
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Overview:
- India’s economic recovery from the Covid pandemic is complete and the economy is expected to grow in the range of 6% to 6.8% in the coming financial year 2023-24.
- Despite the slowdown, India will remain the fastest-growing major economy in the world, as per the Economic Survey 2022-23.
- Prepared by the Chief Economic Advisor, V Anantha Nageswaran, the Economic Survey details the state of the economy, the challenges due to global uncertainties and the roadmap for India’s growth in the remainder of this decade.
We’ll analyze the key highlights of the annual report card of the economy. But in the first place, let us learn about the basics of the Economic Survey.
What is the Economic Survey?
- The Economic Survey of Indiais an annual document of the Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
- The Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance presents the Survey in the Parliamentevery year, just before the Union Budget.
- It is prepared under the guidance of the Chief Economic Adviserof India. This document is presented to both Houses of Parliament during the Budget Session.
- The first Economic Survey of India was presented in 1950-51 as part of the Union Budget.
- After 1964 it was separated from the Budget and presented each year during the Budget Session before the presentation of the budget. The document is non-binding. Nevertheless, is constructed and presented each year due to its significance.
.jpeg)
Content of the Survey:
- The document is the Ministry's view on the state of the economy of the country. This document of the Ministry, the Economic Survey of India
- Reviews the developments in the Indian economyover the past financial year,
- Summarizes the performance on major development programs, and
- Highlights the policy initiatives of the government and the prospects of the economy in the short to medium term.
|
Trivia
Unlike the traditional Economic Survey, the Economic Survey of India for 2016–17, prepared by Chief Economic Adviser Arvind Subramanian, did not have the detailed financial statistics of the Government of India.
|
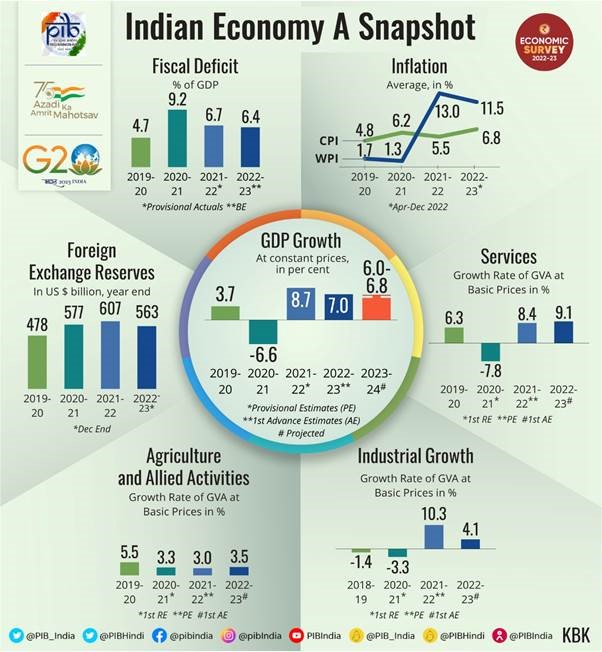
State of the Economy 2022-23: Recovery Complete:
- Recovering from pandemic-induced contraction, Russian-Ukraine conflict and inflation, Indian economy is staging a broad-based recovery across sectors, positioning to ascend to the pre-pandemic growth path in FY23.
- India’s GDP growth is expected to remain robust in FY24. GDP forecast for FY24 to be in the range of 6-6.8 %.
- Private consumption in H1 (The first half of a calendar year) is highest since FY15 and this has led to a boost to production activity resulting in enhanced capacity utilisation across sectors.
- The Capital Expenditure of Central Governmentand crowding in the private Capex led by strengthening of the balance sheets of the Corporates is one of the growth driver of the Indian economy in the current year.
|
CAPITAL EXPENDITURE
Capital expenditure is the money spent by the government on the development of machinery, equipment, building, health facilities, education, etc. It also includes the expenditure incurred on acquiring fixed assets like land and investment by the government that gives profits or dividend in future. Capital spending is associated with investment or development spending, where expenditure has benefits extending years into the future. Capital expenditure includes money spent on the following:
- Acquiring fixed and intangible assets
- Upgrading an existing asset
- Repairing an existing asset
- Repayment of loan
Why is capital expenditure important?
Capital expenditure, which leads to the creation of assets are long-term in nature and allow the economy to generate revenue for many years by adding or improving production facilities and boosting operational efficiency. It also increases labour participation, takes stock of the economy and raises its capacity to produce more in future.
Along with the creation of assets, repayment of loan is also capital expenditure, as it reduces liability.
How is capital expenditure different from revenue expenditure?
Unlike capital expenditure, which creates assets for the future, revenue expenditure is one that neither creates assets nor reduces any liability of the government. Salaries of employees, interest payment on past debt, subsidies, pension, etc, fall under the category of revenue expenditure. It is recurring in nature.
|
- The credit growth to the MSME sector was over 30.6 per cent on average during Jan-Nov 2022.
- Retail inflation is back within RBI’s target range in November 2022.
Read about Retail Inflation: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/retail-inflation-42
- Indian Rupee performed well compared to other Emerging Market Economies in Apr-Dec2022.
- Direct Tax collections for the period April-November 2022 remain buoyant.
Read about Direct taxes: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/direct-taxes-11
- Enhanced Employment generation seen in the declining urban unemployment rate and in the faster net registration in Employee Provident Fund.
- Economic growth to be boosted from the expansion of public digital platforms and measures to boost manufacturing output.
Read about Manufacturing Sector and PMI: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/indias-manufacturing-sector-and-pmi
India’s Medium Term Growth Outlook: with Optimism and Hope:
- Indian economy underwent wide-ranging structural and governance reforms that strengthened the economy’s fundamentals by enhancing its overall efficiency during 2014-2022.
- With an underlying emphasis on improving the ease of living and doing business, the reforms after 2014 were based on the broad principles of creating public goods, adopting trust-based governance, co-partnering with the private sector for development, and improving agricultural productivity.
- The period of 2014-2022 also witnessed balance sheet stress caused by the credit boom in the previous years and one-off global shocks, that adversely impacted the key macroeconomic variables such as credit growth, capital formation, and hence economic growth during this period.
- This situation is analogous to the period 1998-2002 when transformative reforms undertaken by the government had lagged growth returns due to temporary shocks in the economy. Once these shocks faded, the structural reforms paid growth dividends from 2003.
- Similarly, the Indian economy is well placed to grow faster in the coming decade once the global shocks of the pandemic and the spike in commodity prices in 2022 fade away.
- With improved and healthier balance sheets of the banking, non-banking and corporate sectors, a fresh credit cycle has already begun, evident from the double-digit growth in bank credit over the past months.
- Indian economy has also started benefiting from the efficiency gains resulting from greater formalisation, higher financial inclusion, and economic opportunities created by digital technology-based economic reforms.
- Thus Chapter 2 of the Survey shows that India’s growth outlook seems better than in the pre-pandemic years, and the Indian economy is prepared to grow at its potential in the medium term.
Fiscal Developments: Revenue Relish:
- The Union Government finances have shown a resilient performance during the year FY23, facilitated by the recovery in economic activity, buoyancy in revenues from direct taxes and GST, and realistic assumptions in the Budget.
- The Gross Tax Revenue registered a YoY growth of 15.5 per cent from April to November 2022, driven by robust growth in the direct taxes and Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- Growth in direct taxes during the first eight months of the year was much higher than their corresponding longer-term averages.
- GST has stabilised as a vital revenue source for central and state governments, with the gross GST collections increasing at 24.8 per cent on YoY basis from April to December 2022.
Read about GST collections and 47th GST Council Meeting:
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/gst-collections-and-revisiting-47th-gst-council-meeting-recommendations
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/goods-and-services-tax-gst-collections
- Union Government’s emphasis on capital expenditure (Capex) has continued despite higher revenue expenditure requirements during the year. The Centre’s Capex has steadily increased from a long-term average of 1.7 per cent of GDP (FY09 to FY20) to 2.5 per cent of GDP in FY22 PA.
- The Centre has also incentivised the State Governments through interest-free loans and enhanced borrowing ceilings to prioritise their spending on Capex.
Read in this context: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/special-assistance-for-capital-investment-scheme
- With an emphasis on infrastructure-intensive sectors like roads and highways, railways, and housing and urban affairs, the increase in Capex has large-scale positive implications for medium-term growth.
- The Government’s Capex-led growth strategy will enable India to keep the growth-interest rate differential positive, leading to a sustainable debt to GDP in the medium run.

Read:
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/government-borrowing-or-public-debt#:~:text=Public%20Debt%20as%20a%20percentage%20of%20GDP&text=The%20Government's%20liabilities%20account%20for,as%20the%20ratio%20in%202019.
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/indias-external-debt
Monetary Management and Financial Intermediation: A Good Year:
- The RBI initiated its monetary tightening cycle in April 2022 and has since raised the repo rate by 225 bps, leading to moderation of surplus liquidity conditions.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/monetary-policy
- Cleaner balance sheets led to enhanced lending by financial institutions.
- The growth in credit offtake is expected to sustain, and combined with a pick-up in private capex, will usher in a virtuous investment cycle.
- Non-food credit offtake by scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) has been growing in double digits since April 2022.
|
Credit offtake in other words is increase in credit growth. This happens when lenders mobilise funds to commercial sector in order to earn better returns compared to government bonds and securities.
|
- Credit disbursed by Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) has also been on the rise.
All about NBFCs: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/nbfcs-and-its-types#:~:text=NBFC%20is%20governed%20by%20both,savings%2Fcurrent%20accounts%20with%20it.
- The Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio of SCBs has fallen to a seven-year low of 5.0.
Read about GNPA: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/gross-non-performing-assets
- The Capital-to-Risk Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) remains healthy at 16.0.
|
CRAR
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is also known as Capital to Risk (Weighted) Assets Ratio (CRAR),[1] is the ratio of a bank's capital to its risk. It is a measure of a bank's capital.
It is measured as
Capital Adequacy Ratio = (Tier I + Tier II + Tier III (Capital funds)) /Risk weighted assets
The risk weighted assets take into account credit risk, market risk and operational risk.
The Basel III norms stipulated a capital to risk weighted assets of 8%. However, as per RBI norms, Indian scheduled commercial banks are required to maintain a CAR of 9% while Indian public sector banks are emphasized to maintain a CAR of 12%.
Note
Tier 1 capital is a bank's core capital, which consists of shareholders' equity and retained earnings; it is of the highest quality and can be liquidated quickly. This is the real test of a bank's solvency. Tier 2 capital includes revaluation reserves, hybrid capital instruments, and subordinated debt. In addition, tier 2 capital incorporates general loan-loss reserves and undisclosed reserves.
Tier 1 capital is intended to measure a bank's financial health; a bank uses tier 1 capital to absorb losses without ceasing business operations. Tier 2 capital is supplementary, i.e., less reliable than tier 1 capital. A bank's total capital is calculated as a sum of its tier 1 and tier 2 capital.
Tier 3 capital consists of subordinated debt to cover market risk from trading activities.
|
- The recovery rate for the SCBs through Insolvency and Bankruptcy (IBC) was highest in FY22 compared to other channels.
Read all about IBCs: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/insolvency-and-bankruptcy-code-ibc-2016
Prices and Inflation: Successful Tight-Rope Walking:
- While the year 2022 witnessed a return of high inflation in the advanced world after three to four decades, India caps the rise in prices.
- India’s retail inflation rate peaked at 7.8 per cent in April 2022, above the RBI’s upper tolerance limit of 6 per cent. But the overshoot of inflation above the upper end of the target range in India was however one of the lowest in the world.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/retail-inflation-3#:~:text=Retail%20inflation%20tracked%20by%20the,at%20the%20level%20of%20producers.
- The government adopted a multi-pronged approach to tame the increase in price levels:
- Phase wise reduction in export duty of petrol and diesel.
- Import duty on major inputs were brought to zero while tax on export of iron ores and concentrates increased from 30 to 50 per cent.
- Waived customs duty on cotton imports w.e.f 14 April 2022, until 30 September 2022.
- Prohibition on the export of wheat products under HS Code 1101 and imposition of export duty on rice.
- Reduction in basic duty on crude and refined palm oil, crude soyabean oil and crude sunflower oil.
- The RBI’s anchoring of inflationary expectations through forward guidance and responsive monetary policy has helped guide the trajectory of inflation in the country.
- The one-year-ahead inflationary expectations by both businesses and households have moderated in the current financial year.
- Timely policy intervention by the government in housing sector, coupled with low home loan interest rates propped up demand and attracted buyers more readily in the affordable segment in FY23.
- An overall increase in composite Housing Price Indices (HPI) assessment and Housing Price Indices market prices indicates a revival in the housing finance sector. A stable to moderate increase in HPI also offers confidence to homeowners and home loan financiers in terms of the retained value of the asset.
- India’s inflation management has been particularly noteworthy and can be contrasted with advanced economies that are still grappling with sticky inflation rates.
Social Infrastructure and Employment: Big Tent:
- Social Sector witnessed significant increase in government spending.
- Central and State Government’s budgeted expenditure on health sector touched 2.1% of GDP in FY23 (BE) and 2% in FY22 (RE) against 1.6% in FY21.
- Social sector expenditure increases to Rs. 21.3 lakh crore in FY23 (BE) from Rs. 9.1 lakh crore in FY16.
- Survey highlights the findings of the 2022 report of the UNDP on Multidimensional Poverty Index which says that 5 crore people exit poverty in India between 2005-06 and 2019-20.
- The Aspirational Districts Programme has emerged as a template for good governance, especially in remote and difficult areas.
Read about ASP: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/aspirational-district-programme-41
- eShram portal developed for creating a National database of unorganised workers, which is verified with Aadhaar. As on 31 December 2022, a total of over 5 crore unorganised workers have been registered on eShram portal.
Read about e-Shram Portal: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/e-shram-portal-35
- JAM (Jan-Dhan, Aadhaar, and Mobile) trinity, combined with the power of Direct Benefit Transfer, has brought the marginalised sections of society into the formal financial system, revolutionising the path of transparent and accountable governance by empowering the people.
Read about JAM Trinity: https://theprint.in/economy/what-is-the-jan-dhan-account-aadhaar-mobile-trinity-has-it-aided-indias-war-on-poverty/1257768/
- Aadhaar played a vital role in developing the Co-WIN platform and in the transparent administration of over 2 billion vaccine doses.
- Labour markets have recovered beyond pre-Covid levels, in both urban and rural areas, with unemployment rates falling from 5.8 per cent in 2018-19 to 4.2 per cent in 2020-21.
- The year FY22 saw improvement in Gross Enrolment Ratios (GER) in schools and improvement in gender parity. GER in the primary-enrolment in class I to V as a percentage of the population in age 6 to 10 years – for girls as well as boys have improved in FY22.
Read about New Education Policy: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/national-education-policy-2020-14
- Due to several steps taken by the government on health, out-of-pocket expenditure as a percentage of total health expenditure declined from 64.2% in FY14 to 48.2% in FY19.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/indias-health-expenditure
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR), Under Five mortality rate (U5MR) and neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR) have shown a steady decline.
Read about IMR: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/infant-mortality-rate-imr
- More than 220 crore COVID vaccine doses administered as on 06 January, 2023.
- Nearly 22 crore beneficiaries have been verified under the Ayushman Bharat Scheme as on 04 January, 2023. Over 1.54 lakh Health and Wellness Centres have been operationalized across the country under Ayushman Bharat.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/ayushman-bharat-pradhan-mantri-jan-arogya-yojana-ab-pmjay
Climate Change and Environment: Preparing to Face the Future:
- India declared the Net Zero Pledge to achieve net zero emissions goal by 2070.
- India achieved its target of 40 per cent installed electric capacity from non-fossil fuels ahead of 2030.
- The likely installed capacity from non-fossil fuels to be more than 500 GW by 2030 resulting in decline of average emission rate by around 29% by 2029-30, compared to 2014-15.
- India to reduce emissions intensity of its GDP by 45% by 2030 from 2005 levels.
- About 50% cumulative electric power installed capacity to come from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030.
- A mass movement LIFE– Life style for Environment launched.
- Sovereign Green Bond Framework (SGrBs) issued in November 2022.
- RBI auctions two tranches of ₹4,000 crore Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrB).
- National Green Hydrogen Mission to enable India to be energy independent by 2047.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/national-hydrogen-mission-45
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/green-hydrogen-47
https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/green-hydrogen-an-overview
- Green hydrogen production capacity of at least 5 MMT (Million Metric Tonne) per annum to be developed by 2030. Cumulative reduction in fossil fuel imports over ₹1 lakh crore and creation of over 6 lakh jobs by 2030 under the National green Hydrogen Mission. Renewable energy capacity addition of about 125 GW and abatement of nearly 50 MMT of annual GHG emissions by 2030.
- The Survey highlights the progress on eight missions under the NAP on CC to address climate concerns and promote sustainable development.
- Solar power capacity installed, a key metric under the National Solar Mission stood at 61.6 GW as on October 2022.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/solar-energy-in-india
- India becoming a favored destination for renewables; investments in 7 years stand at USD 78.1 billion.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/renewable-energy-in-india-15
https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/renewable-energy-in-india
- 8 lakh individual household toilets and 6.2 lakh community and public toilets constructed (August 2022) under the National Mission on Sustainable Habitat.
|
National Mission on Sustainable Habitat
The National Mission on Sustainable Habitat was approved by the Prime Minister’s Council for Climate Change in June 2010. The Prime Minister released India’s first National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) outlining existing and future policies and programs addressing climate mitigation. There are eight National Missions under the National Action Plan, with the National Mission on Sustainable Habitat being one of them.
The focus of these Missions is to promote understanding of climate change, its adaptation and mitigation, energy efficiency and natural resource conservation.
Objectives of the Mission
The National Mission on Sustainable Habitat seeks to promote:
- Improvements in energy efficiency in buildings through extension of the energy conservation building code - which addresses the design of new and large commercial buildings to optimize their energy demand;
- Better urban planning and modal shift to public transport - make long term transport plans to facilitate the growth of medium and small cities in such a way that ensures efficient and convenient public transport;
- Improved management of solid and liquid waste, e.g. recycling of material and urban waste management – with special focus on development of technology for producing power from waste;
- Improved ability of habitats to adapt to climate change by improving resilience of infrastructure, community based disaster management, and measures for improving advance warning systems for extreme weather events; and
- Conservation through appropriate changes in legal and regulatory framework.
Mission Targets
The key deliverables of the Mission includes:
- Development of sustainable habitat standards that lead to robust development strategies while simultaneously addressing climate change related concerns;
- Preparation of city development plans that comprehensively address adaptation and mitigation concerns;
- Preparation of comprehensive mobility plans that enable cities to undertake long-term, energy efficient and cost effective transport planning; and
- Capacity building for undertaking activities relevant to the Mission.
Yearwise allocation of Funds
No specific funds have been allocated or are sought for the Mission on Sustainable Habitat, which is being implemented through the 4 flagship missions/ programmes of the Ministry of Urban Development, which are-.
a) Atal Mission on Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
b) Swachh Bharat Mission
c) Smart Cities Mission
d) Urban Transport Programme
The end aim is to adapt and mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to achieve sustainability. A report prepared by TERI for the Ministry of Urban Development for the COP21 summit at Paris, estimated that successful implementation of the above flagship missions has a potential for mitigation of GHG emission amounting to 270 MnTonnes by year 2031.
|
Agriculture and Food Management:
- The performance of the agriculture and allied sector has been buoyant over the past several years, much of which is on account of the measures taken by the government to augment crop and livestock productivity, ensure certainty of returns to the farmers through price support, promote crop diversification, improve market infrastructure through the impetus provided for the setting up of farmer-producer organisations and promotion of investment in infrastructure facilities through the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund.
- Private investment in agriculture increases to 9.3% in 2020-21.
- MSP for all mandated crops fixed at 1.5 times of all India weighted average cost of production since 2018.
Read about MSP: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/minimum-support-price-msp-19
- Institutional Credit to the Agricultural Sector continued to grow to 18.6 lakh crore in 2021-22
- Foodgrains production in India saw sustained increase and stood at 315.7 million tonnes in 2021-22.
- Free foodgrains to about 81.4 crore beneficiaries under the National Food Security Act for one year from January 1, 2023.
- About 11.3 crore farmers were covered under the Scheme in its April-July 2022-23 payment cycle.
- Rs 13,681 crores sanctioned for Post-Harvest Support and Community Farms under the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund.
Read about Agricultural Infrastructure Fund: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/agriculture-infrastructure-fund-39
- Online, Competitive, Transparent Bidding System with 1.74 crore farmers and 2.39 lakh traders put in place under the National Agriculture Market (e-NAM) Scheme.
|
e-NAM
About
National Agriculture Market (NAM) is a pan-India electronic trading portal launched on 14th April, 2016 completely funded by Central Government and implemented by Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC). NAM portal networks the existing APMC (Agriculture Produce Marketing Committee) / Regulated Marketing Committee (RMC) market yards, sub-market yards, private markets and other unregulated markets to unify all the nationwide agricultural markets by creating a central online platform for agricultural commodity price discovery. The scheme envisages deployment of a common e-market platform of 585 selected1 regulated wholesale agriculture market yards by March, 2018. The common electronic trading portal will be called as e-NAM.
Objectives
- To integrate markets first at the level of the States and eventually across the country through a common online market platform, to facilitate pan – India trade in agricultural commodities.
- To streamline marketing / transaction procedures and make them uniform across all markets to promote efficient functioning of the markets.
- To promote better marketing opportunities for farmers / sellers through online access to more buyers / markets, removal of information asymmetry between farmer and trader, better and real-time price discovery based on actual demand and supply of agri-commodities, transparency in auction process, prices commensurate with quality of produce, online payment etc. that contribute to marketing efficiency.
- To establish quality assaying systems for quality assurance to promote informed bidding by buyers.
- To promote stable prices and availability of quality produce to consumers.
Beneficiary:
Farmers, Mandis, Traders, Buyers, Processers and Exporters.
Benefits:
Transparent online trading with enhanced accessibility to the market. Real time price discovery for better & stable price realization for producers. Reduced transaction cost for buyers. Availability of information on e-Nam mobile app about commodity prices. The details of price of commodity sold along with quantity are received through SMS. Quality certification. More efficient supply chain & warehouse based sales. Online payment directly to the bank accounts of the farmers.
|
- Organic Farming being promoted through Farmer Producer Organisations (FPO) under the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY).
Read about PKVY: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/paramparagat-krishi-vikas-yojana-and-bharitya-prakratik-krishi-padhati
- India stands at the forefront to promote millets through the International Year of Millets initiative.
Must Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/millet
Industry: Steady Recovery:
- Overall Gross Value Added (GVA) by the Industrial Sector (for the first half of FY 22-23) rose 3.7 per cent, which is higher than the average growth of 2.8 per cent achieved in the first half of the last decade.
|
GVA
Gross Value Added is the value of goods and services produced by an industry, sector, manufacturer, area or region in an economy. It is the total value of output produced, without including the intermediary costs that went into producing them.
GVA is a critical value used to calculate the GDP of the economy. It is also the source from which the first incomes of the System National Accounts (SNA) are counted as primary incomes for the manufacturer.
Read NCERT
|
- Robust growth in Private Final Consumption Expenditure, export stimulus during the first half of the year, increase in investment demand triggered by enhanced public capex and strengthened bank and corporate balance sheets have provided a demand stimulus to industrial growth.
|
PFCE
The Private final consumption expenditure (PFCE) is defined as the expenditure incurred by the resident households and non-profit institutions serving households (NPISH) on final consumption of goods and services, whether made within or outside the economic territory.
|
- The supply response of the industry to the demand stimulus has been robust.
- PMI manufacturing has remained in the expansion zone for 18 months since July 2021, and Index of Industrial Production (IIP) grows at a healthy pace.
Read about PMI: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/purchasing-managers-index-17
- Credit to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) has grown by an average of around 30% since January 2022 and credit to large industry has been showing double-digit growth since October 2022.
Read about MSME: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/msme-sector-21
- Electronics exports rise nearly threefold, from US $4.4 billion in FY19 to US $11.6 Billion in FY22.
- India has become the second-largest mobile phone manufacturer globally, with the production of handsets going up from 6 crore units in FY15 to 29 crore units in FY21.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows into the Pharma Industry has risen four times, from US $180 million in FY19 to US $699 million in FY22.
Read about FDI: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/fdi
- The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes introduced across 14 categories, with an estimated capex of ₹4 lakh crore over the next five years, to plug India into global supply chains. Investment of ₹47,500 crores has been seen under the PLI schemes in the FY22, which is 106% of the designated target for the year. Production/sales worth ₹3.85 lakh crore and employment generation of 3.0 lakh have been recorded due to PLI schemes.
Read about PLI: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/pli-scheme-1
- Over 39,000 compliances have been reducedand more than 3500 provisions decriminalized as of January 2023.
Services: Source of Strength:
- The services sector is expected to grow at 9.1% in FY23, as against 8.4% (YoY) in FY22.
- Robust expansion in PMI services, indicative of service sector activity, observed since July 2022.
Read all about PMI: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/purchasing-managers-index-17
- India was among the top ten services exporting countries in 2021, with its share in world commercial services exports increasing from 3 per cent in 2015 to 4 per cent in 2021.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/indias-exports
- India’s services exports remained resilient during the Covid-19 pandemic and amid geopolitical uncertainties driven by higher demand for digital support, cloud services, and infrastructure modernization.
- Credit to services sector has grown by over 16% since July 2022.
- US$ 7.1 billion FDI equity inflows in services sector in FY22.
- Contact-intensive services are set to reclaim pre-pandemic level growth rates in FY23.
- Sustained growth in the real estate sector is taking housing sales to pre-pandemic levels, with a 50% rise between 2021 and 2022.
- Hotel occupancy rate has improved from 30-32% in April 2021 to 68-70% in November 2022.
- Tourism sector is showing signs of revival, with foreign tourist arrivals in India in FY23 growing month-on-month with resumption of scheduled international flights and easing of Covid-19 regulations.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/tourism-sector-of-india
- Digital platforms are transforming India’s financial services.
- India’s e-commerce market is projected to grow at 18 per cent annually through 2025.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/digital-economy
External Sector:
- Merchandise exports were US$ 332.8 billion for April-December 2022.
- India diversified its markets and increased its exports to Brazil, South Africa and Saudi Arabia.
- To increase its market size and ensure better penetration, in 2022, CEPA with UAE and ECTA with Australia come into force.
- India is the largest recipient of remittances in the world receiving US$ 100 bn in 2022. Remittances are the second largest major source of external financing after service export
- As of December 2022, Forex Reserves stood at US$ 563 bn covering 9.3 months of imports.
- As of end-November 2022, India is the sixth largest foreign exchange reserves holder in the world.
- The current stock of external debt is well shielded by the comfortable level of foreign exchange reserves.
- India has relatively low levels of total debt as a percentage of Gross National Income and short-term debt as a percentage of total debt.
Physical and Digital Infrastructure:
Government’s Vision for Infrastructure Development
- Public Private Partnerships
- In-Principal Approval granted to 56 projects with Total Project Cost of ₹57,870.1 crore under the VGF Scheme, from 2014-15 to 2022-23.
- IIPDF Scheme with ₹150 crore outlay from FY 23-25 was notified by the government on 03 November, 2022.
- National Infrastructure Pipeline
- 89,151 projects costing ₹141.4 lakh crore under different stages of implementation
- 1009 projects worth ₹5.5 lakh crore completed
- NIP and Project Monitoring Group (PMG) portal linkage to fast-track approvals/ clearances for projects
- National Monetisation Pipeline
- ₹ 9.0 lakh crore is the estimated cumulative investment potential.
- ₹ 0.9 lakh crore monetisation target achieved against expected ₹0.8 lakh crore in FY22.
- FY23 target is envisaged to be ₹1.6 lakh crore (27 per cent of overall NMP Target)
- GatiShakti
- PM GatiShakti National Master Plan creates comprehensive database for integrated planning and synchronised implementation across Ministries/ Departments.
- Aims to improve multimodal connectivity and logistics efficiency while addressing the critical gaps for the seamless movement of people and goods.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/pm-gati-shakti
Electricity Sector and Renewables:
- As on 30 September 2022, the government has sanctioned the entire target capacity of 40 GW for the development of 59 Solar Parks in 16 states.
- 2 lakh GWh electricity generated during the year FY22 compared to 15.9 lakh GWh during FY21.
- The total installed power capacity (industries having demand of 1 Mega Watt (MW) and above) increased from 460.7 GW on 31 March 2021 to 482.2 GW on 31 March 2022.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/renewable-energy-in-india-15
Making Indian Logistics Globally Competitive:
- National Logistics Policy envisions to develop a technologically enabled, integrated, cost-efficient, resilient, sustainable and trusted logistics ecosystem in the country for accelerated and inclusive growth.
- Rapid increase in National Highways (NHs) /Roads Construction with 10457 km NHs/roads constructed in FY22 compared to 6061 km in FY16.
- Budget expenditure increased from ₹1.4 lakh crore in FY20 to ₹2.4 lakh crore in FY23 giving renewed push to Capital expenditure.
- 2359 Kisan rails transported approximately 7.91 lakh tonnes of perishables, as of October 2022.
- More than one crore air passengers availed the benefit of the UDAN scheme since its inception in 2016.
- Near doubling of capacity of major ports in 8 years.
- Inland Vessels Act 2021 replaced 100-year-old Act to ensure hassle free movement of Vessels promoting Inland Water Transport.
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/national-logistics-policy
India’s Digital Public Infrastructure:
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI)
- UPI-based transactions grew in value (121 per cent) and volume (115 per cent) terms, between 2019-22, paving the way for its international adoption.
- Telephone and Radio – For Digital Empowerment
- Total telephone subscriber base in India stands at 117.8 crore (as of Sept,22), with 44.3 per cent of subscribers in rural India.
- More than 98 per cent of the total telephone subscribers are connected wirelessly.
- The overall tele-density in India stood at 84.8 per cent in March 22.
- 200 per cent increase in rural internet subscriptions between 2015 and 2021.
- Prasar Bharati (India’s autonomous public service broadcaster) – broadcasts in 23 languages, 179 dialects from 479 stations. Reaches 92 per cent of the area and 99.1 per cent of the total population.
- Digital Public Goods
- Achieved low-cost accessibility since the launch of Aadhaar in 2009
- Under the government schemes, MyScheme, TrEDS, GEM, e-NAM, UMANG has transformed market place and has enabled citizens to access services across sectors
- Under Account Aggregator, the consent-based data sharing framework is currently live across over 110 crore bank accounts.
- Open Credit Enablement Network aims towards democratising lending operations while allowing end-to-end digital loan applications
- National AI portal has published 1520 articles, 262 videos, and 120 government initiatives and is being viewed as viewed as a tool for overcoming the language barrier e.g. ‘Bhashini’.
- Legislations are being introduced for enhanced user privacy and creating an ecosystem for standard, open, and interoperable protocols underlining robust data governance.

Read:
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/upi-service
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/upi
https://sansadtv.nic.in/episode/perspective-economic-survey-2022-23-31-january-2023





