, Zimbabwe shares its borders with Zambia, Mozambique, South Africa, and Botswana.
- Physical Features: The country boasts diverse landscapes, including savannas, mountains (such as the Eastern Highlands), plateaus, and the iconic Victoria Falls on the Zambezi River.
Historical Overview
- Pre-Colonial Era: The region that is now Zimbabwe was home to several kingdoms, notably the Great Zimbabwe Empire, known for its impressive stone structures.
- Colonial Period: Zimbabwe was formerly known as Rhodesia and was under British colonial rule until gaining independence in 1980. The struggle for independence was led by figures like Robert Mugabe.
Political Landscape
- Government: Zimbabwe is a republic with a presidential system. It has faced political challenges, including issues related to governance, human rights, and economic policies.
- Robert Mugabe Era: Robert Mugabe, a prominent figure in the country's history, served as Prime Minister and later as President for several decades, until his resignation in 2017.

Major Rivers
- Zambezi River: The Zambezi, one of Africa's largest rivers, flows through Zimbabwe, creating the iconic Victoria Falls, one of the world's largest waterfalls.
- Limpopo River: Forms part of Zimbabwe's southern border with South Africa and serves as a vital water source for the region.
- Save River: A major river in southeastern Zimbabwe, it is a key waterway supporting agriculture and wildlife in the region.
Mountains and Highlands
- Eastern Highlands: This mountainous region, bordering Mozambique, features high peaks, lush forests, and fertile valleys. Mount Nyangani is the highest peak in Zimbabwe, part of the Eastern Highlands.
- Chimanimani Mountains: A subrange of the Eastern Highlands, known for its scenic beauty, diverse flora, and popular hiking trails.
- Matobo Hills: Located in the southwest, these granite hills are renowned for their unique rock formations, ancient rock art, and spiritual significance to the local communities.
Ecological Aspects
- Wildlife and National Parks: Zimbabwe is home to diverse wildlife, including elephants, lions, rhinoceroses, buffalo, and various antelope species. National parks like Hwange, Mana Pools, and Matobo Hills protect these animals and offer safari opportunities.
- Vegetation and Biodiversity: The country's diverse ecosystems support varied vegetation, from savannas to forests, fostering a rich array of plant species. The Zambezi Valley and Eastern Highlands are particularly diverse in flora.
- Conservation Efforts: Zimbabwe has made efforts to conserve its natural heritage through protected areas, community-based conservation initiatives, and sustainable tourism practices.
Water Bodies and Wetlands
- Kariba Dam: The Kariba Dam, on the Zambezi River, forms Lake Kariba, one of the world's largest man-made lakes, providing hydroelectric power and supporting local ecosystems.
- Chinhoyi Caves: These limestone caves contain an underground pool known as "The Sleeping Pool," renowned for its clear blue water and unique geological formations.
Economy and Resources
- Agriculture: Agriculture forms the backbone of the economy, with crops like tobacco, maize, and cotton being major exports. However, land reforms and economic challenges have impacted agricultural productivity.
- Mineral Resources: Zimbabwe is rich in mineral resources, including gold, platinum, diamonds, and chrome, attracting mining interests. The country has potential in the mining sector.
Socio-Cultural Aspects
- Culture: The country is known for its vibrant culture, traditional music, dance (like the mbira), and art, reflecting the heritage of different ethnic groups such as the Shona and Ndebele.
- Languages: English is the official language, while indigenous languages, including Shona and Sindebele (Ndebele), are widely spoken.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- Economic Challenges: Zimbabwe has faced economic hardships, including hyperinflation and unemployment, leading to social and political unrest.
- Reforms and Development: Efforts to implement economic reforms, improve governance, and attract foreign investment aim to drive sustainable development and address past challenges.
.jpg)
Conclusion
Zimbabwe, with its rich history, diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and natural resources, has faced various challenges but holds immense potential for growth and development. Efforts toward economic stability, good governance, and leveraging its resources could contribute to a brighter future for the nation.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements regarding Zimbabwe:
- The highest peak in Zimbabwe is Mount Nyangani, situated in the Matobo Hills.
- The Limpopo River forms part of Zimbabwe's border with South Africa.
- Victoria Falls, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is located on the Zambezi River in Zimbabwe.
Which of the statements above is/are correct?
A) Only 1 and 2
B) Only 2 and 3
C) Only 1 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: C)
|
















