Successful Conclusion and Key Decisions at G20 Summit 2023

Context
- The 18th G20 Summit of 2023 recently concluded in New Delhi, India, marking the first-ever G20 summit hosted by the country.
Key Details:
- The summit’s theme, “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” or “One Earth, One Family, One Future” is rooted in ancient Sanskrit texts and the goal of sustainable development.
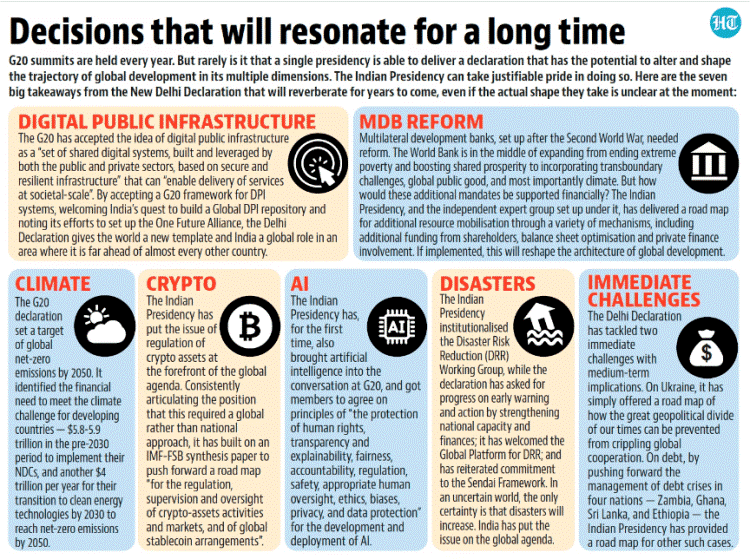
- India was successfully able to achieve consensus around the New Delhi Declaration early on in the G20 Summit, which saw a dilution in the position taken by the U.S. and EU on Russia, besides focus on UN Sustainable Development Goals, climate action, and green development initiatives, multilateral financing, digital public infrastructure, artificial intelligence (AI), and international taxation, among others.
Key outcomes of the G20 Summit 2023:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s diplomatic coup:
- PM Modi views this summit as India’s diplomatic milestone, with its G20 presidency serving as a platform to amplify the Global South’s concerns.
- In a personal capacity, the G20 Summit’s outcomes are important for the Indian leader as he faces general elections next year.
- At the Summit, India was able to leverage its economic significance to garner support from all G20 member nations for a Leaders’ Declaration recognizing the conflict in Ukraine without specifying any aggressor.
- Modi, who chaired the Summit, also advocated for reforming global institutions like the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) to align with the changing world dynamics, which received backing from the United States.
- The timing of the G20 Summit was also opportune, following India’s successful moon landing under the Chandrayaan-3 program.
G20 New Delhi Declaration:
- All 83 paragraphs of the 2023 G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration were unanimously approved, achieving a remarkable 100 percent consensus, even with China and Russia in agreement.
- Notably, this declaration stood out by containing no footnotes or Chair’s Summary, marking a historic moment.
- Within these 83 paragraphs, multiple agreements about the Finance Track were embedded. Furthermore, it featured 8 paragraphs addressing the conflict in Ukraine and its subsequent economic implications.
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman highlighted the achievements of the Indian G-20 Presidency, emphasizing a concrete strategy for strengthening multilateral development banks, a clear path for regulating cryptocurrencies, and the deployment of digital public infrastructure to enhance financial inclusion.
- She also underscored the importance of a faster debt relief plan for vulnerable nations.
- Regarding climate change, the declaration stressed the urgency of mobilizing “US$5.8-5.9 trillion in the pre-2030 period for developing countries” and “US$4 trillion per year for clean energy technologies by 2030” to attain net-zero emissions by 2050. It called for a substantial increase in climate funding, transitioning from billions to trillions of dollars.
African Union accepted as part of the G20:
- Before this, the only African member of the G20 was South Africa.
- At the Delhi Summit of the G20, the African Union, which represents the 55 countries in the African continent, was given full membership, like how the EU is represented.
- India has successfully positioned itself as a champion for developing and underdeveloped nations and seeks to align this with its ambitions for a permanent seat on the UNSC.
- New Delhi is actively seeking support from the African continent, which holds 55 crucial votes, in pursuit of this goal.
- India also invited Nigeria, Egypt, and Mauritius as part of the ‘Guest Countries’ at the G20 summit.
India – Middle East – Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC):
- During the G20 Summit in New Delhi, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed among the governments of India, the U.S., Saudi Arabia, the European Union, the UAE, France, Germany, and Italy to establish the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor.
| IMEC is envisioned as a network of transportation routes encompassing railways and sea lanes. Its primary objective is to promote economic development by fostering integration between Asia, the Arabian Gulf, and Europe. |
Climate action:
- Leaders at the G20 Summit did not reach a consensus on the phase-out of fossil fuels, despite a United Nations report categorizing this phase-out as “indispensable” for achieving net-zero emissions.
- The G20 nations collectively contribute to approximately 80 percent of global emissions. The inability to agree on this crucial issue casts a shadow over upcoming climate discussions set to commence in November in the oil-rich UAE.
- The G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration also featured commitments to mainstream Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), implement sustainable energy transitions, provide sustainable finance, reaffirm the pursuit of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), address plastic pollution, preserve the ocean-based economy, and more.
- Additionally, the summit witnessed the launch of the Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA), a new organization aimed at promoting the development and adoption of sustainable biofuels, along with the establishment of relevant standards and certification.

What is the G20 and how does it work?
- The G20 originated in 1999 in response to the Asian financial crisis of 1997-98, initially serving as an informal platform for finance ministers and central bank governors from both developed and developing economies.
- In 2008, following the global financial crisis, the G20 expanded to include the heads of state of member countries.
- The G20 Presidency rotates annually under a troika system, involving the current, previous, and next host countries.
- In 2022, India took over the G20 Presidency from Indonesia, the preceding member of the troika. The presidency has now been passed to Brazil, the next troika country.
How the G20 works
- The G20 operates through three main tracks: the Finance Track, the Sherpa Track, and the Engagement Groups.
|
Finance Track: Led by finance ministers and central bank governors, this track convenes approximately four times a year. It addresses fiscal and monetary policy issues, including the global economy, infrastructure, financial regulation, financial inclusion, international financial architecture, and international taxation.
|
|
Key working groups within this track cover topics, such as the Framework, International Financial Architecture, Infrastructure, Sustainable Finance, Financial Inclusion, Finance and Health, International Taxation, and Financial Sector Matters.
|
|
Sherpa Track: Established in 2008 when the G20 became a leaders’ summit, the Sherpa Track is comprised of representatives of heads of state. It focuses on socioeconomic concerns like agriculture, anti-corruption, climate change, the digital economy, education, employment, energy, environment, health, tourism, trade, and investment.
Each representative in this track is referred to as a Sherpa, and there are 13 working groups covering areas, such as Agriculture, Anti-corruption, Culture, Development, Digital Economy, Disaster Risk Reduction, Education, Employment, Energy Transitions, Environment and Climate Sustainability, Health, Tourism, and Trade and Investment.
|
|
Engagement Groups: This unofficial track includes non-government participants and engagement groups that provide recommendations contributing to policy-making.
|
|
The Engagement Groups consist of Business20, Civil20, Labour20, Parliament20, Science20, SAI20, Startup20, Think20, Urban20, Women20, and Youth20.
|
Closing thoughts
- India’s G20 Presidency’s theme, "One Earth, One Family, One Future” reflects our G-20 Presidency’s priorities, which include advocacy for inclusive and resilient growth; progress on SDGs; green development and Mission LiFE; technological transformation and public digital infrastructure; reforming multilateral institutions; women-led development; and international peace and harmony. Further, India is also amplifying the voices and concerns of the Global South and developing countries.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=18th-G20-Summit-comes-to-a-close-at-Bharat-Mandapam-in-New-Delhi%3B-PM-Modi-officially-hands-over-the-G20-Presidency-to-Brazilian-President-Luiz-Inacio-Lula-da-Silva&id=467512#:~:text=The%2018th%20G20%20Summit%20successfully,Luiz%20Inacio%20Lula%20Da%20Silva.
https://news.abplive.com/india-at-2047/g20-summit-2023-how-the-green-development-pact-promises-to-address-climate-change-challenges-1628868
https://newsonair.com/2023/09/12/g20-summit-in-india-hailed-as-absolute-success-by-us/
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/g20-summit-new-delhi-world-leaders-narendra-modi-september-9-live-updates/article67287698.ece
.jpg)
Fourth G20 Sustainable Finance Working Group Meeting
Context
- The 4th G20 Sustainable Finance Working Group Meeting (SFWG) began today in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh to finalize the 2023 G20 Sustainable Finance Report.
Details
- Three priority areas have been outlined for the SFWG The first one is Mechanisms for the mobilization of timely and adequate resources for climate finance.
- The second issue that is being discussed is enabling finance for the Sustainable Development Goals. The last topic is the Capacity building of the ecosystem for financing toward sustainable development.
- These priority areas reflect India's focus on sustainability and the theme of India’s G20 Presidency “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” or ‘One Earth. One Family. One Future’.
- The two-day meeting under India's G20 Presidency brings together over 80 delegates from G20 member countries, special invitee countries, and International Organisations.
About SFWG:
- The SFWG has been working on three priority areas to advance the actions as envisaged in the G20 Sustainable Finance Roadmap, namely
- (i) Mechanisms for mobilisation of timely and adequate resources for climate finance;
- (ii) Enabling finance for the Sustainable Development Goals; and
- (iii) Capacity building of the ecosystem for financing toward sustainable development.
Challenges:
- The major challenges to scaling up climate finance include limited availability of concessional funding, complexities in utilising de-risking facilities, and lack of bankable projects.
- Enabling greater capital flows for advancing early-stage technologies focused on adapting and building resilience to climate change also remains a challenge.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Fourth-G20-Sustainable-Finance-Working-Group-Meeting-begins-in-Varanasi&id=467643
.jpg)
Nominations for Padma Awards-2024
Context
- The online nominations for the Padma Awards 2024 are open till the 15th of this month.

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
Details:
- The nomination began on the 1st of May this year. Union Home Ministry said the nominations or recommendations for Padma Awards will be received online on the Rashtriya Puraskar Portal.
- The award will be announced on the occasion of Republic Day next year.
About Padma awards
- The Padma Awards, namely, Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Shri are amongst the highest civilian awards of the country.
- Instituted in 1954, these Awards are announced on the occasion of Republic Day every year.
- The award seeks to recognise work of distinction and is given for distinguished and exceptional achievements and service in all fields, such as Art, Literature and Education, Sports, Medicine, Social Work, Science and Engineering, Public Affairs, Civil Service, Trade, and Industry.
- The Ministry said all persons without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex are eligible for these Awards.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Nominations-for-Padma-Awards-2024-open-till-15-September&id=467615
.jpg)
Infrastructure projects constructed by BRO
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has said that the 90 infrastructure projects constructed by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) worth over 2,900 crore rupees spread across 11 States and Union Territories will go a long way in enhancing infrastructure in the border areas.
Details
- The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi has lauded the 90 infrastructure projects constructed by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO), worth over Rs 2,900 crore and spread across 11 States/Union Territories.
- The projects were dedicated to the nation by the Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh.
About the Border Roads Organisation (BRO):
|
About
|
- It is a statutory body under the ownership of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
|
|
Purpose
|
- BRO develops and maintains road networks in India's border areas and friendly neighboring countries.
- This includes infrastructure operations in 19 states and three union territories (including Andaman and Nicobar Islands) and neighboring countries such as Afghanistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, Tajikistan, and Sri Lanka.
|
|
Working
|
- BRO is instrumental in significantly upgrading and building new India-China Border Roads (ICBRs).
- BRO set a Guinness World Record in November 2021 for the "highest altitude road" at Umling La.
- BRO has been instrumental in constructing some of the great Engineering Marvels like Atal Tunnel, Atal Setu, and Col Chewang Rinchen Setu to name a few.
|
|
Members
|
- Officers from the Border Roads Engineering Service (BRES) and personnel from the General Reserve Engineer Force (GREF) form the parent cadre of the BRO.
- It is also staffed by officers and troops drawn from the Indian Army's Corps of Engineers on extra regimental employment (on deputation).
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=PM-Modi-hails-90-infrastructure-projects-constructed-by-BRO&id=467647

International Government Communication Forum
Context
- Sharjah, UAE – The International Government Communication Forum (IGCF) in Sharjah is set to kick off with a spotlight on the vital role media plays in addressing and raising awareness about sustainability-related topics.
Details:
- As part of the event, a Media Seminar brought together prominent media figures, featuring insightful panel discussions on "Media Coverage and Climate Change" and "The Role of Media in Highlighting Sustainability Issues."
- Experts highlighted the need for comprehensive media coverage across various domains, such as the community, economy, health, and more, recognizing the complexity of sustainability topics.
- Another panel discussion, "Coverage of the Environment in the Media: A Historical Overview," explored historical narratives in environment-related media coverage, featuring Isatou Davies Ann, Director General of Gambia News Agency (GAMNA), and Steven Skillet, Scientific Consultant at Trends Research & Advisory.
About the International Government Communication Forum (IGCF):
|
About
|
- IGCF is one of the key initiatives of the Sharjah Government Media Bureau.
|
|
Established
|
- It was first launched in 2012, and since then it has been organised annually.
|
|
Objectives
|
- The forum's core objective is to refine government communication paradigms, amplifying collaboration among stakeholders engaged locally, regionally, and internationally.
|
|
Role
|
- IGCF is the first-of-its-kind platform in the region that brings together global government communication experts to explore best practices in the field.
|
|
Significance
|
- Since its inauguration, the forum has redefined the communication landscape in the Arab world and internationally with its path-breaking discussions and recommendations that have tangibly impacted communication policies at the regional and international levels.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=International-Government-Communication-Forum-in-Sharjah-Spotlights-Media%26%2339%3bs-Crucial-Role-in-Sustainability-Issues&id=467650







