SPOTLIGHT| INDIA-CHINA EXPECTED TO CONTRIBUTE NEARLY HALF OF GLOBAL GROWTH
Context
- India & China expected to contribute nearly half of global growth this year, says IMF report.
Details:
- The International Monetary Fund has said the growth in the dynamic Asia-Pacific region largely led by India and China is projected to increase to 4.6 per cent this year from that of 3.8 per cent recorded in 2022.
- In its Regional Economic Outlook - Asia and Pacific report released on Tuesday, the Washington-based fund said the region would contribute around 70 per cent of global growth.
- Asia and Pacific will be the most dynamic of the world's major regions in 2023, predominantly driven by the buoyant outlook for China and India.
- The two largest emerging market economies of the region are expected to contribute around half of global growth this year, with the rest of Asia and Pacific contributing an additional fifth.
- Asia's dynamism will be driven primarily by the recovery in China and resilient growth in India, while growth in the rest of Asia is expected to bottom out in 2023, in line with other regions.
- Meanwhile, IMF said 2023 looks to be a challenging year for the global economy, with global growth decelerating as the effects of monetary policy tightening and Russia's war in Ukraine continue to weigh on economic activity.
- Also, persistent inflationary pressures, and recent financial sector problems in the US and Europe, inject additional uncertainty into an "already complex economic landscape".
Introduction:
- India was the first non-socialist country to establish diplomatic relations with China on April 1, 1950.
|
In October 1954, Nehru visited China and signed the Indo-Sino Agreement. The Sino-Indian Agreement 1954 mentioned the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence (Panchsheel).
|
Historical relations:
- While the 1962 India-China border conflict hampered relations, Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi's historic visit in 1988 ushered in a new era.
- In 1993, during Prime Minister Narasimha Rao's visit to China, an Agreement on the Maintenance of Peace and Tranquillity along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) on the India-China Border Areas was signed.
- The recent high-level visits have transformed our ties. The two countries agreed to designate Special Representatives to study the political framework of a boundary settlement during Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee's 2003 visit.
- A Strategic and Cooperative Partnership for Peace and Prosperity was founded during Premier Wen Jiabao's visit in April 2005.
- Border Defence Agreement, 2013: aimed at maintaining peace along the Line of Actual Control (LoAC), which was established in 1993.
PRESENT RELATIONS:
India-China Water Relations:
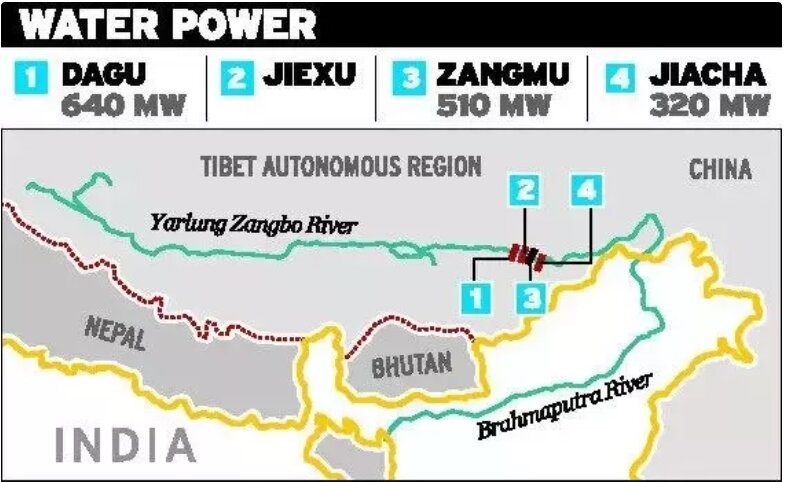
Recently, China has announced its intention to construct run-of-the-river dams on Yarlung Zangbo, a tributary of Brahmaputra (known in China as Siang).
Threats before India
- The dams pose a concern for the population and food security in the lower riparian states of India and Bangladesh.
- Blocking of the river or diverting waters to meet rising demand in other parts of China could pose serious threat to population and environment in lower riparian states.
- Degradation of basin as massive amounts of silt carried by the river would get blocked by dams leading to a fall in the quality of soil and eventual reduction in agricultural productivity.
- Seismic risk: Seismologists consider the Himalayas as most vulnerable to earthquakes and seismic activity.
- Security threat: Using the dams as water bomb in case of a war/conflict.
The Trans-border rivers flowing from China to India fall into two main groups.
- Brahmaputra River system on the Eastern side, which consist of river Siang (main stream of river Brahmaputra) and its tributaries, namely Subansiri and Lohit.
- The Indus River system on the Western side consists of river Indus and the river Sutlej.
-
- Mechanisms for water cooperation between India and China:
- MoU for Hydrological Information of the River Brahmaputra in 2002 (renewed in 2008, 2013, and 2018);
- MoU on Hydrological Data Sharing on the River Sutlej / Langqen Zangbo in 2010 - (renewed in 2015).
- Initiated in 2006, the Expert-Level Mechanism to discuss interaction and cooperation regarding the provision of flood season hydrological data, emergency management.
- Control over key rivers effectively gives China a chokehold on India’s economy – and poses a wider threat to region’s security and increases environmental pollution and disaster vulnerability.
India-China Economic Relations:
| In 2021, India-China trade was $125.7 billion. As a result of the surge in imports, India's trade imbalance with China jumped to $69.4 billion in 2021 from $45.9 billion in 2020 and $56.8 billion in 2019. |
India’s steps to counterbalance economic overdependence on China dependence:
- India imposed a ban on 59 Chinese apps on pretext of national security.
- Increasing scrutiny of Chinese investments, and exclusion of Chinese firms from 5G trials.
- To prevent "opportunistic takeovers" of domestic enterprises, the government has made prior approval obligatory for foreign investments from countries bordering India.
- India has stepped up anti-dumping duties.
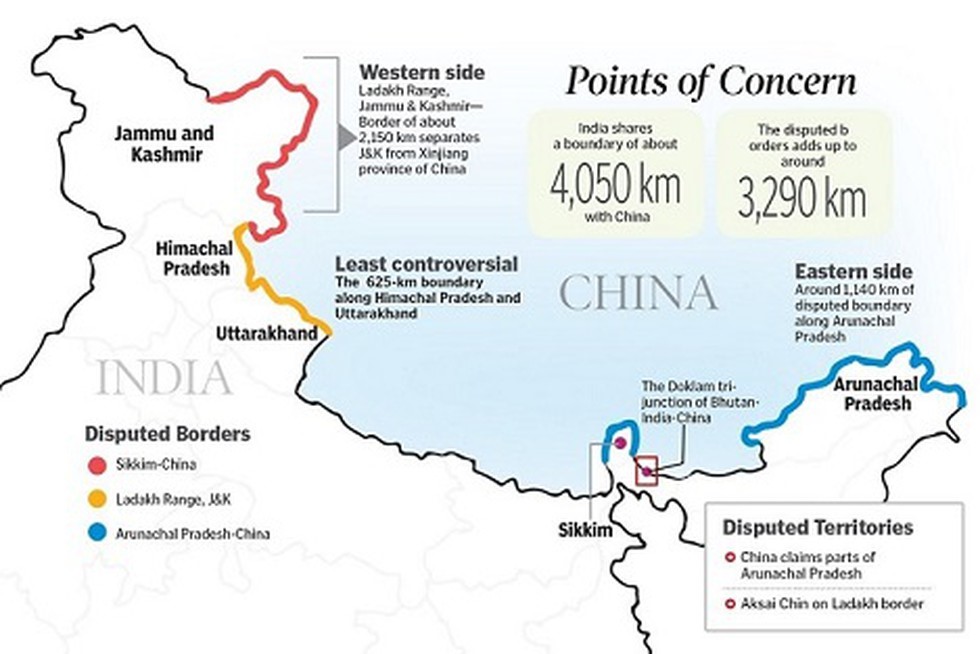
India-China Border Dispute:
- There is no mutually accepted Line of Actual Control between India and China (LAC). The LAC divides Indian and Chinese controlled territory.
- The LAC is 3,488 kilometres long in India, but just 2,000 km in China. The LAC has three sectors: Western, Middle, and Eastern.
- India and China have yet to agree on a common border-arrangement. A fair, reasonable, and mutually acceptable settlement of the Boundary Question has been agreed upon by both sides.
- Several bilateral agreements, conventions, and arrangements have been made to maintain peace and tranquilly along the LAC in India-China border areas.
- China has unilaterally passed a new "Land Boundary Law” on 23 October 2021 which can have implication on our existing bilateral arrangements on border management.
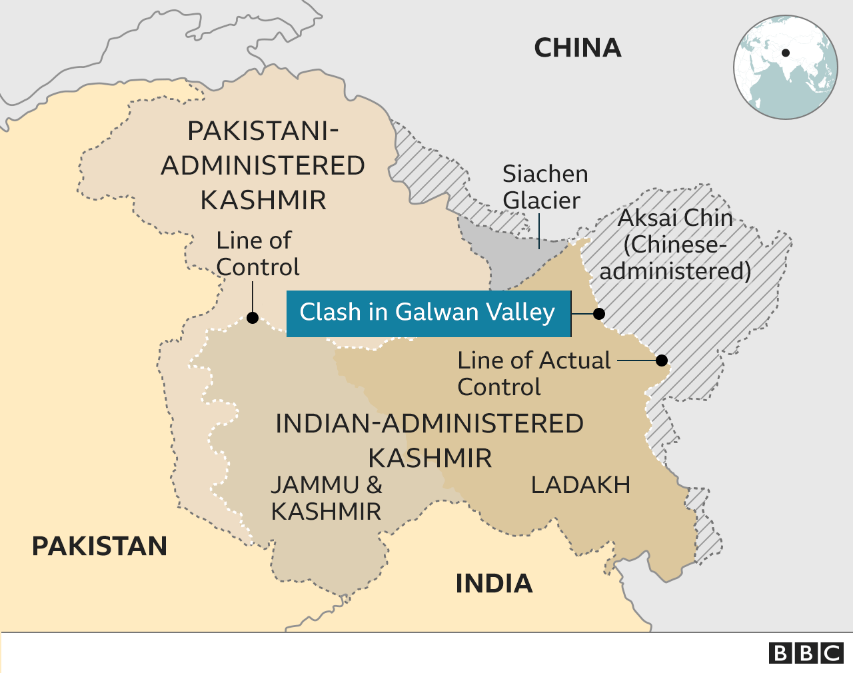
Current military standoff:
- After crossing the LAC near the Galwan River valley (Eastern Ladakh) in May 2020 by the Chinese soldiers, tensions between India and China have risen meteorically.
- In a subsequent fight with Chinese forces, Indian soldiers suffered causalities, after which both sides agreed to sustain engagement and contact through military and diplomatic channels.
- The Border remains tense as China is unwilling to withdraw troops from PP15 (Hot Springs area) and reports say China is rapidly upgrading and installing radars along the LAC.
- Regional military leaders from both sides have engaged in 15 rounds of conversation since the border battles two years ago, but none since March 11.
- The two nations have removed their front-line forces from the northern and southern shores of Pangong Lake and from Gogra Post, but they have been unable to withdraw their troops from other places of contention.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/india-china-trade-relationship
Other irritants for India:
China’ Debt Trap Diplomacy:
- Brahma Chellaney coined the term to characterise what he considered China's predatory lending tactics, which overburden impoverished nations with unsustainable debts and compel them to yield strategic influence to China.
Increasing China’s Presence:
In South Asia:
- China has increased its investments and trade with South Asian nations, threatening India's historic dominance in the region.
In Pacific Ocean:
- Chinese strategy of constructing ports and naval bases around India's maritime reaches, including Cocos Island in Myanmar, Chittagong in Bangladesh, Hambantota (Sri Lanka), Marao Atoll (Maldives), and Gwadar (Pakistan), is viewed as an attempt to surround India
China’s support to Pakistan:
- Pakistan has been empowered by China to continue its campaign of asymmetric warfare against India as a result of investments (g., CPEC) and backing on numerous topics such as Kashmir in the UN Security Council, terrorism in the NSG, etc.
Multilateral Cooperation and Confrontation:
- India-China ties have gained a global and strategic dimension, and their collaboration is essential for addressing global concerns such as climate change, terrorism, protectionism, free trade, and the global financial system.
- Both nations should collaborate to protect the legal rights and interests of emerging nations. China asserted that Sino-Indian relations may be the most significant bilateral cooperation of the century.
- India is essential to the worldwide success of 5G, where Huawei is the market leader.
- India-China cooperation at the WTO: The India-China joint proposal in WTO targeted 'Aggregate Measurement of Assistance' (AMS) or 'Amber Box' support.
Way Forward:
Reduce Economic dependency:
- To lessen its reliance on Chinese goods, India must examine Chinese imports and devise a strategy for the future.
- To lower the trade imbalance, the tourism, entertainment, publishing, and internet service sectors of the cultural business must be addressed
Confidence building mechanisms:
- The lack of trust is a crucial issue in Sino-Indian relations.
- Track II diplomacy can play a more active role in the resolution of this issue.
- The BCIM (Bangladesh–China– India–Myanmar) economic corridor, for instance, is the result of track II talks.
- In the connection, unfavourable publicity must be contained.
- Deeper contacts between the media professionals of the two nations can assist improve the image of both nations.
Multilateral Engagements:
- It is necessary to enhance the frequency of discussions at multilateral summits at the highest levels, such as the East Asia Summit (EAS), the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), the Conference on Interaction and Confidence-Building Measures in Asia (CICA), BRICS, and G-20.
Water cooperation:
- Evolve institutional mechanism for water sharing including data sharing and sensitivity to security concerns.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/india-china-relations-1-38
Wrapping it up
- India's relationship with China is intricate. In recent years, the two parties have agreed to manage their differences and prevent any differences from becoming problems.
- In addition, the two parties concur that the future orientation of India-China relations should be based on mutual respect for each other's developmental objectives, keeping in mind the necessity of respecting each other's concerns, sensitivities, and aspirations.
- India and China must adhere to the Panchsheel (Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence) and increase cooperation on international and regional matters by engaging in more frequent and high-level political interaction.
- Through improved physical connection and economic integration, the two nations may serve as a development engine for the whole subcontinent.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India-%26-China-expected-to-contribute-nearly-half-of-global-growth-this-year%2C-says-IMF-report&id=460267
.jpeg)
EC ISSUES ADVISORY TO POLITICAL PARTIES
Context
- The Election Commission today issued an advisory to all National and State Parties candidates and all Star Campaigners to exercise caution and restraint in their utterances during campaigning and not to vitiate the election atmosphere.
Details:
- The Commission issued this advisory in view of plummeting levels of campaign discourse in the ongoing General Election to Karnataka Legislative Assembly.
- ECI directed Chief Electrol Officers to comply with advisory and initiate appropriate and timely action as per extant regulatory and legal framework.
- ECI stated that it is imperative for all parties and stakeholders to remain within the confines of the Model Code of Conduct and the legal framework in their utterances while campaigning.
- The commission said that it is to maintain the dignity of the political discourse and not to vitiate the campaign and the election atmosphere.
- The Commission noted that National Parties and Star Campaigners enjoy extra enablement’s within the Representation of the People Act.
- ECI has invited the attention of the political parties to the provisions of Model Code of Conduct and other statutory provisions which hold the field and fix the framework of the expected campaign discourse.
How National Part in India is defined?
As per the ECI’s Political Parties and Election Symbols, 2019 handbook, a political party would be considered a national party if it meets any one of the following conditions:
- It is a ‘recognised’ party in four or more states, or
- If its candidates polled at least 6% of total valid votes in any four or more states in the last Lok Sabha or Assembly elections and have a minimum of four MPs in the last Lok Sabha polls, or
- If it has won at least 2% of the total seats in the Lok Sabha from not less than three states.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/national-party-tag
About Model Code of Conduct:
- The Model Code of Conduct for guidance of political parties and candidates is a set of norms which has been evolved with the consensus of political parties who have consented to abide by the principles embodied in the said code and also binds them to respect and observe it in its letter and spirit.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/model-code-of-conduct-the-dos-and-donts
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=EC-issues-advisory-to-political-Parties-and-Campaigners-to-exercise-caution-and-restraint-in-their-utterances-during-campaigning&id=460307

RECOMMENDATION OF TRAI ON EASE OF DOING BUSINESS IN TELECOM SECTOR
Context
- Telecom Regulatory Authority of India, TRAI today released the recommendations on Ease of Doing Business in Telecom and Broadcasting Sector.
Details:
- Ease of doing business has been identified as one of the focus areas of government in the recent decade.
- The TRAI had suo-moto floated a Consultation paper on Ease of Doing Business in the telecom and Broadcasting Sector in 2021.
- TRAI has recommended establishing a user-friendly, transparent, and responsive digital single-window system-based portal.
- The portal should be enabled with new digital technologies for achieving end-to-end inter-departmental online processes.
- Each Ministry should establish a standing Ease of Doing Business Committee to regularly review, simplify and update the existing processes.
- They have to also ensure ease of doing business as an ongoing activity. TRAI has also recommended that the Government may consider and grant Infrastructure Status to Broadcasting and Cable Services Sector.
About Telecom Regulatory Authority of India:
- Background: Telecom Regulatory Authority of India was established on 20 February 1997 by an Act of Parliament to regulate telecom services and tariffs in India. Earlier, regulation of telecom services and tariffs was overseen by the Central Government.
- Established: It is a regulatory body set up by the Government of India under section 3 of the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997.
- Members: It consists of a chairperson and not more than two full-time members and not more than two part-time members.
- Objective:
- TRAI's mission is to create and nurture conditions for the growth of telecommunications in India to enable the country to have a leading role in the emerging global information society.
- One of its main objectives is to provide a fair and transparent environment that promotes a level playing field and facilitates fair competition in the market.
- TRAI regularly issues orders and directions on various subjects such as tariffs, interconnections, quality of service, direct to home services and mobile number portability.
- Amendment: The TRAI Act was amended by an ordinance, effective from 24 January 2000, establishing a Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal to take over the adjudicatory and disputes functions from TRAI.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/telecom-regulatory-structure-in-india
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=TRAI-releases-recommendations-on-Ease-of-Doing-Business-in-Telecom-and-Broadcasting-Sector&id=460309
EK BHARAT SHRESHTHA BHARAT
Context
- I&B Minister Anurag Thakur calls upon youth to visit historical places across to strengthen spirit of Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat.
Detail
- Union Information and Broadcasting Minister called upon the youth to visit several scenic and historical places across the country, which would strengthen the spirit of Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat.
- India has become one of the five largest economies of the world leaving the British who ruled India and in the next three years the country would become the third largest economy in the world.
About Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat
Launched:
- “Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat” was announced by the Prime Minister on 31st October 2015 on the occasion of the 140th birth anniversary of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.
- The Finance Minister announced the initiative in his Budget Speech for 2016-17.
Under Ministry:
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Education.
Objectives:
- To celebrate the Unity in Diversity of our Nation and to maintain and strengthen the fabric of traditionally existing emotional bonds between the people of our Country.
- Promote the spirit of national integration through a deep and structured engagement between all Indian States and Union Territories through a year-long planned engagement between States.
- To establish long-term engagements and,
- To promote the rich heritage and culture, customs and traditions of either State for enabling people to understand and appreciate the diversity that is India, thus fostering a sense of common identity.
- To create an environment which promotes learning between States by sharing best practices and experiences.
Vision:
- To make our people aware about the seamless integral hull of the Modern Indian State spread across a vast landmass on whose firm foundations, the geo-political strength of the country is ensured to benefit one and all.
- To impress upon people at large about the increasing inter-connectedness between the constituents of various cultures and traditions, which is so vital for the spirit of nation building.
- To ease out the feeling of ‘stranger in a strange land’ among the people of different states, cultures and traditions living in various states of India.
- To generate the vibrance of understanding & appreciation amongst the people and forge mutual bonding to securing an enriched value system of unity in the nation.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/ek-bharat-shreshtha-bharat-34
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=I%26B-Minister-Anurag-Thakur-calls-upon-youth-to-visit-historical-places-across-to-strengthen-spirit-of-Ek-Bharat-Shreshtha-Bharat&id=460304

MOU ON INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT COOPERATION
Context
- India, Israel sign MoU on Industrial Research and Development Cooperation with focus on several key technology areas.
About
- Collaboration: The Multi-Sectoral Agreement was signed between CSIR and Directorate of Defense Research and Development (DDR&D), Ministry of Defense of the State of Israel.
Areas of cooperation:
- India and Israel will enhance partnership in areas like innovation and StartUps and usher in a new phase of deeper bilateral collaboration.
- It focusses on several key technology areas, like Aerospace, Electronics Instrumentation, Civil, Infrastructure & Engineering, Ecology, Environment, Earth & Ocean Sciences and Water, Mining, Minerals, Metals & Materials, Chemicals and Petrochemicals, Energy (Conventional & Non-Conventional) and Energy Devices, Agri, Nutrition & Biotech and Healthcare.
- India-Israel are not only bilateral partners, but play a larger role to address some of the greatest challenges confronting our world, through joint investments and new initiatives in Water, Energy, Transportation, space, health and food security sectors, through the grouping of India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States of America – “I2U2” Group.
- It has bilateral consultation mechanisms in all cooperation fields, including water, agriculture, counter-terrorism, and defence.
|
About I2U2 Group:
I2U2 stands for India, Israel, the UAE, and the US, and was also referred to as the ‘West Asian Quad’ by Ahmed Albanna, Ambassador of the UAE to India.
The aim is to discuss “common areas of mutual interest, to strengthen the economic partnership in trade and investment in our respective regions and beyond”.
|

READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/india-israel-relations-9
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India%2c-Israel-sign-MoU-on-Industrial-Research-and-Development-Cooperation-with-focus-on-several-key-technology-areas&id=460301






