AIR SPOTLIGHT: NATIONAL MONETISATION PIPELINE
CONTEXT: Recently, the government of India has launched the National Monetization Pipeline (NMP). The NMP estimates aggregate monetisation potential of Rs 6 lakh crores through core assets of the Central Government, over a four-year period, from FY 2022 to FY 2025.
ABOUT THE PROGRAMME:
- At its core, the idea is to lease out brownfield projects, proceeds from which can be used to finance greenfield projects.
- The ownership of the assets monetised, though, will remain with the government, with the private players taking on the operational risk.
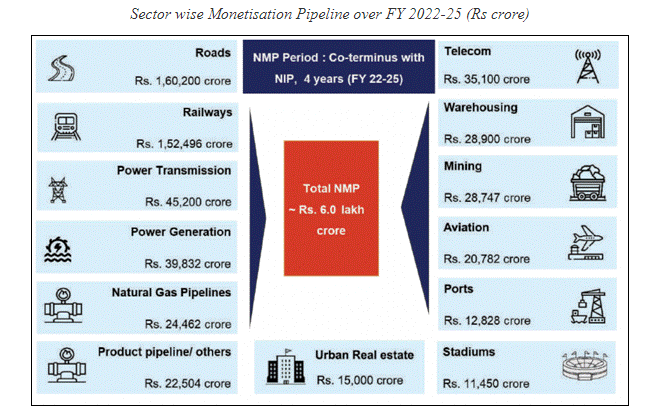
- While roads, railways and power account for around 65 per cent of the proceeds of the programme, the list of assets detailed is spread across sectors such as telecom, aviation, mining and warehousing, suggesting a more wide-ranging programme.
BENEFIT OF THE PROGRAMME:
- Asset monetization, based on the philosophy of Creation through Monetisation, is aimed at tapping private sector investment for new infrastructure creation.
- This is necessary for creating employment opportunities, thereby enabling high economic growth and seamlessly integrating the rural and semi-urban areas for overall public welfare.
- The strategic objective of the programme is to unlock the value of investments in brownfield public sector assets by tapping institutional and long-term patient capital, whichcan thereafter be leveraged for further public investments.
- NMP is envisaged to serve as a medium-term roadmap for identifying potential monetisation- readyprojects, across various infrastructure sectors.
- The NMP is aimed at creating a systematic and transparent mechanism for public authorities to monitor the performance of the initiative and for investorsto plan their future activities.
- Asset Monetisation needs to be viewed not just as a funding mechanism, but as an overall paradigm shift in infrastructure operations, augmentation and maintenance considering private sector’sresource efficiencies and its ability to dynamically adapt to the evolving global and economic reality.
- New models like Infrastructure Investment Trusts & Real Estate Investment Trusts will enable not just financial and strategic investors but also common people to participate in this asset class thereby openingnew avenues for investment.
FRAMEWORK OF ASSET MONETISATION PROGRAMME:
- Monetization through disinvestment and monetization of non-core assets have not been included in the NMP. Further, currently, only assets of central government line ministries and CPSEs in infrastructure sectors have been included.
- Process of coordination and collation of asset pipeline from states is currently ongoingand the same is envisaged to be included in due course.
- This includes selection of de-risked and brownfield assets with stable revenue generation profile with the overall transaction structured around revenue rights.

ESTIMATED POTENTIAL:
- The period for NMP has been decided so as to be co-terminus with balance period under National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP).
- The aggregate asset pipeline under NMP over the four-year period, FY 2022-2025, is indicatively valued at Rs 6.0 lakh crore.
- The estimated value corresponds to ~14% of the proposed outlay for Centre under NIP (Rs 43 lakh crore).
- The sectors included are roads, ports, airports, railways, warehousing, gas & product pipeline, power generation and transmission, mining, telecom, stadium, hospitality and housing.
- In terms of annual phasing by value, 15% of assets with an indicative value of Rs 0.88 lakh crore are envisaged to be rolled out in the current financial year (FY 2021-22).
WHAT IS ASSET MONETISATION?
- Asset monetisation is the process of creating new sources of revenue for the government by unlocking the economic value of unutilised or underutilised public assets.
- A public asset is any property owned by a public body, tangible or intangible. These include roads, railways, stations, pipelines, mobile towers etc. or financial assets like shares in Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs), securities and dividends.
- A sub-optimally utilised or unutilised asset is one that is not using its maximum potential which could otherwise be attained by exploiting it commercially at a market valuation.
- For example, if a government asset is deriving a net value of Rs 50 crore but has the potential to earn Rs 500 crore, it will come under this category.
- The government’s asset monetisation programme aims to correct this anomaly and get the returns it invested in these public assets, and create hitherto unexplored sources of income.
- Experts deem asset monetisation as an effective way to generate revenue for the government but believe that it is still hugely untapped.
- The government does not need to sell assets and it does well to protect assets which give healthy returns. This process is only to innovate and enrich an asset which has largely been unresponsive in terms of revenue.
RECENT STEPS:
- The budget for 2021-22 proposes a national monetization pipeline, of potential brownfield projects.
- Union Budget 2021 has pegged the divestment target for FY22 at Rs 1.75 lakh crore and the Centre has already initiated the process of strategic sale of several firms, has major IPOs planned and will sell two public sector banks and one general insurance company.
- Target of monetizing about 100 such assets in the fields of oil, gas, ports, airports, power etc. has been announced.
- These assets are estimated to have investment opportunities worth Rs 2.5 trillion.
- The mantra with which the government is moving ahead is monetise and modernise.
- All infrastructure ministries have been directed to zero in on potential assets for monetisation.
- A dash board will be set up where the assets can be viewed by potential investors.
- Niti Aayog had identified two lists of core assets. It also recommended the monetisation of special assets such as stadiums and tourism/mountain railways lines.
- A core group of secretaries for asset monetisation (CGAM), headed by the cabinet secretary, reviews the progress of this initiative.
- The Airports Authority of India is the only entity to have completed monetisation of six identified airports and is now gearing up for the next round.
- Shipping ministry was in the process of recycling 11 assets.
- As for the assets of CPSEs, while the government would retain 100% of the proceeds from monetisation of non-core assets of units identified for strategic sale and enemy properties, it could share a large chunk of the proceeds with CPSEs in case operational core assets are monetised.
BACKGROUND:
- Since 2018-19, plans to monetise the assets of the government and PSUs across the board, from key gas pipelines, power transmission lines and sports stadia to office spaces, land and apartments deemed surplus to requirements, have been taking shape.
- DIPAM is working on restructuring and asset monetisation of public sector enterprises for better management and competitiveness in the present world.
- Cabinet in 2019 approved procedure and mechanism for Asset Monetization of CPSEs)/ PSUs/other Government Organizations and Immovable Enemy Properties.
- As per the Budget Estimate for 2019-20, estimates for disinvestment proceeds were kept at Rs. 90,000 crore.
- In July 2019, the government drew up a roadmap for asset monetisation across sectors, to raise ~Rs 3.5 lakh crore over five years. The programme covers core as well as non-core assets and is steered by a well-laid down institutional framework.
- Under the ‘National Asset Monetisation Policy’, the assets identified so far can be broadly divided into two categories: Core or Productive Assets, and Non-Core Assets.
- Core Assets: no outright sale.
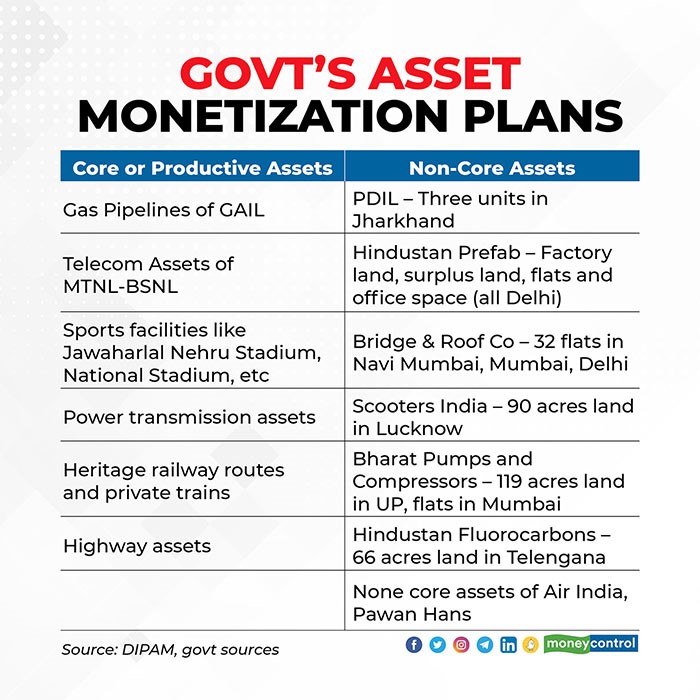
- Non-Core Assets: deemed surplus to requirements and for the most part consist of land, office space, factories, commercial spaces, apartments and properties belonging to the railways, defence and a number of PSUs. Some of these assets could be earmarked for outright sale and hence be counted as part of divestment proceedings. In other cases, there are options of a REIT, long-term lease, or various development models.
- The first consultative meeting on asset monetization was held recently, it was organized by DIPAM in partnership with World Bank
CHALLENGES:
- The national monetization plan seems to be a bit aspirational, considering the target set to be achieved in just four years. India doesn’t have the track record to meet such tall targets.
- The underlying structural and legacy issues combined with market conditions could pose a serious threat to the success of such monetization plans.
- Lack of proper maintenance of asset register and title and encroachment issues have adversely affected the Indian Railways’ plan to monetize its land.
- Land unavailability, delayed approvals and clearances, policy constraints and lack of coordination among stakeholders are other challenges.
- The current market conditions and legacy real estate industry issues could further impact the progress.
- Regulated tariffs in power sector assets.
- Low interest among investors in national highways below four lanes.
- Level of capacity utilization in gas and petroleum pipeline networks.
- Monetization of public assets is a complex and rigorous process that involves stakeholders’ management, efficient coordination, and detailed due diligence of the technical, operational and financial aspects of the assets.
WAY FORWARD:
- Monetisation needs to be repositioned as a tool to leverage institutional capital.
- In order to do so, structured transactions with a mandatory transfer of assets back to the government should be given priority over slump sale models, especially in case of core infrastructure assets.
- Structures such as TOT, InvITs bring in private-sector efficiencies in managing and operating assets under well-defined regulatory frameworks.
- Scanning of assets needs to be a perennial exercise and the ministries must proactively create 3-5 year asset pipelines commensurate with expansion plans.
- There is a need to look beyond the traditional asset classes of highways, railways and airports.
- Pipeline network, operational metro lines, storage infrastructure, transmission towers and rental earning public real estate assets should be explored as potential asset classes with re-imagined structures.
- The government should undertake a cycle of greenfield asset creation followed by monetisation post-construction without holding on to the assets.
- There is a need to carefully manage stakeholders, regulatory and structural issues, which create formal as well as informal barriers.
- Monetisation needs to be made value-accretive for entities undertaking the transactions.
- There is a need to explore mechanisms to plough back tax revenues in the form of performance-linked incentives and ring-fence the monetisation proceeds for expansion investments of respective entities.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=1748297
https://www.dnaindia.com/explainer/report-dna-explainer-what-is-the-national-monetisation-pipeline-nirmala-sitharaman-niti-aayog-2907499
https://www.dnaindia.com/explainer/report-dna-explainer-what-is-the-national-monetisation-pipeline-nirmala-sitharaman-niti-aayog-2907499
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/asset-monetisation-programme
NEWS IN BRIEF: PRELIMS SPECIAL
“Yuktdhara” Geospatial Planning Portal
- “Yuktdhara” Geospatial Planning Portal launched.
- Yuktdhara is a geospatial planning portal for facilitating Gram Panchayat level planning of MGNREGA
- The platform will serve as a repository of assets (Geotags) created under various national rural development programmese. MGNREGA, Integrated Watershed Management Programme, Per Drop More Crop and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana, etc., along with field photographs.
- This G2G service for rural planning fosters decentralised decision making.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/24/govt-launches-new-geospatial-planning-portal-yuktdhara/
Directed Energy Deposition Process
- The scientists from the International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy & New Materials (ARCI) have indigenously made powders suitable for the additive manufacturing process called the Directed Energy Deposition process.
- They made the powder using inert gas atomizer available at ARCI by melting unused scrap material.
- Utilising this, ARCI is developing the Laser-DED process for the repair of aero-engine components made of Ni-based superalloy.
- DED process is an emerging additive manufacturing or 3D printing technique.
- It allows for the creation of objects by melting the material in powder or as a wire with a focused energy source as it is deposited by a nozzle on a surface.
- Despite it being possible to build full parts with DED techniques, they are typically employed for repairing or adding additional material to existing objects.
- It uses a focused energy source, such as a plasma arc, laser or electron beam to melt a material which is simultaneously deposited by a nozzle.
- The DED process is known by other names, including Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS), Direct Metal Deposition (DMD), Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing (EBAM), Directed Light Fabrication, and 3D Laser Cladding, depending on the exact application or method used.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/25/indigenously-developed-powders-by-arci-to-reduce-repair-costs-overhaul-time-of-aero-engine-components/
NDC Transport Initiative for Asia (TIA 2020-2023)
- ‘Forum for Decarbonizing Transport’ launched in India as part of the NDC-Transport Initiative for Asia (NDC-TIA) project.
- Launched by: NITI Aayog and World Resources Institute (WRI), India.
- The NDC Transport Initiative for Asia (TIA 2020-2023) is a joint programme of seven organisations that will engage China, India, and Vietnam in promoting a comprehensive approach to decarbonizing transport in their respective countries.
- The project is part of the International Climate Initiative (IKI).
- NITI Aayog is the implementing partner for the India component of the project.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/25/niti-aayog-chalks-roadmap-for-decarbonizing-indian-transport/
Fair and Remunerative Price for Sugarcane
- Government approved the determination of Fair and Remunerative Price of sugarcane payable by Sugar Mills for sugar season 2021-22.
- With the amendment of the Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966 in 2009, the concept of Statutory Minimum Price (SMP) of sugarcane was replaced with the ‘Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)’ of sugarcane for 2009-10 and subsequent sugar seasons.
- FRP is the minimum price that sugar mills have to pay to sugarcane farmers.
- The cane price announced by the Central Government is decided on the basis of the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) in consultation with the State Governments and after taking feedback from associations of sugar industry.
- The sugarcane industry uses the FRP instead of the MSP, based on the recommendations of the Rangarajan Committee report.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/26/cabinet-approves-highest-ever-fair-and-remunerative-price-of-rs-290-per-quintal-for-sugarcane/
SAMRIDH Scheme
- The “Start-up Accelerators of MeitY for pRoduct Innovation, Development and growth (SAMRIDH)” programme was launched.
- The program aims to create a conducive platform to Indian Software Product start-ups to enhance their products and secure investments
- The programme is being implemented by MeitY Start-up Hub (MSH).
- Not only will the program provide funding support to the start-ups, but it will also help in bringing skill sets together which will help them to become successful.
- The scheme will focus on accelerating 300 start-ups by providing customer connect, investor connect, and international immersion in the next three years.
- Also, an investment of up to ₹ 40 lakh to the start-up based on its current valuation and growth stage will be provided through selected accelerators.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/25/it-minister-ashwini-vaishnaws-vision-for-startups-takes-shape-of-samridh-scheme/
EASE 4.0
- FM unveiled the 4th edition of Public Sector Bank (PSB) Reforms Agenda – EASE 4.0.
- PSB reforms agenda – EASE (Enhanced Access and Service Excellence) was launched based on the recommendations made by PSB Whole Time Directors (WTDs) and senior executives in PSB Manthan in November 2017.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/25/finance-minister-unveils-4th-edition-of-public-sector-bank-reforms-agenda-ease-4-0-in-mumbai/
North Eastern Region (NER) District SDG Index Report
- The first edition of the North Eastern Region (NER) District SDG Index Report and Dashboard 2021–22 was released by NITI Aayog and the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region
- The Index measures the performance of the districts of the eight States.
- The index is based on NITI Aayog’s SDG India Index
- The index offers insights into the social, economic, and environmental status of the region and its districts in their march towards achieving the SDGs.
- Out of the 103 districts considered for ranking, 64 districts belonged to the Front Runner category while 39 districts were in the Performer category in the composite score and ranking of districts.
- East Sikkim ranks first in the region followed by districts Gomati and North Tripura in the second position.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/26/niti-aayog-m-o-doner-release-first-edition-of-north-eastern-region-district-sdg-index-dashboard-2021-22/
MANTHAN-2021
- Manthan-2021 is a hackathon aimed at identifying innovative concepts and technology solutions for addressing the security challenges of the 21st century faced by India’s intelligence agencies.
- It is organized by the Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D) in coordination with the Innovation Cell of the Ministry of Education and AICTE.
- Total prize money of Rs.40 lakh has been announced for the winners.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/28/manthan-2021-indias-first-ever-hackathon-on-national-security/
Stop TB Partnership
- Union Health Minister took charge as Chairperson of Stop TB Partnership Board.
- The Minister will hold the responsibility with immediate effect until 2024.
- He will lead the efforts of the Stop TB Partnership Secretariat, partners, and the TB community at large, towards reaching the UN TB targets by 2022, a milestone moment in the effort to end TB by 2030.
- The Stop TB Partnership was established in 2001 to eliminate tuberculosis as a public health problem.
- The secretariat is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and, since 2015, has been administered by the United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS). Previously it was hosted by the World Health Organization.
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/26/health-minister-mansukh-mandaviya-takes-over-charge-as-chairperson-of-stop-tb-partnership-board/
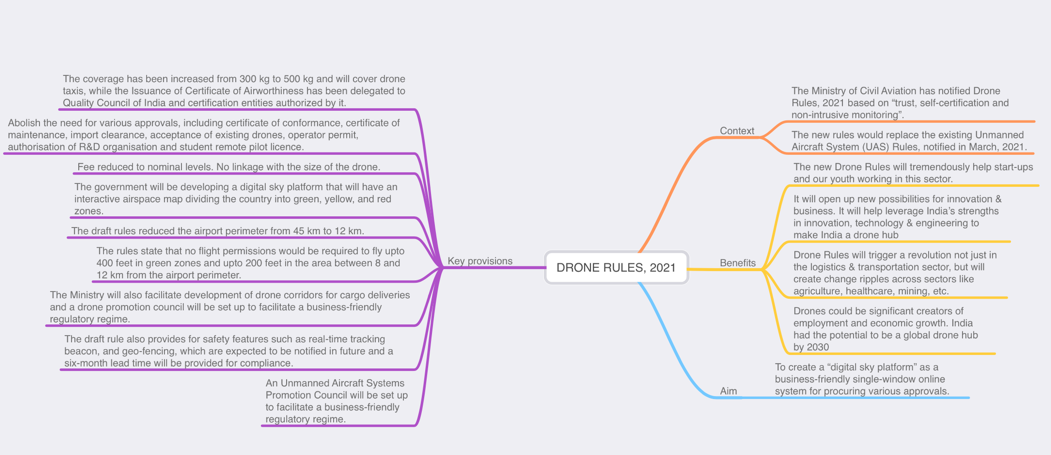
Drone Rules, 2021
https://newsonair.com/2021/08/26/ministry-of-civil-aviation-notifies-liberalised-drone-rules-2021/








