PERSPECTIVE: INDO-PACIFIC IN FOCUS
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Despite multiple crises in Europe and the Middle East, the 2+2 strategic dialogue demonstrated that Washington has not entirely lost sight of what needs to be done in the Indo-Pacific.
Details:
- India is an ancient maritime nation and home to some of the oldest sea ports in the world. For millennia, our people have traveled across the vast oceans carrying with them goods, ideas, and religion, and establishing civilizational links crisscrossing across the globe.
- With its 7500 km long coastline and 1200 islands, India has had an enduring maritime tradition and a wide maritime footprint. India’s holistic approach towards shaping a stable maritime order is reflected in the vision of ‘SAGAR’, which stands for ‘Security and Growth for All in the Region’.
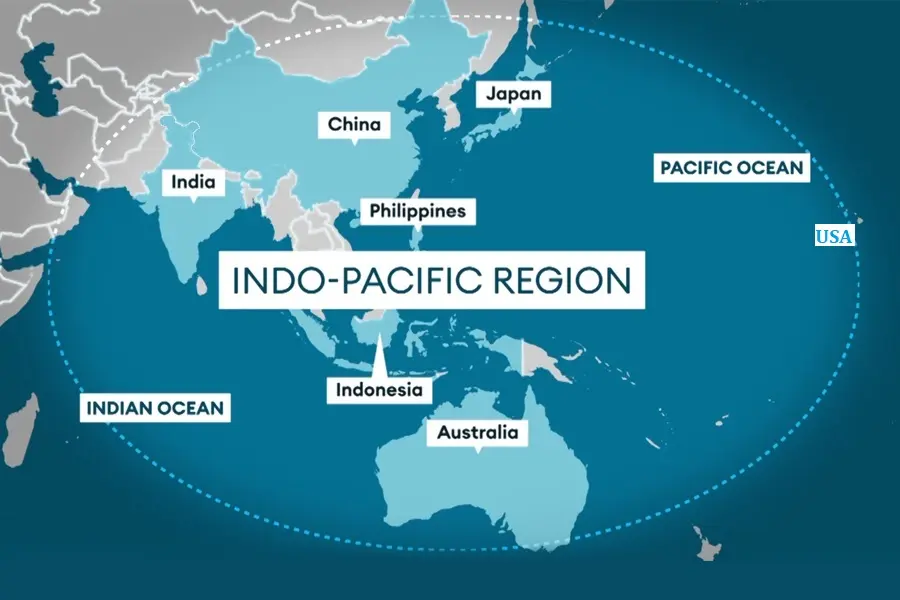
- In 2018, at the Shangrila Dialogue in Singapore, Prime Minister Narendra Modi spoke of the Indo-Pacific region as a natural region extending from the shores of East Africa to the Western Pacific, where the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean flow in a seamless continuum.
- Recently, the 5th edition of the Indo-Pacific Regional Dialogue (IPRD) was held at Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi, with the broad theme “Geopolitical impacts upon Indo-Pacific Maritime Trade and Connectivity”.
INTRODUCTION:
- The term "Indo-Pacific" has gained prominence in the global discourse over the past decade, marking a significant shift in strategic considerations.
Strategic Theater Linkage
- Around ten years ago, discussions about the Indo-Pacific began to surface, highlighting the interconnectedness of the Indian and Pacific Oceans as a crucial strategic theater.
Diverse Perceptions
- The popularity of the Indo-Pacific concept stems from the diverse ways nations perceive it, each attributing its own set of benefits and concerns to the evolving geopolitical landscape.
Absence of Absolute Concepts
- It's important to note that there are no fixed or absolute concepts defining the Indo-Pacific, and interpretations may vary among nations. The fluidity of the term allows for flexible strategic considerations.
Geographical Boundaries
- The Indo-Pacific concept does not adhere to strict geographical boundaries, emphasizing the dynamic nature of this evolving strategic framework.

Present Context:
Geographical Significance
- The Indo-Pacific region stands out as a hub of global significance, encompassing four continents: Asia, Africa, Australia, and America.
Population and Economic Powerhouse
- With 60% of the world's population and contributing two-thirds of the global economic output, the Indo-Pacific region emerges as a dynamic and economically vital area on the global stage.
Dynamism and Vitality
- The region's dynamism is self-evident, reflecting its vibrant economic activity and influence on the world stage.
Global Economic Center
- Given its substantial population and economic prowess, the Indo-Pacific region solidifies its position as a key global economic center, shaping the trajectory of international commerce and interactions.
India’s Approach to the Indo-Pacific:
Cooperative Security Architecture:
- India's perspective emphasizes cooperation with key partners like the US, Australia, Japan, and Indonesia to establish a security architecture in the Indo-Pacific. Unlike a confrontational approach, India envisions working together to foster peace and security in the region through dialogue.
Common Rules-Based Order:
- India advocates for the evolution of a common rules-based order in the Indo-Pacific through diplomatic engagement. The aim is to ensure common prosperity and security, addressing concerns related to China's influence. The emphasis is on building a framework that promotes stability and adherence to agreed-upon rules.
Trade and Investment Equality:
- India supports a rule-based, open, balanced, and stable trade environment in the Indo-Pacific, aligning with its expectations from agreements like the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). The goal is to create an atmosphere that benefits all nations, ensuring equal sharing of trade and investment opportunities in the region.

Significance of the Indo-Pacific:
Indo-Pacific Geography and Scope:
- The expansive region of the Indo-Pacific spans from Africa to America, embodying a vision of a free, open, and inclusive area involving nations and stakeholders.
Democratizing the Region:
- India's perspective emphasizes the need to democratize the Indo-Pacific, avoiding dominance by any single player, be it historical American influence or a potential Chinese hegemony.
Geopolitical and Economic Hub:
- The Indo-Pacific region holds geopolitical importance with dynamic and populous countries like India, China, Japan, Australia, and Indonesia, making it a critical center for global geopolitics.
Economic Dynamics and Trade Routes:
- Being a major driver of the global economy, the region boasts key maritime trade routes like the Strait of Malacca, hosting crucial ports facilitating trade between Asia, Europe, and Africa.
Security Challenges and Competition:
- The Indo-Pacific witnesses increasing strategic competition among major powers, with security concerns such as nuclear-armed states and territorial disputes, notably the South China Sea disputes.
Balancing China's Rise:
- The rise of China shapes the region's significance, prompting countries to seek a balance in alliances and partnerships to ensure their security in the face of China's expanding influence.
Maritime Security Priorities:
- Ensuring the security of maritime trade routes is paramount in the Indo-Pacific, addressing issues like piracy, territorial disputes, and the protection of crucial sea lanes.
Regional Organizations and Forums:
- Active engagement in various regional organizations and forums, including ASEAN, QUAD, and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), plays a pivotal role in addressing regional issues and enhancing cooperation.
Connectivity and Infrastructure Focus:
- Infrastructure development and connectivity projects are gaining prominence in the Indo-Pacific, with initiatives like China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the U.S. "Free and Open Indo-Pacific" strategy shaping the economic and political landscape.
Environmental and Ecological Concerns:
- The Indo-Pacific's diverse ecosystems, including coral reefs and marine biodiversity, raise global concerns about climate change, environmental issues, and the need for sustainable practices.
Recent developments and strategies about the Indo-Pacific region:
USA’s Indo-Pacific Strategy (February 2022):
- In February 2022, the United States unveiled its Indo-Pacific Strategy in collaboration with allies and partners. The strategy aims to promote a shared vision of a free, open, connected, prosperous, secure, and resilient Indo-Pacific region.
Canada’s Indo-Pacific Strategy:
- Canada's Indo-Pacific Strategy focuses on advancing and safeguarding its interests by contributing to a more secure, prosperous, inclusive, and sustainable region. The strategy emphasizes four key regions: China, India, the North Pacific (Japan and Korea), and ASEAN.
Japan’s Vision of a “Free and Open Indo-Pacific”:
- Japan envisions a "Free and Open Indo-Pacific" to enhance regional stability and prosperity. The vision emphasizes improving connectivity between Asia and Africa to foster a free and open environment in the Indo-Pacific.
Indian Vision of Indo-Pacific:
- India advocates for a "free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific" region. It emphasizes peaceful dispute resolution while respecting the sovereignty and territorial integrity of all nations in the Indo-Pacific.
ASEAN’s Outlook on the Indo-Pacific:
- ASEAN perceives the Indo-Pacific as a region of dialogue and cooperation rather than rivalry. The outlook envisions the Indo-Pacific as a zone of development and prosperity for all, emphasizing collaboration among nations in the region.
AUKUS Security Partnership:
- AUKUS is a security partnership announced by the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia. The partnership focuses on enhancing cooperation in security and defense issues, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region, to address shared challenges in the region.

Initiatives taken by India in the Indo-Pacific region:
India's Stance at HACGAM:
- India reaffirms its commitment to open and rule-based maritime borders during the 18th Heads of Asian Coast Guard Agencies Meeting (HACGAM) in New Delhi on October 15, 2022.
SAGAR Initiative:
- Strategic partnerships expanded through the SAGAR initiative, providing a mechanism for India to collaborate with Indian Ocean region littorals in Asia and Africa.
Indo-Pacific Regional Dialogue (IPRD):
- IPRD, a Track 1.5 event, fosters discussions on public policy with a balanced representation of government and non-government agencies and institutions.
Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI):
- Pillars of cooperation under IPOI encompass Maritime Security, Maritime Ecology, Maritime Resources, Capacity Building and Resource Sharing, Disaster Risk Reduction and Management, Science, Technology and Academic Cooperation, Trade, Connectivity, and Maritime Transport.
QUAD Membership:
- India actively participates as a member of the Quadrilateral security dialogue, promoting regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
Indo-Pacific Division in MEA:
- India establishes an Indo-Pacific division in the Ministry of External Affairs, dedicated to handling all matters related to the Indo-Pacific region.
Challenges in the Indo-Pacific region:
- Territorial Disputes: The Indo-Pacific region is marked by numerous territorial disputes, notably the ongoing tensions over the South China Sea and the East China Sea.
- Regional Power Dynamics: A Shift in the Balance of Power is evident in the region, with China's assertiveness challenging the traditional dominance of the United States and its allies, leading to increased regional power competition.
- Economic Complexities: The region grapples with Economic Challenges such as uneven economic development, trade imbalances, and escalating debt levels, requiring strategic cooperation for sustainable growth.
- Environmental Concerns: The Indo-Pacific houses the world's most diverse and fragile ecosystems, including coral reefs and mangroves, facing imminent threats from climate change, pollution, and overfishing, necessitating urgent environmental conservation efforts.
- Non-Traditional Security Threats: The region confronts Non-Traditional Security Threats, ranging from transnational crime and terrorism to cyberattacks. Effective responses demand coordinated efforts among governments, security forces, and civil society actors.
Measures can help to harmonize the recent developments in the India-Pacific region:
Bilateral Collaboration:
- The Indo-Pacific region faces numerous challenges, and countries can effectively tackle issues like maritime security and counter-piracy through bilateral cooperation. An example of this is the collaborative efforts between nations to enhance security measures in shared maritime spaces.
Multilateral Engagement:
- Multilateral organizations, including ASEAN, APEC, and the Indian Ocean Rim Association, serve as crucial platforms for fostering cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
- These entities play a pivotal role in facilitating diplomatic dialogues, promoting economic collaboration, and addressing shared concerns on a larger scale.
Regional Initiatives:
- Regional efforts, exemplified by initiatives like the Quad (comprising the United States, Japan, India, and Australia), contribute significantly to promoting security and economic integration in the Indo-Pacific.
- Collaborative endeavors within such frameworks can effectively address common challenges, ranging from climate change to cybersecurity.
Global Cooperation:
- International organizations, particularly the United Nations, play a vital role in supporting endeavors to establish peace, security, and sustainable development in the Indo-Pacific.
- These entities contribute to humanitarian assistance and provide a global platform for coordinating efforts to address regional challenges collectively.

Prospects for India in the Indo-Pacific:
Forging Strategic Alliances:
- Cultivating strategic partnerships with Indo-Pacific nations like Japan, Australia, and the United States can pave the way for collaborative efforts in security, trade, and other crucial areas.
Countering China's Influence:
- India's proactive engagement in the region positions it as a key player in counterbalancing China's growing influence, fostering stability through enhanced regional partnerships.
Championing Maritime Security:
- Leveraging its extensive coastline and significant Indian Ocean presence, India can take the lead in ensuring maritime security, combating piracy, and safeguarding vital shipping lanes.
Climate Change Cooperation:
- India has the potential to collaborate with Indo-Pacific nations to tackle climate change, addressing issues like rising sea levels and extreme weather events through collective efforts.
Driving Economic Integration:
- As one of the world's fastest-growing economies, India can spearhead increased economic collaboration, fostering growth and connectivity with other countries in the Indo-Pacific region.
CITATIONS:
https://sansadtv.nic.in/episode/perspective-indo-pacific-in-focus-18-november-2023
https://thediplomat.com/2023/11/india-us-22-strategic-dialogue-keeps-indo-pacific-in-focus/
https://m.timesofindia.com/india/second-ind-aus-22-tomorrow-focus-on-indo-pacific-quad/articleshow/105322244.cms
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-us-hold-22-ministerial-dialogue-with-focus-on-indo-pacific-critical-minerals-and-global-challenges/article67520341.ece
https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/secure-open-indo-pacific-key-area-of-focus-at-india-us-2-2-ministerial-meet-101699609155833.html




