



India-Nepal Bilateral Ties

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details:
INTRODUCTION:
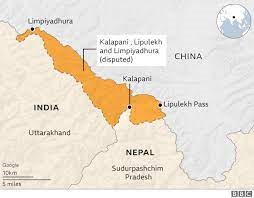
Background of relations:
India’s importance to Nepal:
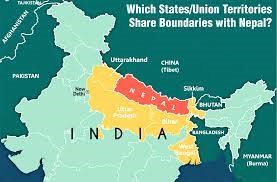
Navigating Complex Dynamics
Way Forward:
Steps that can be taken
Conclusion
CITATIONS:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vecNZ5hwza8
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India-Nepal-review-progress-of-all-bilateral-projects&id=350296
https://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/ForeignRelation/India-Nepal_Bilateral_Brief_Feb_2020.pdf
© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved