Key Provisions of The Public Examinations Prevention of Unfair Means Bill 2024
Context:
- The Parliament has passed the 'Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024' with the Rajya Sabha assent to it today. The Bill is intended to prevent unfair means in the public examinations.
Key Details:
- These Public examinations refer to examinations conducted by the Union Public Service Commission, Staff Selection Commission, Railway Recruitment Board, National Testing Agency, and Departments of the central government.
- The Bill prohibits collusion or conspiracy to facilitate indulgence in any unfair means. Unfair means unauthorized access or leakage of question paper or answer key, assisting a candidate during a public examination, tampering with computer networks, conducting fake examinations, and issuing fake admit cards and offer letters.
- Candidates as defined in the Bill will not be liable for action within the purview of the Bill and will continue to be covered under the extant administrative provisions of the concerned public examination authority.
About the Objectives of the Bill:
| The primary objective of the proposed legislation is to instill greater transparency, fairness, and credibility in public examination systems. It seeks to assure aspiring youth that their sincere efforts will be duly rewarded and their future secured. By effectively deterring individuals, organized groups, or institutions engaged in unfair practices, the bill aims to restore public trust in the examination process. |
The Need for a Comprehensive Bill to Address Question Paper Leaks:
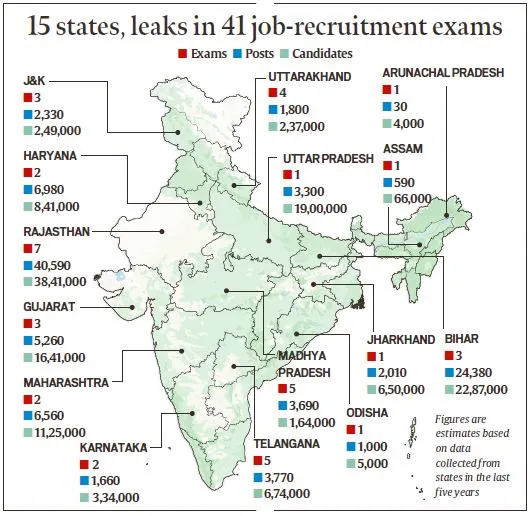
- Instances of Question Paper Leaks: In recent years, the country has witnessed an alarming surge in question paper leaks during recruitment exams. Shockingly, there have been at least 48 reported instances of paper leaks across 16 states in the last five years, disrupting the hiring process for government jobs.
- Approximately 1.51 crore applicants vied for 1.2 lakh posts, making the impact widespread and detrimental.
- Malpractices Lead to Delay in Examinations: The prevalence of malpractices in public examinations has not only disrupted the examination process but has also led to significant delays and cancellations.
- This adversely affects the aspirations of millions of youth, whose futures are intertwined with the timely conduct of these exams.
- Currently, there is a notable absence of a specific substantive law to effectively address the adoption of unfair means or offenses committed in this context.
- Identifying and Addressing Vulnerabilities: Recognizing the urgent need to address vulnerabilities within the examination system, comprehensive central legislation becomes imperative.
- The proposed bill aims to provide legal mechanisms to identify, penalize, and deter individuals, organized groups, or institutions that exploit weaknesses in the system for monetary or wrongful gains.
- To Bring Greater Transparency: The primary objective of the proposed bill is to instill greater transparency, fairness, and credibility in public examination systems.
- It seeks to reassure the youth that their sincere and genuine efforts will be duly recognized and rewarded.
- By establishing a legal framework, the bill aims to restore faith in the examination process and assure candidates that their future is safeguarded against unfair practices.
- Ensuring Fair Rewards for Genuine Efforts: The Bill is designed to serve as a deterrent, clearly showing that engaging in any form of unfair means during examinations will have legal consequences.
- By addressing the root causes of question paper leaks and malpractices, the legislation aims to uphold the integrity of the examination system and protect the interests of the aspiring youth.
Key Provisions of the Bill:
- Definition of Public Examination: Under Section 2(k) of the Bill, a Public Examination is defined as any examination conducted by a “public examination authority” listed in the Schedule of the Bill or any other authority notified by the Central Government. The designated authorities include UPSC, SSC, RRBs, IBPS, and NTA, which conducts exams like JEE (Main), NEET-UG, UGC-NET, and CUET.
- Additionally, all Central Government Ministries or Departments and their attached offices for staff recruitment are covered, with provisions for adding new authorities as necessary.
- Punishments: Section 9 establishes that all offenses under the Bill are cognizable, non-bailable, and non-compoundable.
- Cognizable offenses allow police investigation without Magistrate permission, while non-compoundable offenses necessitate a trial even if the complainant and accused reach a compromise.
- Punishment for using unfair means or offenses can range from three to five years imprisonment and fines up to Rs 10 lakh.
- Failure to pay the fine can lead to additional imprisonment as per the Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita, 2023.
- Punishment for Service Providers: Service providers engaged by public examination authorities are also liable for fines up to Rs 1 crore and may be required to pay proportionate examination costs if involved in illegal practices.
- Definition of Unfair Means: Section 3 outlines various actions, such as question paper leakage, tampering with documents, or creating fake websites, that constitute unfair means in public examinations for monetary or wrongful gain.
- Investigation and Enforcement: Offenses will be investigated by officers not below the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police or Assistant Commissioner of Police.
- Model Draft for States: The Bill serves as a model for states to adopt, aimed at preventing criminal disruptions in state-level public examinations.
- High-Level National Technical Committee: Establishment of a committee focused on developing protocols for securing digital platforms, implementing IT security systems, and formulating national standards for both IT and physical infrastructure to ensure efficient and reliable examination conduct.
Concerns Related to the Bill:
- Discretion of State Governments: While the bill aims to serve as a model for states to adopt, the broad discretion granted to state governments raises concerns about potential variations in implementation. Divergent approaches across states may weaken the overall effectiveness of the law in preventing unfair means in public examinations.
- Exploitable Loopholes in Sanctions: The provisions of the bill, particularly regarding the punishment for offenders, may inadvertently contain exploitable loopholes. For instance, if fines imposed on service providers are not proportionate to their financial gains from unfair means, the deterrent effect of sanctions may be insufficient to curb malpractices.
- Lack of Clarity on National Technical Committee: The bill proposes the establishment of a High-Level National Technical Committee on Public Examinations. However, the lack of clarity regarding the committee's composition, qualifications, and mandate raises concerns. Without specific guidelines, questions may arise about the expertise and impartiality of committee members in devising foolproof IT security systems and national standards for examination conduct.
- Potential for Legal Challenges: Legal challenges may arise concerning the bill's provisions on recognizability, non-availability, and non-compoundability of offenses. Debates may emerge regarding the proportionality of stringent measures to the gravity of the offenses and whether they adhere to principles of natural justice.
Closing thoughts
- Comprehensive oversight mechanisms are imperative for ensuring accountability and transparency in the examination process. By monitoring the conduct of examinations, establishing effective complaint-handling procedures, and conducting regular audits, authorities can uphold the integrity of the examination system and instill confidence in its fairness and reliability.
- Only through proactive oversight can malpractices be effectively detected and prevented, thereby safeguarding the integrity of the examination process.
https://www.newsonair.gov.in/Text-Bulletin-Details.aspx?id=45496#:~:text=The%20Parliament%20has%20passed%20the,means%20in%20the%20public%20examinations.
https://www.newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Parliament-gives-nod-to-bill-intended-to-control-unfair-means-in-Public-Examinations&id=476890
https://www.hindustantimes.com/education/news/parliament-clears-bill-to-curb-malpractices-in-competitive-exams-101707559539584.html
https://indianexpress.com/article/india/rs-passes-bill-to-curb-exam-malpractices-paper-leaks-9153991/
https://www.livelaw.in/top-stories/parliament-clears-public-examinations-prevention-of-unfair-means-bill-2024-249093
https://newsonair.gov.in/Spotlight.aspx#
200th Birth anniversary celebrations of Maharshi Dayanand Saraswati
Context
- President Droupadi Murmu participated in the 200th Birth anniversary celebrations of Maharshi Dayanand Saraswati, the founder of Arya Samaj at his birthplace Tankara in Morbi district.
Key Details:
- Gujarat Governor Acharya Devvrat and Chief Minister Bhupendra Patel were also present on the occasion. Arya Samaj members from all over the world have gathered in large numbers to witness the celebrations.
- This will be the culmination of the yearlong celebrations of the 200th Birth anniversary celebrations of Maharshi Dayanand Saraswati.
About Maharshi Dayanand Saraswati:
|
Early Life and Education
|
- Born as Mool Shankar in 1824 in Gujarat. Received traditional education in Sanskrit scriptures and Vedas.
|
|
Quest for Truth and Enlightenment
|
- Embarked on a journey of self-discovery and enlightenment, engaging in discussions with scholars and studying ancient texts.
|
|
Founding of Arya Samaj
|
- Established Arya Samaj in 1875, advocating for truth, righteousness, and social justice based on Vedic teachings. Promoted abolition of caste discrimination.
|
|
Reformist Ideologies
|
- Opposed societal evils such as idol worship, child marriage, caste discrimination, and untouchability. Emphasized the Vedas as the ultimate source of knowledge.
|
|
Promotion of Education
|
- Established schools and educational institutions to impart Vedic knowledge alongside modern subjects. Advocated for universal education.
|
|
Legacy and Influence
|
- Continues to inspire social and religious movements in India. Arya Samaj remains a prominent institution promoting his teachings.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Prez-Droupadi-Murmu-addresses-200th-Birth-anniversary-celebrations-of-Maharshi-Dayanand-Saraswati-at-Tankara-in-Morbi%2c-Gujarat&id=477049
India-Bangladesh open trade through Maia(West Bengal)-Sultanganj (Bangladesh) river ports
Context
- India-Bangladesh opened trade through Maia(West Bengal)-Sultanganj (Bangladesh) river ports on the Ganga River on Monday.
-Sultanganj_(Bangladesh)_river_ports.jpg)
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
Details:
- Shantanu Thakur, Indian Minister of State for Ports, Shipping and Waterways flagged off the First Cargo vessels carrying stones from Maia inland customs port.
- At Sultanganj, Bangladesh State Minister for Shipping Khalid Mahmud Chowdhury and the High Commissioner of India to Bangladesh Pranay Verma jointly inaugurated Sultanganj, Godagari Port of Call and flagged off a cargo vessel from Sultanganj, Bangladesh to Maia port, India.
- Speaking on the occasion, the High Commissioner highlighted the new river route as part of the growing trade and connectivity between India and Bangladesh
Key Details:
|
Distance between Maia Port and Sultanganj Port
|
- Riverine distance is 16km, with 4.5km in India and 11.5km in Bangladesh.
|
|
Cargo Capacity
|
- Once operational, each cargo can transport 200-300 tonnes of goods, reducing reliance on road transportation.
|
|
Impact on Transportation Costs
|
- Expected to lower transportation costs due to the utilization of waterways, which will subsequently decrease commodity prices and boost trade between India and Bangladesh.
|
|
Boost to Trade and Connectivity
|
- Improved connectivity through the river port will facilitate increased trade activities between the two countries, fostering economic growth and closer bilateral relations.
|
|
Goods Imported from India
|
- Stones, fly ash, coal, fruits, vegetables, and spices are expected to be imported from India to Bangladesh through the river port.
|
|
Goods Exported from Bangladesh
|
- Jute and garments are anticipated to be exported from Bangladesh to India via the river port, enhancing bilateral trade and promoting the exchange of goods between the two nations.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India-Bangladesh-open-trade-through-Maia(West-Bengal)-Sultanganj-(Bangladesh)-river-ports-on-Ganga-river&id=477080
India’s UPI services launched in Sri Lanka and Mauritius
Context
- India's Unified Payment Interface (UPI) services have been rolled out in Sri Lanka and Mauritius.

Details
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi, President of Sri Lanka Ranil Wickremesinghe, and Prime Minister of Mauritius Pravind Jugnauth witnessed the launch of UPI services in the island nations.
- The RuPay card services were also launched in Mauritius.
Key points:
|
Occasion
|
- Celebration of a special day for three friendly countries in the Indian Ocean region.
|
|
Digital Connectivity
|
- Emphasized historical relations being connected digitally. Highlighted commitment to the development of people.
|
|
Fintech Connectivity
|
- Stressed on strengthening cross-border transactions and connections through Fintech connectivity.
|
|
Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
|
- India's UPI performing a new responsibility of uniting partners with India. Expressed confidence in Sri Lanka and Mauritius benefiting from UPI services.
|
|
Digital Public Infrastructure
|
- Revolutionary change in India through Digital Public Infrastructure. Mentioned widespread digital payments even in rural areas.
|
|
Neighborhood First Policy
|
- India's policy prioritizing neighboring countries. Maritime vision: SAGAR (Security And Growth for All in the Region). Goal: peace, security, and development in the entire region.
|
|
COVID Vaccination Drive
|
- India's successful vaccination drive via the COWIN platform during the pandemic.
|
|
Technology and Governance
|
- Technology leading to increased transparency, reduced corruption, and an inclusive economy.
|
|
Sri Lankan Prime Minister Ranil Wickremasinghe's Address
|
|
Historical Trade Relations
|
- Mentioned millennia-old trade and payment relations between India and Sri Lanka.
|
|
Technological Upgrade
|
- Initiative upgrades ancient trade relations technologically.
|
|
Cultural Heritage
|
- South Indian coins found in Sri Lankan villages signify active trading corporations.
|
|
Tourism and Economic Impact
|
- Anticipated benefits for Sri Lankan villages with increased Indian tourism.
|
|
Appreciation for Ram Mandir Opening
|
- Congratulated PM Modi for the Ram Mandir inauguration.
|
|
Mauritius Prime Minister Pravind Jugnauth's Address
|
|
Cultural and Commercial Linkages
|
- Strong historical cultural, commercial, and people-to-people linkages between India and Mauritius.
|
|
Rupay Card Collaboration
|
- Collaboration between Rupay card and MoCAS for domestic card usage in Mauritius.
|
|
G-20 Commitment
|
- Highlighted commitment at the G-20 meeting to improve access to digital services and leverage digital transformation for inclusive growth.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India%e2%80%99s-UPI-services-launched-in-Sri-Lanka-and-Mauritius&id=477054
Accelerated Computing: A Game-Changer in Artificial Intelligence
Context
- At the World Government Summit 2024, Jensen Huang, CEO of NVIDIA Corporation, discussed the groundbreaking impact of accelerated computing on artificial intelligence development in a conversation with Omar Sultan Al Olama, UAE Minister of Artificial Intelligence.

Details:
- Huang highlighted accelerated computing as a transformative shift from traditional central processing units (CPUs) to specialized domain-specific acceleration.
- This transition, he emphasized, is essential for achieving sustainable, energy-efficient, and high-performance computing, paving the way for groundbreaking AI applications.
Key descriptions:
|
Transformative Shift
|
- Huang highlights accelerated computing as a transformative shift from traditional CPUs to specialized domain-specific acceleration. This shift is crucial for sustainable, energy-efficient, and high-performance computing, enabling groundbreaking AI applications.
|
|
Democratization of Technology
|
- Accelerated computing, according to Huang, has democratized access to high-performance computing.
- NVIDIA's technology allows researchers worldwide to leverage accelerated computing, fueling innovation and advancing global AI research and development.
|
|
Sovereign AI Concept
|
- Huang champions the concept of sovereign AI, emphasizing the significance of data ownership and national investment in AI infrastructure.
- He urges countries to safeguard their data to preserve cultural heritage and ensure equitable distribution of AI capabilities globally.
|
|
Ethical Considerations
|
- Acknowledging ethical implications, Huang underscores the need for targeted regulation focused on specific AI use cases.
- Navigating ethical considerations prudently, he highlights the potential of AI to drive positive societal change while mitigating disruptive effects.
|
|
Jensen Huang's Leadership at NVIDIA
|
- As the co-founder, president, and CEO of NVIDIA, Jensen Huang has led the company's rise as a leader in accelerated computing.
- NVIDIA's GPUs, originally designed for graphics processing, have become essential for parallel processing tasks in machine learning, establishing them as a key player in AI development.
|
|
Monopoly in AI Chip Development
|
- NVIDIA, under Huang's leadership, holds a monopoly in the development of AI chips. Their high-performance GPUs, initially designed for graphics processing, have proven to be ideal for machine learning tasks, making them a crucial player in the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Accelerated-Computing%3a-A-Game-Changer-in-Artificial-Intelligence%2c-Says-NVIDIA-CEO--at-WGS-24&id=477070





-Sultanganj_(Bangladesh)_river_ports.jpg)

