RSTV: SKILL INDIA
Context: Skill India aims to provide skill development and vocational training to millions of Indians. It was launched in 2015 and has completed nine years of successful implementation. It has helped many people acquire new skills, enhance their employability, and contribute to the nation's economic growth.
Skill India
About
- Skill India is a flagship initiative of the Government of India that aims to train and develop the skills of millions of Indians and make them employable or self-reliant in various sectors of the economy.
- It was launched in 2015; Skill India is one of the world's largest skill development programs that involve multiple stakeholders such as central and state governments, industry associations, educational institutions, civil society organizations, and foreign partners.
- The vision of Skill India is to create a skilled workforce that can contribute to the economic growth and social development of the country.
Background
- India is a young nation with more than 60% of its population in the working age group (15-59 years) and more than 54% below the age of 25 years. This demographic dividend offers a great opportunity for India to become a global leader in various sectors.
- However, it also poses a huge challenge as only a small fraction of the workforce has formal vocational training or skills.
- According to the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) report, only 2.2% of the workforce aged between 15-59 years had received formal vocational training and 8.6% had received non-formal vocational training. This means that more than 89% of the workforce lacked any kind of skill training.
- The low level of skill development in India is attributed to various factors such as;
- Lack of awareness, access, quality, relevance, and recognition of vocational education and training.
- Inadequate infrastructure and resources.
- Poor linkages between industry and academia.
- A mismatch between demand and supply of skills.
- The social stigma attached to vocational education.
- Low participation of women and marginalized groups in skill development.
To address these challenges and harness the potential of the youth, the Government of India launched the Skill India Mission in 2015 with an ambitious target of skilling at least 300 million people by 2022.
The mission has four key objectives:
- To align the skill development programs with the demand of various sectors and regions.
- To create an ecosystem of quality training institutions and trainers.
- To promote entrepreneurship and self-employment among the youth.
- To foster a culture of innovation and lifelong learning.
The Mission has several schemes and programs under its umbrella, such as:
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
- It is the largest scheme under the Skill India Mission, which provides free short-term training and recognition of prior learning to the youth. It also offers placement assistance and incentives to the trainees and trainers.
National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)
- NAPS incentivize employers to engage apprentices and provides financial support to them for imparting on-the-job training.
Skill Loan Scheme
- It is a scheme that provides loans ranging from Rs. 5,000 to Rs. 1.5 lakh to the youth who want to pursue skill development courses.
- The loans are available at concessional rates of interest and have flexible repayment options.
Pradhan Mantri Yuva Yojana (PMYY)
- PMYY is a scheme for entrepreneurship education and training, which aims to create a pipeline of entrepreneurs and innovators in the country.
National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)
- NSDC is a public-private partnership that catalyzes skill development initiatives by providing funding, capacity building, and quality assurance support to various stakeholders.
National Skill Development Agency (NSDA)
- NSDA is a nodal agency that coordinates and harmonizes the skill development efforts of various ministries and departments at the central and state levels.
Sector Skill Councils (SSCs)
- SSCs are industry-led bodies that identify skill gaps, develop occupational standards, design curricula, and certify trainees and trainers in their respective sectors.
Key features of Skill India Mission are:
- It covers various sectors and domains, such as manufacturing, services, agriculture, construction, tourism, health, etc.
- It offers both short-term and long-term courses, ranging from a few hours to a few years, depending on the level and type of skill required.
- It provides industry-relevant and demand-driven training, with the involvement of employers and sector skill councils in designing and delivering the courses.
- It follows a competency-based framework, with assessment and certification by independent agencies.
- It leverages technology and digital platforms, such as the e-Skill India portal, to enable online skilling and access to learning resources.
- It promotes apprenticeship and internship opportunities, both domestically and internationally, to provide hands-on experience and exposure to the trainees.
- It aligns with the National Policy for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship 2015, which provides a vision and roadmap for skilling in India.

Major achievements of the Skill India programme
- As of June 2023, more than 2 crore candidates have been trained and certified under the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
- As of June 2023, more than 1000 Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendra (PMKK) have been established across the country, covering all districts and aspirational districts.
- As of June 2023, more than 50 India International Skill Centres (IISC) have been operationalized across the country, catering to more than 1 lakh candidates.
- Skill India Digital Platform was launched to offer features such as skill courses, job exchange, apprenticeship portal, skill centre locator, success stories, etc. As of June 2023, more than 10 crore users have registered on the platform and availed its services.
- As of June 2023, more than 5 lahks overseas Indians have been skilled under the Skill India International Project.
Significances of Skill India
- It helps to bridge the gap between the supply and demand of skilled labour in various industries, such as manufacturing, services, agriculture, etc.
- It improves the quality and standards of skills training and certification, ensuring that the skills are relevant and aligned with the market needs.
- It empowers the youth with skills that can enable them to access better opportunities and livelihoods, both within and outside the country.
- It fosters a culture of lifelong learning and continuous upskilling, enhancing the adaptability and resilience of the workforce in a dynamic and changing environment.
- It supports the creation of new enterprises and startups, especially in rural and remote areas, by providing skills training, mentoring, financial assistance, and market linkages.
- It contributes to the social and economic development of the country, by reducing poverty, unemployment, inequality, and migration.
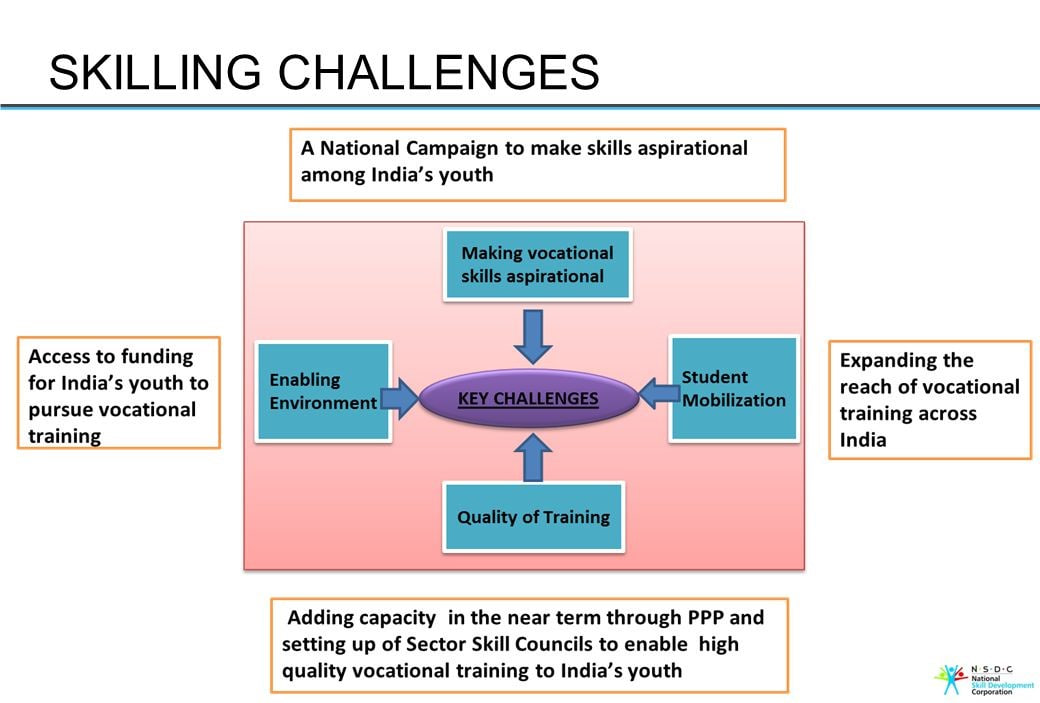
Challenges of Skill India
Quality and relevance of training
- The quality and relevance of the training provided under Skill India are often questionable. Many training providers lack adequate infrastructure, equipment, curriculum, trainers, and assessment systems.
- The training is not aligned with the industry demand and the changing needs of the labour market. As a result, many trainees do not acquire the skills that are required for employment or entrepreneurship.
Access and equity
- The access and equity of skill development opportunities are also uneven across different regions, sectors, and groups.
- There are significant gaps in the coverage and participation of rural areas, women, persons with disabilities, minorities, and other disadvantaged sections of society. These groups face various barriers such as lack of awareness, information, guidance, mobility, affordability, and social norms that prevent them from accessing and benefiting from skill development programs.
Coordination and convergence
- The lack of coordination and convergence among various stakeholders involved in skill development.
- Multiple ministries, departments, agencies, schemes, and programs operate in silos and often overlap or contradict each other. This leads to duplication, wastage, inefficiency, and confusion among the beneficiaries and the service providers.
- There is a need for a coherent and integrated policy framework and a common platform for collaboration and coordination among all the actors.
Monitoring and evaluation
- The monitoring and evaluation of the skill development programs are also weak and inadequate.
- There is no comprehensive data system that captures the inputs, outputs, outcomes, and impacts of the various interventions. The existing data sources are often unreliable, inconsistent, incomplete, or outdated.
- There is no robust mechanism for feedback, learning, accountability, and improvement. This hampers the evidence-based planning, implementation, and management of skill development programs.
Financing and sustainability
- The financing and sustainability of the skill development programs are also major challenges. The skill development sector requires huge investments in infrastructure development, capacity building, quality assurance, innovation, and scaling up.
- Public funding is limited and often delayed or diverted. The private sector participation is also low and mostly confined to certain sectors or regions. There is a need for mobilizing more resources from various sources and ensuring their efficient and effective utilization.
Promoting Skill India is essential for enhancing the employability and productivity of the youth, as well as for boosting the economic growth and social development of the country.
Some steps that can be taken to promote Skill India:
Create awareness and interest among the target groups
- Create awareness and interest among the potential beneficiaries of Skill India, such as students, school dropouts, women, rural and urban poor, and differently-abled persons. This can be done through various channels such as mass media, social media, community mobilization, workshops, seminars, exhibitions, and roadshows.
- The awareness campaigns should highlight the benefits and opportunities of skilling, such as better jobs, higher income, improved quality of life, and social recognition.
Provide access and affordability to skill training
- Provide access and affordability to quality skill training for the target groups. This can be done by expanding the network of skill development centres, vocational institutes, industrial training institutes, and online platforms across the country.
- The skill training should be aligned with the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF) and industry standards. The skill training should also be subsidized or free for the disadvantaged sections of society.
Ensure relevance and quality of skill training
- Ensure relevance and quality of skill training for the target groups. This can be done by involving the industry, academia, and civil society in designing and delivering skill training programs.
- The skill training programs should be based on the current and future market demand and should impart both technical and soft skills. It should also have regular assessment and feedback mechanisms to monitor and improve the learning outcomes.
Facilitate placement and entrepreneurship
- Facilitate placement and entrepreneurship for the skilled workforce. This can be done by creating linkages between the skill training providers and the employers, both in the public and private sectors.
- The placement services should provide career guidance, counselling, job fairs; resume writing, interview preparation, and post-placement support.
- The entrepreneurship services should provide mentoring, incubation, funding, networking, and market access for aspiring entrepreneurs.
Recognize and reward the skilled workforce
- Recognize and reward the skilled workforce for their achievements and contributions. This can be done by providing certificates, badges, incentives, scholarships, awards, and social recognition for skilled workers and learners.
- The recognition and reward system should also encourage continuous learning and upskilling for the skilled workforce.

Conclusion
- Skill India is a visionary mission that aims to empower the youth of India with skills that can transform their lives and the nation. By providing them with opportunities for learning, employment, and entrepreneurship, Skill India is creating a generation of skilled employees and leaders who can meet the modern-day market demands and drive the economic growth and social development of the country.
https://sansadtv.nic.in/episode/awaaz-desh-ki-%E0%A4%B8%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%95%E0%A4%BF%E0%A4%B2-%E0%A4%87%E0%A4%82%E0%A4%A1%E0%A4%BF%E0%A4%AF%E0%A4%BE-%E0%A4%B8%E0%A4%AC%E0%A4%B2-%E0%A4%87%E0%A4%82%E0%A4%A1%E0%A4%BF%E0%A4%AF%E0%A4%BE




