AIR Discussions (JUNE 4th Week)
NATIONAL SICKLE CELL-ANAEMIA ELIMINATION MISSION
Context: Prime Minister of India inaugurated the National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission in Madhya Pradesh.
Details
- The mission is a landmark initiative to tackle the serious health issues caused by sickle cell disease, especially among the tribal communities.
National Sickle Cell-Anaemia Elimination Mission
- The National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission, which was announced in the Union Budget 2023, will cover 278 districts of 17 high-priority states in the country. These states are Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Assam, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- The mission aims to eradicate sickle cell disease as a public health concern by 2047. He also handed over sickle cell genetic status cards to the beneficiaries.
- It is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
The mission has four main objectives:
- To screen all newborns and pregnant women for sickle cell anaemia and provide them with appropriate counselling and treatment.
- To provide free and regular blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and bone marrow transplantation to patients with severe sickle cell anaemia.
- To create awareness and education among the general public and health care providers about the prevention, diagnosis, and management of sickle cell anaemia.
- To promote research and innovation in the field of sickle cell anaemia, including the development of new drugs, vaccines, and gene therapies
SICKLE CELL-ANAEMIA: A Serious Genetic Disorder
About
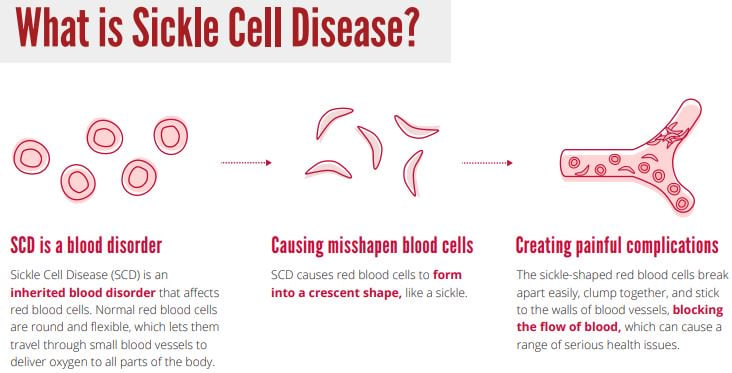
- Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disorder that affects the shape and function of red blood cells. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
- In people with sickle cell anaemia, some of the red blood cells become sickle-shaped, meaning they are curved and rigid. This makes it harder for them to pass through the blood vessels and deliver oxygen to the tissues.
- As a result, people with sickle cell anaemia can experience episodes of pain, anaemia, infections, organ damage, and even stroke.
- Sickle cell anaemia is caused by a mutation in the gene that code for haemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells. The mutation results in a type of haemoglobin called haemoglobin S, which tends to form long chains when exposed to low oxygen levels. These chains distort the shape of the red blood cells and make them sticky and fragile.
Some common symptoms include:
Painful Crises
- These are episodes of severe pain that occur when sickle-shaped red blood cells block the blood flow to certain organs or tissues. The pain can affect any part of the body, such as the chest, abdomen, bones, joints, or muscles.
- The frequency and duration of these crises vary from person to person and can range from a few hours to several days.
Anaemia
- This is a condition where the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen. People with sickle cell anaemia have a lower-than-normal number of red blood cells because they are destroyed faster than they can be replaced.
- Anaemia can cause fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, and pale skin.
Infections
- People with sickle cell anaemia have an increased risk of developing infections, especially in the lungs, kidneys, bones, and spleen. This is because sickle-shaped red blood cells can damage these organs and impair their function.
- People with sickle cell anaemia may have a reduced immune response due to the loss of spleen function or the use of immunosuppressive drugs.
Organ damage
- Over time, sickle cell anaemia can cause chronic damage to various organs and tissues due to reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery. Some of the organs that can be affected include the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, eyes, and skin.
- For example, sickle cell anaemia can cause a stroke (a sudden interruption of blood flow to the brain), pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lungs), kidney failure (loss of kidney function), liver cirrhosis (scarring of liver tissue), retinopathy (damage to the retina of the eye), and leg ulcers (open sores on the skin).
Challenges
Physical and emotional stress
- People with sickle cell anaemia have to cope with frequent pain crises, hospitalizations, medical treatments, complications, and limitations in their daily activities. They may also experience anxiety, depression, anger, frustration, isolation, and low self-esteem due to their condition.
Social and economic barriers
- People with sickle cell anaemia may face discrimination, stigma, lack of awareness, and lack of support from their communities and society at large.
- They may also have difficulties accessing quality healthcare services, education opportunities, employment options, and financial resources due to their condition.
Genetic counselling
- People with sickle cell anaemia or those who carry the trait may need genetic counselling to understand their risk of passing on the disorder to their children and to make informed reproductive decisions.
Steps Taken by Government
- Establishing national policies and programs for screening, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and research on sickle cell anaemia.
- Providing subsidies, insurance coverage, and social welfare benefits for people with sickle cell anaemia and their families.
- Promoting public awareness, education, and advocacy on sickle cell anaemia and its impact on individuals and society.
- Supporting community-based organizations, non-governmental organizations, and professional associations that provide services and support for people with sickle cell anaemia and their families.
However, there is still room for improvement and more action is needed to ensure that people with sickle cell anaemia and their families receive the best possible care and support.
Some of the ways forward include:
- Improving the quality and accessibility of health care services, including primary care, specialist care, emergency care, and palliative care for people with sickle cell anaemia and their families.
- Enhancing the availability and affordability of effective treatments and therapies for sickle cell anaemia, such as hydroxyurea, blood transfusions, bone marrow transplants, gene therapy, and pain management.
- Increasing the funding and collaboration for research and innovation on sickle cell anaemia, especially on finding a cure and developing new treatments and technologies.
- Strengthening the capacity and coordination of health care providers, policymakers, researchers, educators, and civil society actors to address the needs and challenges of people with sickle cell anaemia and their families.
- Empowering people with sickle cell anaemia and their families to participate in decision-making, advocacy, and leadership roles in their communities and society.
Conclusion
- The NSCAEM is a visionary and ambitious project that aims to transform the lives of millions of Indians suffering from sickle cell anaemia. It is also a testament to the commitment and dedication of the government and its partners to ensure health for all. The NSCAEM is not just a mission, but a movement that seeks to create a healthier and happier India.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=PM-Modi-to-launch-National-Sickle-Cell-Anaemia-Elimination-Mission-in-MP&id=463422

NEWS IN SHORT
DARK PATTERNS
Context: The government has asked online platforms to avoid dark patterns that compromise consumer interests. The Secretary of the Department of Consumer Affairs strongly recommended internet platforms not to involve in unfair trade practices by introducing dark patterns into their web dashboards to manipulate customer choice and breach consumer rights.
Details
- The dark patterns involve using a design and choice architecture to trick, coerce or influence consumers to make choices not in their best interest and constitute unfair trade practice.
- The Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs said that Consumers can report dark patterns instances and report manipulative online practices on the National Consumer Helpline by calling 1915.
Dark Patterns
- Dark patterns are design choices that manipulate users into taking actions that they might not otherwise take, such as buying a product, signing up for a service, or sharing personal information.
- It can be found in many websites and apps, and they often exploit cognitive biases, emotional triggers, or deceptive wording to influence user behaviour.
Some examples of dark patterns are:
- Bait and switch: The user is promised one thing, but then given something else or forced to agree to additional terms.
- Confirm shaming: The user is made to feel guilty or ashamed for not choosing a certain option, such as a subscription or a donation.
- Countdown timer: The user is pressured to make a decision quickly by showing a fake or arbitrary timer that creates a sense of urgency or scarcity.
- Hidden costs: The user is not informed of the full price or fees until the final stage of the checkout process, making it harder to cancel or compare alternatives.
- Misdirection: The user is distracted from the important information or choices by highlighting or emphasizing something else, such as a testimonial or a badge.
Concern
- Dark patterns are a serious threat to consumer rights and trust in the digital economy.
- It undermines the autonomy and dignity of consumers by exploiting their cognitive biases and vulnerabilities.
- It distorts the market competition by creating an uneven playing field for online platforms that respect consumer choice and consent.
Steps Taken by Government
- The Government has taken several steps to protect consumers from dark patterns and other unfair trade practices in the online space.
- The Consumer Protection Act, 2019, which came into force last year, has provisions to deal with misleading advertisements, unfair contracts, e-commerce liabilities and consumer redressal mechanisms.
- The Government has also issued guidelines for e-commerce entities to ensure transparency, accountability and fair treatment of consumers.
Conclusion
- The Government is committed to ensuring that consumers have a safe, secure and fair online experience and that their rights are respected and protected. The Government appeals to all online platforms to adhere to the principles of consumer sovereignty, fair competition and ethical business practices and refrain from adopting dark patterns harming consumer interest.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Govt-urged-online-platforms-to-refrain-from-adopting-dark-patterns-harming-consumer-interest&id=463446

MAHILA SAMMAN SAVINGS CERTIFICATE
Context: The government authorized all public sector banks and qualifying private sector banks to implement and operationalize the Mahila Samman Savings Certificate, 2023. This scheme allows for the opening of a two-year account on or before March 31, 2025. The scheme is currently open for subscription in Post Offices and qualified Scheduled Banks.
Details
- The Mahila Samman Savings Certificate, 2023 is a unique initiative by the government to promote women's welfare and empowerment in the country. The scheme will help women to secure their future and achieve their goals with ease and confidence.
Mahila Samman Savings Certificate, 2023
About
- Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme is a small savings scheme that offers attractive interest rates and tax benefits to women investors. The scheme can be opened at any Post Office or registered bank in India.
- The scheme is designed to suit the needs and preferences of women, who may have different saving goals and risk appetites than men.
Features
- Single-holder accounts: Only women can open and operate these accounts. They can open an account for themselves or on behalf of a minor girl.
- Flexible investment limit: The minimum amount required to open an account is Rs 1000, and the maximum amount that can be invested in a year is Rs 2 lakh. This allows women to invest according to their income and capacity.
- Competitive interest rate: The scheme offers an annual interest rate of 7.5%, which is higher than most other small savings schemes. The interest is compounded annually and credited to the account at the end of each financial year.
- Short maturity period: The scheme has a maturity period of two years, which means that women can access their funds after a relatively short time. This can help them meet their short-term or medium-term financial goals, such as education, marriage, health, etc.
- Partial withdrawal facility: The scheme allows women to withdraw up to 40% of the balance in their account after one year from the date of opening but before maturity. This can help them in case of any emergency or urgent need.
- Premature closure option: The scheme also allows women to close their account before maturity in case of certain situations, such as death of the account holder or guardian, or life-threatening disease of the account holder. In such cases, the interest payable on the principal amount will be calculated as per the rate applicable to the scheme for which the account was held.
Significance
- Tax benefits: The scheme is eligible for deduction under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961, up to Rs 1.5 lakh per annum. This means that women can reduce their taxable income by investing in this scheme.
- Safety and security: The scheme is backed by the government and hence offers guaranteed returns and safety of capital. Women do not have to worry about market fluctuations or default risks while investing in this scheme.
- Financial independence: The scheme empowers women to save and invest for their future and goals. It also helps them build a corpus that can be used for various purposes, such as education, entrepreneurship, retirement, etc.
- Social impact: The scheme also contributes to the social and economic development of women and society at large. It promotes financial literacy, inclusion and awareness among women, especially those who are from rural areas or low-income groups. It also supports the government's initiatives for gender equality and women empowerment.
Conclusion
- Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme is a new small savings scheme that offers attractive returns and tax benefits to women investors. It is a simple and convenient way for women to save and invest for their future and goals. It also supports the government's vision of empowering women and creating a more inclusive and equitable society.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Govt-permitted-all-Public-Sector-Banks-and-eligible-Private-Sector-Banks-to-implement-and-operationalise-Mahila-Samman-Savings-Certificate%2c-2023&id=463440
FAIR AND REMUNERATIVE PRICE
Context: The Union Cabinet has approved the fair and remunerative price (FRP) of 315 rupees per quintal for sugarcane for the season 2023-24. This is the highest-ever FRP for sugarcane announced by the government.
Details
- The approval of the FRP of 315 rupees per quintal for sugarcane for the season 2023-24 will ensure that sugarcane farmers get a fair and remunerative price for their produce, which will help them improve their income and livelihood.
- The move will also benefit about five crore sugarcane farmers and their dependents, as well as five lakh workers employed in the sugar mills and related ancillary activities.
Fair and Remunerative Price
- Fair and remunerative price (FRP) is a concept that aims to ensure that farmers get a fair and adequate return for their produce, while also taking into account the interests of consumers and the environment.
- FRP is different from minimum support price (MSP), which is a government intervention to protect farmers from market fluctuations and distress sales.
- FRP is determined by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), an advisory body that recommends the prices of various crops to the government.
Features of FRP
- It is based on the cost of production, quality, demand and supply, inter-crop price parity, terms of trade, and likely impact on the general price level.
- It is announced before the sowing season so that farmers can make informed decisions about what to grow and how much to invest.
- It is applicable to all sugarcane growers, irrespective of the size of their landholding or the type of irrigation they use.
- It is linked to a basic recovery rate of sugar from sugarcane, which is currently 10%. If the recovery rate is higher than 10%, then the FRP is increased proportionately.
- It is the minimum price that sugar mills have to pay to sugarcane farmers. However, mills can pay more than FRP if they want to attract more supply or reward quality.
Significances
- It ensures that sugarcane farmers get a fair share of the value added by sugar mills, which can improve their income and livelihoods.
- It provides a stable and predictable income for sugarcane farmers, which can reduce their vulnerability to market risks and uncertainties.
- It encourages sugarcane farmers to adopt better agronomic practices and improve their productivity and quality, which can enhance their competitiveness and profitability.
- It promotes the sustainability of sugarcane cultivation; by taking into account the environmental and social costs and benefits of production.
- It contributes to the food security and nutrition of the country, by ensuring an adequate supply of sugar and its by-products, such as ethanol, molasses, bagasse, etc.
Challenges
- FRP may not reflect the actual cost of production of sugarcane farmers, especially in regions where input costs are higher or yields are lower than the national average.
- It may not be sufficient to cover the rising cost of living of sugarcane farmers, especially in times of inflation or crop failure.
- It may not be enforced effectively, as some sugar mills may delay or default on payments to sugarcane farmers, citing financial constraints or excess supply.
- It may not be aligned with the market realities, as the demand and supply of sugar may vary depending on domestic consumption, exports, imports, stocks, etc.
- It may not be compatible with the global trade rules, as it may be seen as a form of subsidy or market distortion by other countries.
Way forward
- FRP should be revised periodically, based on the latest data and analysis of the cost of production, quality, demand and supply, inter-crop price parity, terms of trade, and likely impact on general price level.
- It should be implemented effectively, by ensuring timely and transparent payments to sugarcane farmers, strengthening dispute resolution mechanisms, and penalizing defaulting sugar mills.
- It should be complemented by other measures, such as improving crop diversification, enhancing value addition, promoting ethanol blending, rationalizing taxes and duties, facilitating exports and imports, etc.
- It should be harmonized with the global trade norms, by ensuring that it does not distort the market or affect the competitiveness of the Indian sugar industry.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Union-Cabinet-approves-highest-ever-Fair-and-Remunerative-Price-of-315-rupees-per-quintel-for-Sugarcane-Farmers&id=463352

NANDI PORTAL
Context: The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) launched the NANDI portal to streamline the approval process for new drugs and vaccines for animals.
Details
- NANDI (NOC Approval for New Drug and Inoculation System) portal aims to facilitate faster and more transparent clearance of applications for animal health products in India.
Features of the NANDI portal
- It is a single-window system that allows applicants to submit their applications online and track their status in real-time.
- It provides a dashboard for the DAHD officials to monitor and review the applications and issue NOCs (No Objection Certificates) or queries as per the guidelines.
- It is integrated with the e-office system of the DAHD, which enables paperless and efficient workflow management.
- It is compliant with the IT Act 2000 and the Aadhaar Act 2016, ensuring the data security and privacy of the applicants.
Significances
- It will reduce the time and cost involved in the approval process of new drugs and vaccines for animals, which will benefit the animal health industry and the farmers.
- It will enhance the quality and safety of animal health products, as it will ensure adherence to national and international standards and regulations.
- It will promote innovation and research in the field of animal health, as it will encourage more applicants to develop new products and technologies for animal welfare.
- It will contribute to the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India), as it will boost the domestic production and export of animal health products.
Challenges
- The portal is a new initiative that requires awareness and capacity building among the stakeholders, especially the applicants, who may face technical or procedural difficulties in using the portal.
- It requires coordination and cooperation among various departments and agencies involved in the approval process, such as the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), etc.
- It faces challenges in terms of ensuring compliance with the evolving norms and standards of animal health products, both at national and international levels.
Way forward
- The DAHD should conduct regular training and sensitization programs for the applicants and the officials to familiarize them with the features and functionalities of the portal.
- It should establish a feedback mechanism to receive suggestions and grievances from the stakeholders and resolve them in a timely manner.
- It should also collaborate with other departments and agencies to harmonize and streamline the approval process of animal health products across different platforms and jurisdictions.
- It should also update and upgrade the portal as per the changing needs and expectations of the stakeholders and the industry.
Conclusion:
- The NANDI portal is a commendable initiative by the DAHD to simplify and expedite the approval process of new drugs and vaccines for animals. It will not only benefit the animal health industry and the farmers but also enhance the quality and safety of animal health products. It will also foster innovation and research in the field of animal health, which will ultimately contribute to animal welfare and national development.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Union-Minister-Parshottam-Rupala-launches-NOC-Approvals-for-New-Drugs-%26-Inoculation-System&id=463204

REPORT ON CRITICAL MINERALS
Context: The Ministry of Mines has recently released India's first-ever report on Critical Minerals for India, which identifies 30 critical minerals essential for the country's economic and strategic interests.
Details
- The report is based on a comprehensive assessment of the demand and supply scenarios of these minerals in India and the world, as well as the opportunities and challenges for their exploration and development.
Critical minerals
About
- India is a country with a vast potential for mineral exploration and development. The country has a rich and diverse geological endowment, hosting a variety of mineral resources such as coal, iron ore, bauxite, manganese, copper, gold, diamond, and rare earth elements.
- However, despite its mineral wealth, India still relies heavily on imports for meeting its domestic demand for many strategic and critical minerals.
- Critical minerals are those that have high economic importance and supply risk, due to their essentiality for various sectors and limited availability from few sources.
- These minerals are vital for the development of advanced technologies such as electric vehicles, renewable energy, aerospace, defence, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and telecom. Some examples of critical minerals are lithium, cobalt, nickel, graphite, rare earth, platinum group metals, and titanium.
Key highlights of the report
- India has a moderate to high potential for 12 out of the 30 critical minerals identified in the report, such as beryllium, chromium, gallium, germanium, graphite, indium, lithium, manganese, niobium, rare earth, tantalum, and titanium.
- India has a low to moderate potential for 10 out of the 30 critical minerals identified in the report, such as antimony, cobalt, fluorspar, magnesium, nickel, platinum group metals, scandium, tin, tungsten, and vanadium.
- India has a low or negligible potential for 8 out of the 30 critical minerals identified in the report, such as arsenic, boron, helium-3 (for fusion energy), molybdenum, rhenium (for aerospace), selenium (for solar cells), tellurium (for solar cells), and zirconium.
- India's demand for critical minerals is expected to grow significantly in the coming years due to the increasing consumption of various sectors such as electric vehicles (lithium-ion batteries), renewable energy (solar panels and wind turbines), defence (missiles and radars), agriculture (fertilizers and pesticides), pharmaceuticals (drugs and vaccines), and telecom (optical fibres and semiconductors).
- India's supply of critical minerals is currently dependent on imports from a few countries such as China (rare earths), South Africa (platinum group metals), Australia (lithium), Congo (cobalt), and Indonesia (nickel). This exposes India to various risks such as price volatility, geopolitical uncertainties, trade restrictions, and environmental and social issues.
Significance of developing critical minerals in India
- Developing critical minerals can enhance India's self-reliance and security in mineral resources, reducing its dependence on imports and improving its trade balance.
- It can boost India's economic growth and create employment opportunities in the mining sector and downstream industries.
- It can support India's transition to a low-carbon economy and help achieve its 'Net Zero' targets by promoting clean energy and green technologies.
- It can strengthen India's strategic capabilities and national security by enabling the development of advanced defence systems and critical infrastructure.
Challenges faced by India in developing critical minerals
- The exploration and development of critical minerals require high capital investment, advanced technology, skilled manpower, and long gestation periods.
- It faces various regulatory hurdles, such as complex land acquisition, environmental clearance, forest clearance, and mining lease processes.
- It faces various social challenges, such as a lack of awareness, local opposition, and community conflicts.
- Its faces various environmental challenges, such as water scarcity, land degradation, biodiversity loss, and climate change impacts.
Report suggests the following way forward
- Formulate a comprehensive policy framework and a dedicated action plan for the exploration and development of critical minerals in India.
- Establish a dedicated agency or a nodal ministry for coordinating and facilitating activities related to critical minerals in India.
- Enhance the institutional capacity and human resource development for the exploration and development of critical minerals in India.
- Promote research and development and technology transfer for the exploration and development of critical minerals in India.
- Encourage private sector participation and foreign direct investment for the exploration and development of critical minerals in India.
- Foster international cooperation and strategic partnerships for the exploration and development of critical minerals in India.
- Ensure environmental sustainability and social responsibility for the exploration and development of critical minerals in India.
Conclusion
- The report on Critical Minerals for India is a landmark initiative by the Ministry of Mines, which reflects the vision and commitment of the government to achieve self-reliance and security in mineral resources. The report provides valuable guidance for policy formulation, strategic planning, and investment decisions in the mining sector. The report is expected to pave the way for India's leadership role in the global arena of critical minerals.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Union-Minister-of-Mines%2c-Pralhad-Joshi-unveils-India%26%2339%3bs-first-ever-report-on-Critical-Minerals-for-India&id=463375





