PERSPECTIVE: Transforming Lives Through Digital Platforms
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- India will host the Speakers of the Parliaments of G20 countries next week for the Parliament-20 meeting that will be held from 12th to 14th October in New Delhi.
Details:
- Presiding officers of the Parliaments of the member countries and invitee nations will attend the deliberations. Like the G20 summit, the P20 will also have high-level sessions on various themes, including one on Transformation in People’ Lives through Public Digital Platforms.
- Technology as an enabler of rapid transformations for bridging digital divides and accelerating progress for inclusive and sustainable development has been one of the key priorities of India’s G20 presidency and has been endorsed by world leaders in the New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration.
- In this broadcast, we’ll discuss India’s unprecedented digital transformation, its impact and how India’s approaches and best practices can now be adopted by others to build more equitable, inclusive societies and how the P20 can help implement and accelerate this inclusive growth.
INTRODUCTION:
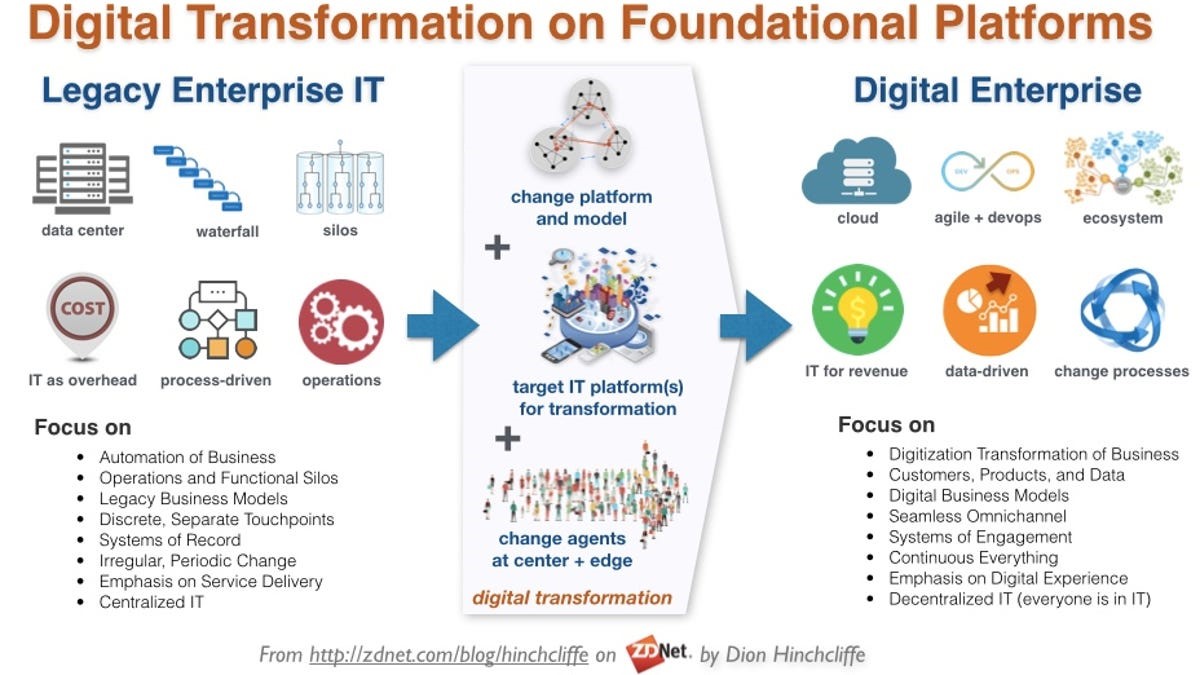
- Digital transformation is a multifaceted concept that has been defined in various ways. One approach involves organisations fundamentally changing their ways of working by redefining their capabilities, processes, and relationships based on technology-driven methods.
- Essentially, this means that companies must recognise the potential of digital technologies and use them to transform their operations, whether that involves rethinking how they produce goods or services or improving their customer interactions.
- Another definition considers digital transformation a strategy that uses digital resources to create added value for the organisation. In this sense, it is a means of leveraging the power of digital technologies to improve business outcomes, such as revenue growth or cost savings.

|
Digital transformation is the integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, fundamentally changing how you operate and deliver value to customers. It's also a cultural change that requires organizations to continually challenge the status quo, experiment, and get comfortable with failure.
|
What is a Digital Platform?
- Website – A government agency’s website is its main and sometimes only online presence. It’s where citizens find information, services, and media like photos and videos.
- Outbound Communications – This refers to all the tools and technology a government organization uses to proactively communicate with the community. This includes email, SMS (texting), and social media.
- Databases, Services, and Systems – Whether it’s a license renewal, information request, social security payment, federal grant application, or something else along those lines, this describes where citizens go to get things done.
- Public Meetings and Records – In addition to meetings that are open to the public, this also includes all records and materials having to do with the legislative process.
|
India today is the world’s largest digitally connected democracy, with 830 million Internet users. Digital transactions have grown manifold in recent years, making India the undisputed leader in real time digital payments.
|

What accelerated Digital Transformation in India?
Government Initiatives:
- The Indian government has launched various initiatives to promote digital transformation. The "Digital India" campaign, launched in 2015, aims to make government services available to citizens electronically. Initiatives like Aadhaar (biometric identification), Unified Payments Interface (UPI), and Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) have played a crucial role in digitizing various aspects of governance and economy.
Demonetization:
- In 2016, the Indian government implemented demonetization, a policy that involved the sudden withdrawal of high-denomination currency notes. This move led to a surge in digital transactions as people turned to electronic payment methods, mobile wallets, and online banking for their financial transactions.
Mobile Penetration:
- The widespread availability and affordability of smartphones have played a pivotal role in digital adoption. As more people gained access to smartphones and affordable data plans, there was a significant increase in internet usage, driving digital services and online transactions.
Digital Payments:
- The growth of digital payment systems, including UPI, mobile wallets, and online banking, has transformed the way people make transactions. The convenience, speed, and security of digital payments have led to a shift from traditional cash-based transactions to electronic modes.
E-commerce Boom:
- The rise of e-commerce platforms, such as Flipkart and Amazon, has transformed the retail landscape. Increased consumer confidence in online shopping, along with the convenience of doorstep delivery, has fueled the growth of the digital economy.
Start-up Ecosystem:
- India has seen a flourishing start-up ecosystem focused on digital technologies. Start-ups in areas like fintech, edtech, healthtech, and e-commerce have introduced innovative solutions, contributing to the overall digital transformation of the country.
COVID-19 Pandemic:
- The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital technologies as people and businesses adapted to remote work, online education, telemedicine, and digital communication. The necessity for contactless services and the increased awareness of digital solutions further propelled the digital transformation in various sectors.
Policy Reforms:
- Regulatory changes and policy reforms have supported digital innovation. For example, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced policies to promote digital payments, and there have been efforts to streamline regulations to encourage technological advancements.

How is Digital Technology Impacting Different Sectors in India?
Finance and Banking:
- Digital Payments: The rise of digital payment systems, such as UPI (Unified Payments Interface) and mobile wallets, has revolutionized the way financial transactions are conducted.
- Online Banking: Digital banking services have made it convenient for individuals and businesses to manage their finances, transfer funds, and conduct transactions online.
- Fintech Innovation: The fintech sector has witnessed significant growth with the introduction of digital lending, robo-advisors, and blockchain-based solutions.
Healthcare:
- Telemedicine: Digital technology has facilitated the growth of telemedicine, enabling remote consultations, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Health Information Systems: Electronic health records (EHR) and health information systems have improved patient data management and healthcare delivery.
- Health Apps: Mobile applications provide access to health information, fitness tracking, and personalized health monitoring.
Education:
- Online Learning: The education sector has experienced a surge in online learning platforms, offering courses, degree programs, and skill development opportunities.
- E-Learning Tools: Digital technology has enabled the use of interactive e-learning tools, virtual classrooms, and educational apps for a more engaging learning experience.
- EdTech Innovation: EdTech startups have introduced innovative solutions for personalized learning, adaptive assessments, and educational content delivery.
E-commerce:
- Online Shopping: E-commerce platforms have transformed retail, providing consumers with a wide range of products and services accessible through online marketplaces.
- Logistics and Delivery: Digital technology has optimized logistics and delivery services, ensuring timely and efficient supply chain management.
Agriculture:
- Precision Farming: Digital tools like sensors, drones, and satellite imagery are used for precision farming, optimizing crop yield and resource utilization.
- Market Access: Digital platforms connect farmers directly to buyers, providing better market access and eliminating intermediaries.
Government Services:
- Digital Governance: Government services are increasingly delivered online, enhancing accessibility and transparency.
- Aadhaar Integration: The Aadhaar system, a biometric identification program, has streamlined identity verification and improved the delivery of government subsidies and services.
How is India Addressing Data Protection in the Digital Age?
Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019:
- The Indian government introduced the Personal Data Protection Bill in 2019 to regulate the processing of personal data in India.
- The bill outlines principles for the processing of personal data, defines the rights of individuals, and establishes obligations for entities handling data.
Data Protection Authority (DPA):
- The proposed legislation includes the establishment of a Data Protection Authority of India (DPA), which would be responsible for overseeing and enforcing data protection laws.
Consent Framework:
- The bill emphasizes the importance of obtaining explicit consent from individuals for the processing of their personal data.
- It introduces provisions for obtaining consent, withdrawal of consent, and the conditions under which data can be processed.
Data Localization:
- The bill includes provisions for data localization, requiring certain categories of personal data to be stored within the borders of India. Critical personal data may have more stringent localization requirements.
Accountability and Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA):
- The legislation emphasizes the accountability of data fiduciaries (entities processing data) and introduces the concept of Data Protection Impact Assessment to assess the potential impact of data processing activities on privacy.

Conclusion
- The transformative power of digital platforms lies in their ability to bridge gaps, empower individuals, and create new opportunities. As technology continues to advance, the potential for positive impact on people's lives continues to grow. However, it's essential to address challenges such as digital divide, privacy concerns, and ethical considerations to ensure that the benefits are accessible to all.
CITATIONS:
https://sansadtv.nic.in/show/perspective
https://enterprisersproject.com/what-is-digital-transformation
https://keralakaumudi.com/en/news/news.php?id=1168293&u=
https://www.cnbctv18.com/india/p20-summit-2024-narendra-modi-inauguration-agenda-who-will-attend-18023761.htm
https://govos.com/blog/what-is-a-digital-transformation-platform/
https://brill.com/view/journals/dias/9/1-2/article-p5_2.xml?language=en
https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/digital-transformation





