GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES IN THE COOPERATIVE SECTOR
Context
- Union Home Minister, and Minister of Cooperatives, Shri Amit Shah launched the first multi-state cooperative Society for Exports of India, which will provide a global platform for the country’s organic products and share half its returns.
Key Details:
- With farmers launching the enterprise. He said it is one among 3 national cooperatives being planned by the Modi government.
- In order to strengthen the cooperative movement in the country, deepen its reach to the grassroots, make the cooperative sector self-reliant, and attract investment in the cooperative sector various initiatives have been taken by the Ministry of Cooperation across the country including tribal areas, such as.
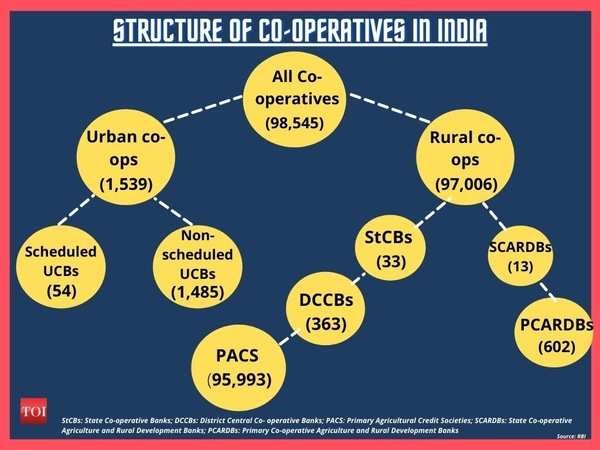
| The cooperative movement in India has a long and rich history, dating back to the 19th century. The first cooperative society in India was established in 1904 by Sir Frederick Nicholson, who was inspired by the success of the Rochdale Pioneers in England. The society was called the ‘Cooperative Credit Society’ and it provided loans to farmers at low interest rates. |
Cooperative under the Indian Constitution
- The Indian Constitution recognizes the importance of cooperatives and provides for their promotion and regulation.
- Article 19(1)(c) of the Constitutionguarantees the right to form cooperatives as a fundamental right.
- Article 43 of the Constitutiondirects the State to promote cottage industries and cooperatives in rural areas.
- Article 243ZH of the Constitutionempowers the Parliament and the State Legislatures to enact laws for the incorporation, regulation, and winding up of cooperative societies.
- The government enacted various laws and policies to support and regulate the cooperatives, such as the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act of 1984, the National Policy on Cooperatives of 2002, and the Constitution (97th Amendment) Act of 2011.

Making Primary Cooperatives Transparent and economically vibrant (14 initiatives):
- Model Bye-Laws for PACS making them multipurpose, multidimensional and transparent entities: Prepared and circulated to all the States/ UTs for adoption as per their respective State Cooperatives Act to enable PACS to undertake more than 25 business activities. Model byelaws have been adopted by 27 States/ UTs.
- Strengthening of PACS through Computerization: Process to onboard 63,000 PACS on an ERP-based national software, with an outlay of ₹2,516 Crore started.
- New Multipurpose PACS/ Dairy/ Fishery Cooperatives in uncovered Panchayats: A plan has been approved to set up 2 lakh new multi-purpose PACS or primary dairy/ fisheries cooperatives covering every Panchayat/ village in the next five years.
- World’s Largest Decentralized Grain Storage Plan in the Cooperative Sector to Ensure Food Security: The Pilot Project is under implementation to create godowns and other agriinfra for grain storage at the PACS level.
- PACS as Common Service Centers (CSCs) for better access to e-services: More than 17,000 PACS onboarded as CSCs to improve their viability, provide e-services, and generate employment in rural areas.
- Formation of new Farmer Producer Organization (FPOs) by PACS: 1,100 additional FPOs to be formed by PACS in those blocks where FPOs have not yet been formed or the blocks are not covered by any implementing agency.
- PACS was given priority for Retail Petrol/ diesel outlets: PACS have been included in the Combined Category 2 (CC2) for allotment of retail petrol/ diesel outlets. Existing PACS with wholesale petrol pump licenses are permitted to convert into retail outlets.
- PACS eligible for LPG Distributorship for diversifying its activities: PACS have now been allowed to apply for LPG Distributorships.
- PACS as Jan Aushadhi Kendra for improving access to generic medicines at rural level: PACS have been allowed to operate Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras which will provide additional income source them.
- PACS as Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samriddhi Kendras (PMKSK) for fertilizer distribution: PACS have been allowed to operate PMKSK to ensure easy accessibility of fertilizer & related services to farmers in the country.
- Convergence of PM-KUSUM at PACS level for energy security: Farmers associated with PACS can adopt solar agricultural water pumps and install photovoltaic modules in their farms.
- PACS to carry out O&M of rural piped water supply schemes (PWS): PACS have been allowed to carry out the Operations and maintenance (O&M) of PWS in rural areas.
- Micro-ATMs to Bank Mitra Cooperative Societies for providing doorstep financial services: Micro-ATMs are now being given to cooperative societies like Dairy and fisheries, by the Cooperative Banks.
- Rupay Kisan Credit Card to Members of Milk Cooperatives: Rupay Kisan Credit Cards are being provided to the members of cooperatives through Cooperative Banks for providing credit at comparatively lower interest rates.
Capacity Building in Cooperatives (3 initiatives):
- Establishment of the World’s Largest Cooperative University: A National Cooperative University being established for Cooperative education, training, consultancy, research and development, and a sustainable and quality supply of trained manpower.
- New Scheme of Cooperative Education and Training: To strengthen the cooperative movement, build capacity of faculty of VAMNICOM, NCCT, and JCTC, promote quality research and studies on important areas of the Cooperative sector, etc.
- Promotion of training and awareness through the National Council for Cooperative Training (NCCT): NCCT conducted 3,287 training programs and provided training to about 2,01,507 participants in FY 2022-23.
Significances
- The cooperatives in India have made significant contributions to various sectors of the economy and society.
Agriculture
- Cooperatives have played a vital role in enhancing the productivity, income, and welfare of farmers. They have provided inputs, credit, marketing, processing, and storage facilities to millions of farmers. Some examples of successful agricultural cooperatives are Amul, IFFCO, etc.
Banking
- Cooperatives have provided banking services to millions of people who are excluded from the formal banking system. They have offered savings, deposits, loans, insurance, and remittance facilities to their members at affordable rates. Some examples of successful banking cooperatives are Saraswat Bank, Karnataka State Cooperative Apex Bank, etc.
Housing
- Cooperatives have helped millions of people to access affordable and quality housing. They have constructed, maintained, and managed housing complexes for their members. Some examples of successful housing cooperatives are Delhi Cooperative Housing Finance Corporation, Maharashtra State Cooperative Housing Federation, etc.
Education
- Cooperatives have promoted education and skill development among their members and communities. They have established and run schools, colleges, universities, vocational training centers, etc. Some examples of successful education cooperatives are the Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited (IFFCO) Foundation, the National Cooperative Union of India (NCUI), etc.
Health
- Cooperatives have provided health care services to their members and communities. They have set up and run hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, diagnostic centers, etc. Some examples of successful health cooperatives are Kerala State Cooperative Hospital Complex and Centre for Advanced Medical Services (KCHCAMS), Seva Bharati Health Cooperative Society, etc.
Challenges faced by Cooperatives
Lack of awareness
- Many people are not aware of the benefits and opportunities offered by cooperatives. They also lack the knowledge and skills to form and manage cooperatives effectively.
Lack of capital
- Many cooperatives face difficulties in raising adequate funds for their operations and expansion. They also face high-interest rates and repayment burdens from external sources.
Lack of governance
- Many cooperatives suffer from poor governance practices that affect their efficiency and accountability. They also face interference and domination from political parties, bureaucrats and vested interests.
Lack of innovation
- Many cooperatives fail to adapt to the changing needs and preferences of their members and customers. They also lag in adopting new technologies and business models that can enhance their competitiveness and sustainability.
Way forward for cooperatives:
Creating awareness
- The cooperatives need to create awareness among the public about the concept, principles and benefits of cooperatives. They also need to educate and train their members and staff on the best practices of cooperative management and development.
Mobilizing capital
- The cooperatives need to mobilize capital from various sources, such as their members, the government, banks, financial institutions, etc. They also need to improve their financial management and audit systems to ensure transparency and accountability.
Strengthening governance
- The cooperatives need to strengthen their governance structures and processes to ensure democracy, autonomy and participation. They also need to resist and prevent any external interference or influence that may compromise their integrity and independence.
Fostering innovation
- The cooperatives need to foster innovation and creativity among their members and staff. They also need to adopt and use new technologies and business models that can improve their quality, efficiency and sustainability.
Closing thoughts
- Cooperatives in India have a long and glorious history of serving the economic and social needs of millions of people. They have also contributed to the national development goals of poverty alleviation, rural development, employment generation, etc. However, they face many challenges that limit their growth and performance. Therefore, they need to take some measures to overcome these challenges and enhance their competitiveness and sustainability. Cooperatives in India have a bright future ahead of them if they can leverage their strengths and opportunities while addressing their weaknesses and threats.
https://newsonair.gov.in/Spotlight.aspx#
http://risingkashmir.com/home-minister-amit-shah-launches-national-cooperative-for-exports-limited-ncel
https://m.timesofindia.com/india/20-new-initiatives-in-cooperative-sector-in-20-months-amit-shah/articleshow/97708679.cms
https://www.thehindu.com/business/budget/cooperatives-that-start-manufacturing-activities-before-march-31-2024-to-benefit-from-lower-tax-rate-of-15/article66458434.ece

India to resume some Visa services in Canada
Context
- India will resume visa services in Canada for certain categories from tomorrow. The categories are Entry visa, Business visa, Medical visa, and Conference visa.
Details
- High Commission of India in Ottawa said in a release that the decision has been taken after a considered review of the security situation that took into account some recent Canadian measures in this regard.
- It said the High Commission of India in Ottawa and its Consulates General in Toronto and Vancouver were constrained to suspend visas temporarily because of safety and security considerations.
About India-Canada Relations:
|
Economic relations
|
- Trade between India and Canada has been growing steadily. Both countries have expressed interest in expanding economic ties.
- Negotiations for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) have been ongoing to enhance trade and investment.
|
|
Political relations
|
- Diplomatic dialogues and high-level visits contribute to the strengthening of political ties between India and Canada.
- Both countries share common values as democratic nations and are members of international forums like the United Nations.
|
|
Education and Technology Collaboration
|
- There is a significant exchange of students and professionals between India and Canada.
- Educational institutions in both countries have established partnerships, and there is a flow of skilled workers and expertise in areas such as technology and innovation.
|
|
Cultural and People-to-People Ties
|
- Cultural exchanges play a role in fostering mutual understanding. Events and programs promote cultural awareness and appreciation between the two nations.
- The Indian diaspora in Canada is substantial and actively contributes to the social and economic fabric of the country.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India-to-resume-some-Visa-services-in-Canada&id=470064

Phosphatic and Potassic fertilisers
Context
- The Government has approved Nutrient-Based Subsidy (NBS) rates for Rabi season, 2023-24 on Phosphatic and Potassic fertilisers applicable from the 1st of October this year till the 31st of March next year.

Details:
- Addressing the media after a Cabinet meeting this afternoon, Union Minister for Information and Broadcasting Anurag Singh Thakur said that the Nutrient-Based Subsidy will be 47.02 rupees per kilo for nitrogen, 20.82 rupees per kilo for phosphorus and 2.38 rupees per kilo for potash.
- He said that an expenditure of 22 thousand 303 crore rupees is expected on Nutrient-Based Subsidy.
- This move will result in the availability of fertilisers to farmers at subsidised, affordable, and reasonable prices.
About Phosphatic and Potassic fertilisers:
|
Features
|
Phosphatic Fertilizers
|
Potassic Fertilizers
|
|
Nutrient Focus
|
- Phosphatic fertilizers are rich in phosphorus, a vital nutrient for plant growth. Phosphorus is crucial for processes like photosynthesis, energy transfer, and the development of roots and flowers.
|
- Potassic fertilizers are a source of potassium, an essential nutrient that plays a key role in various physiological processes within plants. Potassium is important for water uptake, enzyme activation, and overall plant health.
|
|
Common Forms
|
- Common phosphatic fertilizers include superphosphate, triple superphosphate, and diammonium phosphate (DAP).
|
- Common potassic fertilizers include potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and potassium nitrate.
|
|
Application
|
- These fertilizers are often used to improve flowering, fruiting, and root development in plants. They are especially beneficial for crops like fruits, vegetables, and flowering plants.
|
- Potassic fertilizers are used to enhance the resistance of plants to diseases and environmental stress. They contribute to the overall health and vigor of plants, especially during periods of drought or other adverse conditions.
|
Key differences:
- Phosphatic fertilizers primarily provide phosphorus, while potassic fertilizers supply potassium.
|
- Phosphatic fertilizers support root and flower development, as well as overall energy transfer in plants. Potassic fertilizers contribute to stress resistance, water uptake, and enzyme activation.
|
- Superphosphate, DAP, and triple superphosphate are examples of phosphatic fertilizers. Potassic fertilizers include potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and potassium nitrate.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Government-approves-subsidy-of-over-22-thousand-crore-rupees-on-Phosphatic-and-Potassic-fertilisers-for-current-Rabi-season&id=470039
'Meri Mati Mera Desh' campaign
Context
- A number of Amrit Kalash special trains are being run across the country for delegations to arrive in New Delhi under the 'Meri Mati Mera Desh' campaign. These trains will start to reach New Delhi from the 27th of this month.

Details
- The Culture Ministry informed that the train from Tripura and Meghalaya will reach Delhi on Friday, while trains from Assam and Sikkim trains will reach on the 28th of October.
- Amrit Kalash special trains from Chandigarh, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Lakshadweep with over one thousand five hundred delegates will reach on 29th October.
- Train from Rajasthan will reach New Delhi on 30th of this month. Nationwide 'Meri Mati Mera Desh' Campaign was launched on 9th August this year, to pay tributes to the ‘Veers’ who laid down their lives for the country.
- 'Amrit Kalash Yatra' carrying soil in 7500 urns from every corner of the country will conclude in New Delhi on 30th of this month. After that, an 'Amrit Vatika' will be built near the National War Memorial by fusing the soil and saplings of 7500 urns.
- This 'Amrit Vatika' will also become a grand symbol of 'Ek Bharat Shrestha Bharat'.
| The 'Meri Maati Mera Desh' campaign is a part of the larger 'Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav' initiative launched by the Centre earlier this year to commemorate 75 years of India's independence. The initiative aims to showcase India's progress and potential in various fields, as well as to inspire and empower the youth to contribute towards nation-building. |
Key Components of the Campaign:
|
Shilaphalakam
|
- Installing a memorial plaque in every gram panchayat or village, bearing the names of the freedom fighters, defence personnel, CAPF personnel, and state police personnel who have laid down their lives in the line of duty.
|
|
Vasudha Vandhan
|
- Planting 75 saplings of indigenous species in every gram panchayat or village, creating an Amrit Vatika (a sacred grove) that will symbolize the renewal of 'Mother Earth'. The saplings will be nurtured by the local community and will provide ecological benefits such as soil conservation, water recharge, biodiversity enhancement, and carbon sequestration.
|
|
Veeron Ka Vandan
|
- Saluting the freedom fighters and their families, as well as the retired and deceased defence, CAPF, and state police personnel and their families. This will acknowledge their contribution to the nation's freedom and security and will express gratitude and respect for their service.
|
|
Collection of Soil
|
- Collecting soil from every gram panchayat or village by young volunteers and others, who will bring it to the block level in 'Mitti Kalash' (earthen pots).
|
|
Amrit Vatika
|
- One of the main highlights of the campaign is the development of a unique garden called Amrit Vatika along the Kartavya Path in Delhi. The garden will be made with soil brought from all parts of the country, representing the different regions, cultures and traditions of India
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Number-of-Amrit-Kalash-special-trains-being-run-across-country-for-delegations-to-arrive-in-New-Delhi-under-%26%2339%3bMeri-Mati-Mera-Desh%26%2339%3b-campaign&id=470058

Education Ministry clarifies that NCERT crafted ten special modules on Chandrayaan-3
Context
- The Education Ministry today clarified that NCERT has meticulously crafted ten special modules on Chandrayaan-3 which offer a comprehensive overview of various facets of this mission, encompassing scientific, technological, cultural, and social aspects.

Details:
- In response to some media reports regarding ‘mixing science with mythology’ with reference to the Chandrayaan 3 Special Modules, the Ministry of Education has clarified that it is important to equip teachers and students with knowledge that transcends traditional textbooks.
- It said this endeavour aims to instill a sense of pride in India and its accomplishments.
- The Ministry added that it is essential to extend curricular material beyond textbooks, presenting the nation's achievements in a manner that is both accessible and captivating for the educational community.
| The Education Ministry said the content within these modules has been thoughtfully designed to be interactive and engaging. It includes graphics, photographs, illustrations, activities, and challenging questions. These modules cater to students across the stages of school education, spanning from grades 1 to 12. |
About National Council of Educational Research and Training:
- It is an autonomous organization in India that was established in 1961 by the Government of India. NCERT is tasked with advising the central and state governments on academic matters related to school education.
- NCERT engages in educational research to understand and address issues related to school education. This research contributes to the development of policies and practices in the education sector.
- NCERT works on incorporating educational technology into the teaching-learning process. This includes the development of digital content and tools for education.
- NCERT conducts various programs and workshops to train teachers and enhance their skills. The aim is to improve the quality of education imparted in schools.
- NCERT is known for promoting a holistic and child-centric approach to education. The organization plays a crucial role in shaping the educational landscape in India by providing a framework for curriculum development, teacher training, and educational research.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Education-Ministry-clarifies-that-NCERT-crafted-ten-special-modules-on-Chandrayaan-3&id=470059









