SPOTLIGHT| INDIA'S DIGITAL PUBLIC INFRASTRUCTURE
Context
The G20 second Digital Economy Working Group meeting has begun in Hyderabad with a focus on digital public infrastructure.
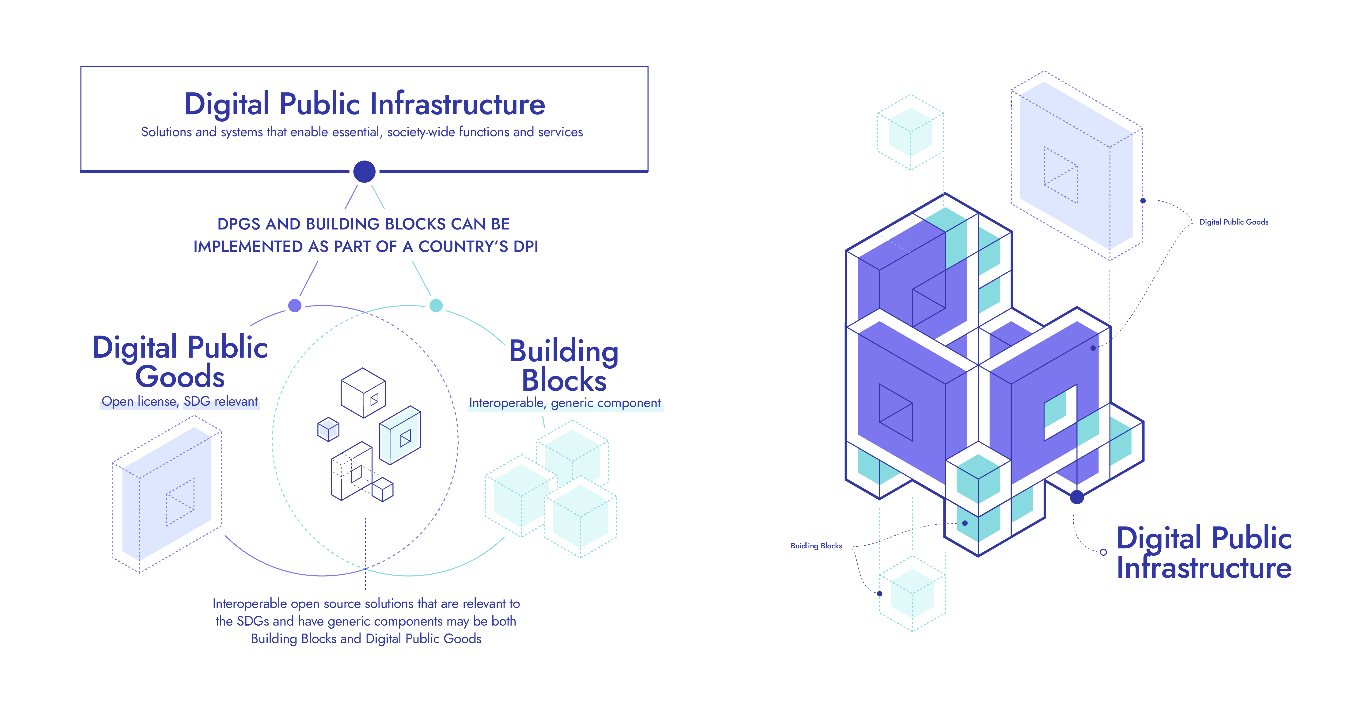
About Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- It refers to solutions and systems that enable the effective provision of essential society-wide functions and services in the public and private sectors.
- This includes but is not limited to digital forms of ID and verification, civil registration, payment (digital transactions and money transfers), data exchange, and information systems (including sector-specific, i.e. health or education).
- A country's digital public infrastructure may include implementations of multiple proprietary and/or open-source solutions (including digital public goods).
|
Fact
According to the World Bank, in 2020, about 62% of the country’s jobs were affected, nearly 22% of the population needed some form of humanitarian assistance, and 23.8% of children suffered from malnutrition.
|

| “The Philippines' digital public infrastructure includes a digital identity system, called PhilSys which is an implementation of the digital public good MOSIP.” |
Need of DPI:
- Just like railways and roads were instrumental for how economies and societies have evolved and integrated, digital public infrastructure positively transforms how people and businesses around the world access services and economic opportunities and how governments can meet the needs of their constituents.
- When confronted with crises, digital public infrastructure is key to building national resilience.
- For example: On average, 51 percent of their population with cash transfers, whereas countries that could not rely on existing databases to cross-reference eligibility reached only 16 percent.
- The design and implementation of digital public infrastructure must also consider and mitigate the risks of exclusion of those without digital access and skills, cybersecurity threats, and personal data protection vulnerabilities.
- In an increasingly digital world, the need for digital public infrastructure to foster resilience and enable service delivery and innovation is more crucial than ever.
| DPI is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each country will have unique needs for DPI and a unique set of challenges in building it. However, the basic functionality is inherently similar everywhere, opening up opportunities for global cooperation. |
Importance of Digital Public Infrastructure:
- It is foundational and cross-cutting. Verifying an identity or making and receiving a payment are at the core of most transactions, and thus having digital public infrastructure prevents the need to re-invent the wheel with every new system.
- This is a distinction between digitalization in specific sectors, which is very important, and the processes supported by a digital public infrastructure.
- It complements and works together at policy, process, and technology levels.
- For example, a person can use their digital ID to exercise consent over sharing their personal data from official sources, or a small business could use payment transaction data to access cheaper credit.
- These connections can also be described as a digital stack.
- It enables sectoral applications to be easily built ‘on top’.
- Government agencies and the private sector can focus on their core business and innovate when they do not need to recreate the wheel and can instead depend on the processes that digital stacks support, enabled by common standards (e.g., for data and semantics) and open application programming interfaces (APIs) that allow different systems to communicate with each other.
- Public benefit – not necessarily public ownership.
- The ‘public’ refers to governments having a primary role and responsibility in deciding whether and how DPI is provided in the interests of the broader society and economy, such as through regulating, operating, and/or partnering with the private sector.
|
“Estonia’s digital public infrastructure for digital data exchange is powered by X-Road which is a digital public good.”
|
|
|
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
|
Digital Public Good (DPG)
|
Building Block
|
|
What does it do?
|
Facilitates and manages the operation of a digital society
|
Advances the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
|
A component that provides a generic digital service at scale and is reusable across use cases and sectors
|
|
What does it enable?
|
A widely useful whole-of-government approach to digital development that enables societal functions across sectors
|
Attainment of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) across and within sectors
|
A widely useful whole-of-government approach to digital development that enables societal functions across sectors
|
|
What are the licensing Requirements?
|
None (may include a combination of solutions with diverse licences)
|
Open source (accepted licence defined in the DPG Standard)
|
None
|
|
Who reviews solutions against this definition?
|
There is no review process for determining DPI
|
Reviewed by the DPGA, against the DPG Standard
|
Reviewed by GovStack Initiative as Building Block Compliant
|
|
The concept of digital public infrastructure has been pioneered by India (the India Stack) and Singapore (the Singapore Government Technology Stack and National Digital Identity Stack).
|
What is the impact of DPI?
- Evidence that DPI results in progress against the Sustainable Development Goals and national priorities is needed to drive financing, funding, and political commitment.
- Gathering evidence on which attributes and investments have the highest value will help us direct them.
- A growing body of research supports the impacts of individual layers on narrow outcomes, but very little research exists on the impact of DPI as a whole across multiple use cases.
- It will take time and ingenuity to assess the broad and varied nature of DPI impacts.
- In the meantime, we can track how DPI makes specific, highly important capabilities possible, such as the ability to rapidly and securely deliver targeted cash transfers, or to detect and organize response to an outbreak.
How will we measure progress on DPI?
- Despite important advances, the development community is only beginning to create broadly comparable performance measures for identity, payments, and data exchanges as individual layers.
- A vision for DPI would go beyond that, establishing common measures across layers, and assessing the stack as a whole.
- Crucially, measurement systems would need to look at the systems themselves, the experience of people using it, and its role in society, answering questions such as: Are systems secure? Do the layers interoperate? Do women use them less than men? Do people trust them?
How we co-develop capacity?
- Governments, development agencies, and international organizations will all need to invest more in capacity and shift the types of capacity they prioritize.
- Greater support for cross-functional, cross-agency capacity promotes a DPI mindset.
- For example, the creation of government digital service teams that provide expertise and coordination across silos leads to a horizontal approach to problem solving and the use of common tools.
- National digital strategies that specify the role of DPI and an approach to DPGs can help set overall vision, so long as they are specific, flexible, and realistic.
- Good data governance and data protection rules, both general and specific to DPI, are important, but must also be supported by institutions and processes that enforce and update them.
- DHIS2 and its global community successfully proved the strategy that supporting implementation-oriented academic programs relevant to DPI and DPGs can serve as long-term generators and repositories of expertise.
Key components of DPI in India
Digital identity
- As a part of building a Robust Digital ID, it is essential that key demographic data was verified properly to facilitate authentication of identity by various systems. To achieve these 3 distinct methods of verification were adopted:
- Based on supporting documents
- Based on Introducer system
- Based on the NPR (National Population Register) process of public scrutiny
- Further, as part of Aadhaar issuance process, each enrolment request undergoes requisite quality checks with the necessary bio-metric deduplication, thereafter UIDAI issues a digital ID to the resident.
Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is an instant real-time payment system developed by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- It facilitates inter-bank peer-to-peer (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) transactions.
DigiLocker
- DigiLocker, the authentic documents exchange platform under the Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has successfully integrated with Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
- The DigiLocker can be used as a health locker for storing and accessing health records such as vaccination records, doctor prescriptions, lab reports, hospital discharge summaries etc.
Internet of things
- Internet of things is an integrated system in which devices are connected in a network of information in such a way that they can communicate with each other without any human intervention.
DigiYatra
- DigiYatra envisages that travellers pass through various checkpoints at the airport through paperless and contactless processing, using facial features to establish their identity, which would be linked to the boarding pass.
- With this technology, the entry of passengers would be automatically processed based on the facial recognition system at all checkpoints – including entry into the airport, security check areas, aircraft boarding, etc.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/digital-public-goods
Key issues
- Where there is still 25 % illiteracy the target of high level of digital illiteracy is one of the biggest challenge in the success of digital India programme.
| According to ASSOCHAM-Deloitte report on Digital India, November, 2016, around 950million Indians are still not on internet. Reliance Jio has contributed a lot in his regard. |
- Creating an awareness regarding the Digital India scheme among common masses is also a great challenge.
- It is a colossal task to have connectivity with each and every village, town and city.
- Connecting 250000 Gram Panchayats through National Optical Fibre is not an easy task.
- The biggest challenge is ensuring that each panchayat point of broad band is fixed up and functional.
- It is found that 67% of NOFN points are non functional even at the pilot stage.
- India has very low internet speed. According to the third quarter 2016 Akamai report on internet speed, India is at the105th position in the world in average internet speed and it is the lowest in the entire Asia Pacific region .
- This lowest internet speed cannot facilitate online delivery of various services.
- India’s digital infrastructure is comprehensively inadequate to tackle the growing increase in digital transactions. The biggest challenge faced by the Digital India programme is slow and delayed infrastructure development.
- The private participation in government projects in India is poor because of long and complex regulatory processes.
| ASSOCHAMDeloitte Report pointed out that currently Over 50000 villages remain deprived of mobile connectivity because providing mobile connectivity in such locations is not commercially viable for service providers. |
Way forward:
- Digital literacy should provide knowledge to secure their online data.
- Massive awareness is to be created particularly in rural areas.
- Digital divide needs to be addressed.
- This mission needs content and service partnerships with telecom companies and other firms to develop infrastructure.
- The success of the digital India project depends upon maximum connectivity with minimum cyber security risks. For this there should be a strong anti cyber crime team.
- To improve skill in cyber security, cyber security courses should be introduced with academics.
- There is a need for effective participation of various departments and demanding commitment and efforts. Various policies in different areas should support this goal.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=2nd-meeting-of-G20-Digital-Economy-Working-Group-begins-in-Hyderabad%3B-Focus-on-digital-public-infrastructure-and-cyber-security&id=459446

NEWS IN SHORT
NEW IT RULES ON FACT CHECKING AND ONLINE GAMING
Context
- To regulate "online real money games," the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology announced an amendment to the Information Technology Rules, 2021
About
- The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Regulations, 2023 of the IT Ministry require real money gaming platforms to register with a self-regulatory body (SRB) that will evaluate if the game is "permissible.".
Aim of the amendments
- To enforce greater due diligence by online gaming and social media intermediaries in respect of online games & fake or false misleading information related to Government business.
- To protect the safety and trust of the Digital Nagriks, the Ministry of Electronics and IT, Government of India.
What are the amendments?
|
Intermediaries
|
● It has been made obligatory on the part of intermediaries to make reasonable effort to not host, publish or share any online game that can cause the user harm, or that has not been verified as a permissible online game by an online gaming self-regulatory body/body designated by the Central Government.
● The intermediary will also have to ensure that no advertisement or surrogate advertisement or promotion of an online game that is not a permissible online game, is hosted on its platform.
|
|
The self-regulatory body
|
● It will have the authority to inquire and satisfy itself that the online game does not involve wagering on any outcome, that the online gaming intermediary and the game complies with the rules, the requirements under law for being competent to enter into a contract (currently at 18 years).
● A framework made by the self-regulatory body regarding safeguards against user harm, including psychological harm, measures to safeguard through parental controls, age-rating mechanism, and measures to safeguard users against the risk of gaming addiction.
|
|
Online gaming intermediaries
|
● These include the displaying of a mark of verification by the self-regulatory body on such games; informing their users of the policy for withdrawal or refund of deposit, manner of determination and distribution of winnings, fees and other charges payable; obtaining the KYC details of the users; and not giving credit or enabling financing by third parties to the users.
|
|
Role of government
|
● The Government may notify multiple self-regulatory bodies, which shall be representative of online gaming industry but it will function at arm’s length from their members, and a Board consisting of Directors who are free from conflict of interest and represent all relevant stakeholders and experts, including online games users, educationists, psychology or mental health experts, ICT experts, persons with child rights protection experience and individuals having experience in relevant fields of public policy and administration.
|
https://newsonair.com/2023/04/15/union-minister-rajeev-chandrasekhar-says-under-amended-it-rules-harmful-content-like-betting-wagering-will-not-be-permitted-on-internet/

OUTCOMES OF 2ND G20 FINANCE MINISTERS AND CENTRAL BANK GOVERNORS MEETING
Context
- The 2nd Finance Ministers and Central Banks Governors Meeting is one of the ministerial meetings organized as part of the G20 Leaders Summit 2021, which will be hosted by Italy in October 2021.
Details
|
Focus points
|
● The meeting was organised in three sessions covering the Global Economy, International Financial Architecture, Sustainable Finance, Financial Sector, Financial Inclusion, and International Taxation.
|
|
Goal
|
● The G20 aims to take the lead in ensuring a swift international response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
● Able to provide equitable, worldwide access to diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines – while building up resilience to future health-related shocks.
● The goal of this FMCBG meeting was to deliberate on the progress made by the various workstreams of the G20 Finance Track on the deliverables that were tasked to them by the Ministers and Governors in the February G20 FMCBG Chair’s Summary and Outcome Document and to seek guidance on the way forward.
|
|
Key challenges
|
● The global economic outlook, including the war in Ukraine, food and energy insecurity, climate change, and recent risks to financial stability.
|
|
Common objectives
|
● G20 can contribute to building a common understanding on fostering a conducive environment for global economic recovery, and ensuring that the most vulnerable countries and sections of the population are adequately protected.
|
|
Key agenda
|
● The implementation of recommendations of the Independent Panel of MDBs’ Capital Adequacy Frameworks (CAF).
● “Strengthening Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs)”.
● Discussions focused on strengthening multilateral coordination towards addressing the increasing debt distress in low-income and vulnerable middle-income countries.
● Discussions also covered the impact of climate change-related policies on capital flows, among others.
● During the second session on Sustainable Finance, Financial Sector, and Financial Inclusion, discussions focussed on the mobilisation of resources for climate change, the role of the multilateral financial institutions in catalysing private finance flows for Sustainable Development Goals and the role of the G20 in scaling up and encouraging wider adoption of social impact investment instruments.
|
https://newsonair.com/2023/04/14/g20-fmcbg-meeting-concludes-with-a-pledge-to-recover-global-economy/
VANDE BHARAT EXPRESS REVOLUTION IN INDIAN RAILWAYS
Context
- The Indian Railways plans to operate 102 Vande bharat express trains by March 2024.
Detail
|
Earlier named
|
● Train 18 was inaugurated on 15 February 2019.
|
|
Safety Features
|
● Advanced state-of-the-art safety features including Kavach technology.
|
|
Operational Speed
|
● The train has been provided with bogies having fully suspended traction motors for 160 kmph.
|
|
Advanced features
|
● The train has been designed to increase Indian Railways' Green footprint by dispensing with the power cars and saving about 30 per cent of electricity with the advanced regenerative braking system.
|
|
Emergency features
|
● Loco pilot and train guard can easily communicate with each other as well as passengers, the loco pilot of the Vande Bharat Express.
|
|
Others
|
● The new Vande Bharat trains would have improved features including reclining seats, automatic fire sensors, CCTV cameras, on-demand content with wifi Facility, three-hour battery backup and GPS systems to make travelling safer and more comfortable.
|
|
Environment friendly
|
● It also has a photocatalytic ultraviolet air purification system in the roof-mounted package unit (RMPU) for air purification.
|
https://newsonair.com/2023/04/17/indian-railways-successfully-conducted-a-trial-run-of-keralas-first-vande-bharat-express-train/

VIBRANT VILLAGES PROGRAMME
Context
- Home Minister Amit Shah launches ‘Vibrant Villages Programme’ in Kibithoo of Arunachal Pradesh.
About
|
Launched
|
● This village development scheme was first announced in the 2022 Budget.
|
|
Objective
|
● The aims of the scheme are to identify and develop the economic drivers based on local, natural, human and other resources of the border villages.
|
|
Target
|
● The programme’s targets are to provide comprehensive development of villages on the border with China and improvement in the quality of life of people living in identified border villages.
|
|
Significance
|
● The development in these villages will help prevent migration, and thus also boost security.
|
|
Funds Allocation
|
● Under the programme, the government has allocated Rs 4,800 crore for infrastructure development and to provide livelihood opportunities in the border areas.
● Out of the total outlay, Rs 2,500 crore will be spent exclusively on the creation of road infrastructure.
● The total outlay is for financial years 2022-23 to 2025-26.
|
|
States covered
|
● Under this centrally sponsored scheme, 2,967 villages in 46 blocks of 19 districts have been identified for comprehensive development.
● These villages about the border in the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh and the Union Territory of Ladakh.
● In the first phase, around 662 villages have been identified for priority coverage.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Home-Minister-Amit-Shah-launches-%E2%80%98Vibrant-Villages-Programme%E2%80%99-in-Kibithoo-of-Arunachal-Pradesh&id=459059





