Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- India is ready to host the 18th G20 Summit on the 9th and 10th of September.
Details:
- To be held at the newly-built Bharat Mandapam in Pragati Maidan, the Leaders' Summit will mark the culmination of 200-plus meetings held throughout the year across 60 Indian cities.
- At the G20 Leaders’ Summit, delegates and leaders from 40 countries will participate.
- These include representatives from member states and the invitee countries, making it the biggest participation ever in the history of the G20 Summit.
- The G20 presidency is a significant moment for India, one that could potentially alter the way the world views it.
.jpg)
INTRODUCTION:
- India has always been described as a land of paradoxes. Be it India’s culture, diversity, or sheer population size, it is complicated and fascinating.
- For about two decades now, the engines of the nation’s economic growth have been firing impressively. Companies have become larger and many have left a rather large global imprint.
- So, India’s presidency of the G20 forum which represents 85 percent of global GDP and 75 percent of international trade is hugely important as it comes at an inflection point when a confident India is looking to flex its muscles globally after it breezed past the years of the pandemic and emerged relatively unscathed.
|
India assumes the G20 Presidency on the 1st of December 2022 from Indonesia and will convene the G20 Leaders' Summit for the first time in the country in 2023.
A nation deeply committed to democracy and multilateralism, India's G20 Presidency would be a watershed moment in her history as it seeks to play an important role by finding pragmatic global solutions for the wellbeing of all, and in doing so, manifest the true spirit of 'Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam' or the 'World is One Family'.
|
India's G20 priorities:
India has identified a wide array of cutting-edge priorities that are being deliberated by various G20 working groups, to help address the key challenges we face and to plan for a better future. Let me highlight three of them.
Financing tomorrow’s cities:
- The first agenda relates to financing tomorrow’s cities and establishing them as the foremost engines of economic growth. While cities generate over 80% of global gross domestic product, unplanned and rapid urbanization constrain their economic potential.
- It is estimated that by 2050, nearly twice as many people will live in cities. To sustain their economic potential, cities need to become more livable through upgraded infrastructure and services, such as reliable water, transport, power, waste management, and affordable housing.
Energy transition:
- The second agenda where India can lead the way is in the energy transition. Enabling an orderly and just transition from carbon-intensive energy to renewable energy would not only help combat climate change, but also help bolster energy security, raise economic productivity and create jobs, improve environmental outcomes, and prune health costs. In other words, decarbonization is development.
- Today, India is the world’s third-largest producer of renewable energy, with further expansion underway.
- India’s success in scaling up solar energy, along with recently announced programs such as the National Hydrogen Mission, Production-Linked Incentives for electric vehicles and the manufacture of solar technologies and battery energy storage, and incentive mechanisms for supporting offshore wind, all allow the country to lead by example and drive global collaboration to reduce the cost of achieving net-zero emission.
| India has made efforts for the G20 to focus on the need to expand and diversify critical minerals and renewable energy supply chains for economies to secure uninterrupted and affordable access to renewable energy and energy storage, both prerequisites for the overall transition to net-zero emission. |
Health care
- The third agenda relates to health care. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the compelling need for a united global approach to fortify health systems to effectively address emerging health crises.
- India’s G20 Presidency is a medium of change towards more resilient, responsive, and sustainable health systems and to advance previously established G20 pandemic preparedness efforts.
- G20 can help shape a global health agenda focused on ensuring universal, affordable, and quality health services.
- Giving priority to enhancing health emergency prevention and preparedness (with a focus on One Health and linkages between climate change and health), strengthening cooperation in the pharmaceutical sector, and leveraging digital health innovations and solutions to aid universal health coverage, is critical.
| India can lend its experience in framing a successful national digital health architecture through a supportive regulatory environment, private-public partnerships, and digital health interventions such as CoWIN and the National Digital Health Mission. |
Green Development, Climate Finance, and LiFE:
- Climate finance and technology, along with “ensuring just energy transitions for developing nations across the world”, are key priority areas for India during its presidency.
- With LiFe, a “behavior-based movement that takes from the country’s rich, ancient sustainable
- traditions, India plans to “nudge consumers, and in-turn markets, to adopt environmentally-conscious practices”.
Multilateral Institutions for the 21st Century
- Efforts to reform multilateralism and create a more accountable, inclusive, and representative international system that is fit for addressing 21st-century challenges.
Women-led Development
- Emphasis on inclusive growth and development, with a focus on women empowerment and representation to boost socio-economic development and the achievement of SDGs.
.jpg)
Significance of India’s G20 Presidency:
- First, agenda-setting is a fundamental and primary tool for securing and extending power and influence in international politics, particularly in multilateral platforms. The year-long G20 presidency offers India a significant opportunity to set global agendas, articulate policies and build consensus over critical economic, development, socio-political and security issues.
- Second, in global platforms, India always wanted to promote and endeavour to be the voice of the Global South. India can utilize its G20 leadership role to advance the interests of the Global South and New Delhi's credentials as a voice of the Global South.
- Third, reforming multilateral institutions to make them more inclusive and responsible is one of the foremost priorities of Indian foreign policy.
Challenges in presidential priorities:
- Confronted with issues like climate change, economic recovery, pandemic and increasing geopolitical tensions, the global community is looking for effective and accountable multilateral institutions that could deliver better in the field.
- Therefore, India placed reformed multilateralism that is fit for addressing the 21st-century challenges as one of its presidential priorities. If G20, under India's leadership, facilitates progress on this long-pending issue, it will increase India's stature and status in global politics.
- Finally, India's presidency comes at a time of escalating global tensions coinciding with a period of flux globally.
- The world faces multiple challenges, including post-COVID-19 economic recovery, climate change, food and energy security crisis, supply chain disruptions and conflicts.
- The international community expects India to be instrumental in building a global consensus for addressing these issues and shaping the future agenda of global common goods.
- Similarly, the world is also expecting India to bridge the increasing divide between countries, not only the developing and developed world split but the rupture among the West as well, especially in the context of the Russia–Ukraine War.
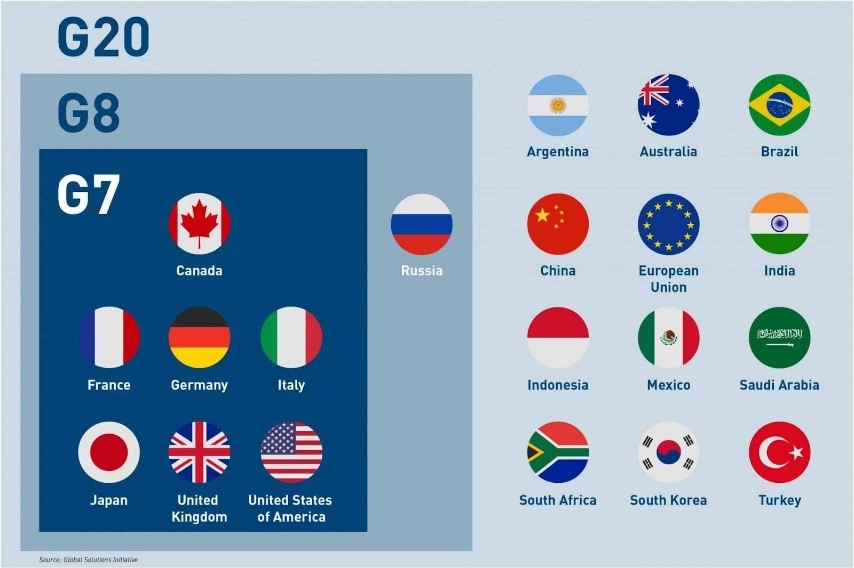
About G20 group:
Accelerated, resilient, and inclusive growth:
- India is concentrating on areas that can usher in structural transformation, such as promoting labour rights and secure labour welfare, addressing the global skills gap and so on.
Accelerating progress on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- India has already had success in getting the G20 members, which includes 19 countries and the European Union, on board with this goal. Following the G20 development ministers’ meeting in Varanasi, foreign minister S Jaishankar said India bagged its “biggest achievement” as the group unanimously agreed to an action plan to speed up progress on SDGs and sustainable development lifestyles.
Technological Transformation and Digital Public Infrastructure:
- According to MEA, India will endorse a “human-centric approach to technology, and facilitate greater knowledge-sharing in priority areas like digital public infrastructure, financial inclusion, and tech-enabled development in sectors ranging from agriculture to education”.
What are the significant achievements of G20?
Over the past two decades, through consistent and mutual efforts, the G20 has been able to significantly impact the governance of member nations. Some of the significant contributions of G20 include:
- The member nations contribute to approximately 90 percent of global GDP and 80 percent of global trade.
- Battling against the financial crisis such as - the Global Financial Crisis 2008-09, the Eurozone Crisis in 2010, etc.
- With a USD 10 trillion rescue package that concentrated on tackling the economic and health crises, the G20 took the lead in the worldwide struggle against the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The G20 Debt Service Suspension Initiative (DSSI) benefitted 50 countries and helped to address unsustainable debt burdens and provide long-term reserves to low-income, emerging markets and developing countries.
- Focusing on boosting women's engagement in the labor market, the International Labor Organization has continued its ongoing study on Women at work in G20 Countries.

Conclusion
- The G20 presidency of India falls during a period of intense turmoil in global economic ties. India inherits the presidency amid numerous serious economic difficulties, including inflationary pressures threatening global financial stability, rising income inequality, disruptions to supply chains, food and energy security, and the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It is quite challenging to cover a broad spectrum of sectors and redress the issues. However, under the leadership of PM Narendra Modi, India is set to accomplish the milestone.
- Over 190 meetings have been planned under the G20 2023 Indian Presidency which is expected to be a challenging and exciting policy endeavor.
CITATIONS:
https://sansadtv.nic.in/show/perspective
https://www.adb.org/news/features/indias-g20-presidency-opportunity
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/indias-approach-to-g20-presidency-is-extension-of-its-domestic-focus-on-progress-and-development-8655069/
https://www.businesstoday.in/magazine/deep-dive/story/indias-g20-presidency-heres-what-it-means-for-key-sectors-of-the-countrys-economy-395764-2023-08-26
https://www.firstpost.com/explainers/india-g20-presidency-significance-challenges-global-south-12738262.html




