RSTV: JAL JEEVAN MISSION
Context: The Jal Jeevan Mission aims to deliver safe and adequate drinking water to all rural households by 2024 via individual household tap connections. The initiative also includes mandated source sustainability measures such as recharge and reuse through greywater management, water conservation, and rainwater collection.
Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM)
About
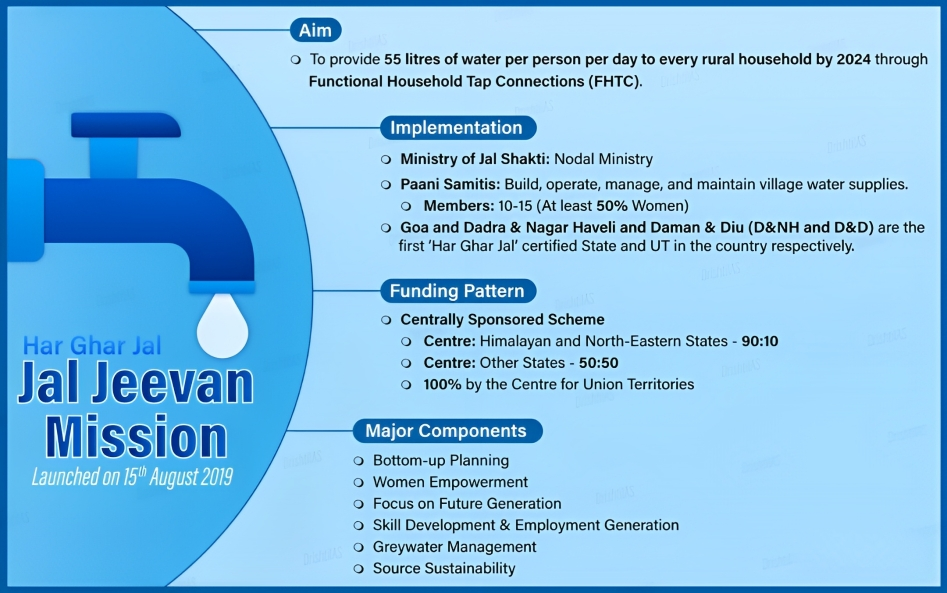
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) is a flagship program of the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti, which aims to provide safe and adequate drinking water to every rural household in the country by 2024.
- The mission was launched by Prime Minister on 15 August 2019, with a budget of Rs. 3.6 lakh crore.
- The mission is based on the principle of 'Har Ghar Jal' (water in every home) and seeks to improve the quality of life and health of rural people.
Background
- India is facing a severe water crisis, with about 163 million people lacking access to safe drinking water, according to a report by WaterAid.
- The country is also ranked 120th among 122 countries in the water quality index by the World Health Organization.
Main Reasons for water scarcity and contamination are:
- Overexploitation and depletion of groundwater resources due to increasing demand and population growth.
- Pollution of surface water sources due to industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, sewage and solid waste disposal.
- Lack of adequate infrastructure and management for water supply, treatment and distribution.
- Climate change and erratic rainfall patterns affect the availability and recharge of water sources.
- Socio-economic and gender inequalities that limit the access and affordability of water for marginalized groups.
To address these challenges, the Government of India launched the Jal Jeevan Mission, which is a holistic and integrated approach to ensure water security and sustainability in rural India.
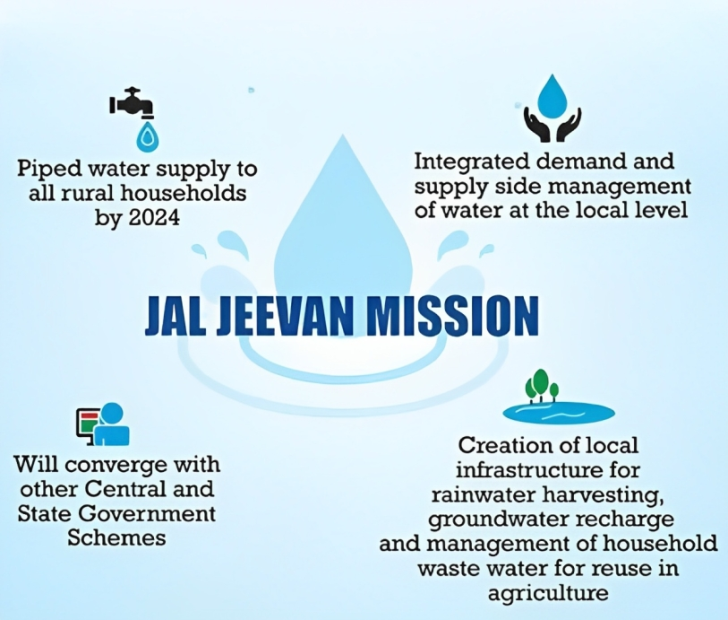
Features of Jal Jeevan Mission
Demand-driven and community-participatory approach
- The JJM recognizes that the people are the best judges of their own needs and preferences. Therefore, it adopts a bottom-up approach, where the village panchayats and local communities are involved in planning, implementing and managing the water supply schemes.
- The villagers have to contribute 10% of the capital cost as well as bear the operation and maintenance costs of the schemes. This ensures that the schemes are sustainable and responsive to the local context and demand.
Use of local and alternative water sources
- The JJM acknowledges that water is a finite and precious resource that needs to be conserved and managed wisely. Therefore, it promotes the use of local and alternative water sources such as rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, surface water, greywater reuse, etc., to ensure water availability throughout the year.
- The mission also encourages the adoption of water-efficient practices such as drip irrigation, micro-irrigation, etc., to reduce water demand.
Quality assurance of water supplied
- The JJM ensures that the water supplied to the households is safe and potable, by setting up water quality testing laboratories at various levels and providing regular monitoring and surveillance.
- The mission educates the people about the importance of water quality and hygiene and empowers them to report any issues or complaints regarding the water supply.
Convergence with other schemes and programs
- The JJM realizes that water supply is not an isolated issue, but linked to various aspects such as sanitation, health, nutrition, education, environment, etc. Therefore, it provides convergence with other schemes and programs such as Swachh Bharat Mission, MGNREGA, National Rural Livelihood Mission, etc., to create synergies and complementarities.
- For example, the Swachh Bharat Mission helps in improving sanitation and hygiene, which in turn reduces water contamination and diseases. Similarly, MGNREGA helps in creating assets for water conservation and recharge, which in turn enhances water availability and security.
Capacity building and skill development of stakeholders
- The JJM recognizes that the success of any program depends on the capacity and skills of its stakeholders. Therefore, it enhances the capacity and skills of various stakeholders such as gram panchayats, village water and sanitation committees, self-help groups, etc., through training and awareness programs.
- The mission creates opportunities for employment and entrepreneurship in the rural water sector, by involving local youth, women, artisans, etc., in various activities such as plumbing, masonry, testing, etc.
Technology and innovation for efficiency and effectiveness
- The JJM leverages technology and innovation for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of water supply systems. For example, it uses smart meters, sensors, GIS mapping, etc., to monitor and manage the water supply network. It uses digital platforms such as mobile apps, web portals, etc., to provide information and services to people.
- The mission also encourages innovation and best practices from various states, districts and villages, and facilitates their replication and scaling up.

Significances of Jal Jeevan Mission
Improved health and hygiene
- By ensuring access to safe and adequate water at the household level, Jal Jeevan Mission reduces the risk of water-borne diseases, infections and malnutrition that affect millions of rural people every year.
- The mission promotes hygiene practices such as handwashing, sanitation and menstrual hygiene management, which are essential for preventing the spread of diseases and improving the quality of life.
Reduced drudgery and enhanced opportunities
- Jal Jeevan Mission frees women and children from the burden of fetching water from distant and often unsafe sources, which consumes a lot of their time and energy. This enables them to pursue education, empowerment and livelihood opportunities that can improve their socioeconomic status and well-being.
- The mission provides water for domestic needs such as cooking, cleaning, washing, etc., which reduces the workload and improves the comfort of rural households.
Boosted rural economy
- Jal Jeevan Mission creates employment opportunities for local people in the planning, implementation, operation and maintenance of water supply systems. The mission also enhances agricultural productivity by providing irrigation water for crops and livestock.
- The mission supports cottage industries such as dairy, poultry, handicrafts, etc., that depend on water as a raw material or an input. It promotes tourism by improving the availability and quality of water in rural areas, which attracts visitors and generates income for the local communities.
Conserved and protected environment
- Jal Jeevan Mission reduces the stress on groundwater resources, which are depleting at an alarming rate due to overexploitation and climate change. The mission prevents pollution of surface water sources such as rivers, lakes, ponds, etc., by reducing the discharge of untreated wastewater and solid waste.
- The mission increases green cover and biodiversity by promoting rainwater harvesting, watershed management, afforestation, etc., which enhance the ecological balance and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Fostered social harmony and cohesion
- Jal Jeevan Mission ensures equitable distribution of water among different sections of society, especially the poor, women, SCs/STs, etc., who often face discrimination and exclusion in accessing water.
- The mission encourages community participation and ownership in the planning, implementation, operation and maintenance of water supply systems, which fosters social harmony and cohesion among different groups.
- The mission contributes to the national goals of achieving universal access to safe drinking water under Sustainable Development Goal 6 and ensuring 'Ease of Living' for all citizens.
|
Status of JJM as of June 2023
●Out of the total 19.46 crore rural households in India, 12.43 crore (63.8%) have been provided with FHTCs under the JJM.
●Out of the total 6.02 lakh villages in India, 1.68 lahks (27.9%) have been declared as 'Har Ghar Jal' villages, where every household has access to piped water supply.
●The average per capita water availability in rural areas has increased from 40 litres per day (lpd) in 2019 to 55 lpd in 2023.
●The percentage of rural households with access to safe drinking water has increased from 83% in 2019 to 92% in 2023.
●The percentage of rural households with access to water quality testing facilities has increased from 35% in 2019 to 65% in 2023.
|
Challenges for Jal Jeevan Mission
Funding and resource gap
- The JJM requires a massive investment of about Rs 3.6 lakh crore to achieve its target. However, the current budget allocation and fund release are not sufficient to meet the demand and cost of the mission.
- There is a lack of adequate resources such as pipes, pumps, filters, meters, etc. for implementing the water supply schemes.
Coordination and convergence issues
- The water sector in India involves multiple departments, agencies and stakeholders at the central, state and local levels. However, there is a lack of effective coordination and convergence among them for planning, implementing and monitoring the JJM activities. This leads to duplication, delays and discrepancies in the execution of the mission.
Community awareness and participation
- The JJM envisages a community-led and community-managed approach to ensuring the sustainability and maintenance of the water supply systems. However, there is a lack of awareness and participation among the rural communities about their roles and responsibilities in the JJM.
- Many rural households are not willing to pay user charges or contribute to the operation and maintenance costs of the water supply systems.
- There is a lack of behavioural change among rural people regarding water conservation and management practices.
Technical expertise and manpower
- The JJM requires a high level of technical expertise and skilled manpower for designing, installing and operating the water supply schemes in diverse geographical and hydrological conditions. However, there is a shortage of qualified and trained engineers, technicians, plumbers, etc. for carrying out the JJM activities. Moreover, there is a lack of standardization and quality control in the water supply systems.
Data and information gap
- The JJM requires reliable data and information on the status of water availability, quality, usage and demand in different regions. However, there is a lack of accurate and updated data and information on these aspects.
- There is a lack of data sharing and dissemination mechanisms among the various stakeholders involved in the water sector.
Enforcement and regulation mechanisms
- The JJM requires strict enforcement and regulation mechanisms for ensuring compliance with the norms and standards of water quality and quantity. However, there is a lack of effective monitoring and evaluation systems for assessing the performance and impact of JJM activities.
- There is a lack of accountability and grievance redressal mechanisms for addressing the issues and challenges faced by rural communities in accessing safe and adequate water supply.

Way Forward for Jal Jeevan Mission
Increasing the Fund allocation and resources
- Increasing the allocation and mobilization of funds and resources from various sources such as central and state governments, external agencies, the private sector, CSR, etc. This will help to bridge the gap between the demand and supply of funds and ensure timely and adequate financial support for the mission activities.
Strengthening the institutional framework
- Strengthening the institutional and governance framework for ensuring effective coordination and convergence among various actors and schemes in the water sector. This will help to avoid duplication and wastage of resources and ensure synergy and alignment of goals and strategies among different stakeholders.
Enhancing the awareness
- Enhancing the awareness and participation of the rural communities in planning, implementing and managing the water supply systems, and ensuring their ownership and accountability. This will help to foster a sense of responsibility and empowerment among the communities and enable them to monitor and maintain the water supply systems in their villages.
Capacity Building
- Building the capacity and skills of the gram panchayats, village water and sanitation committees, self-help groups, etc., to enable them to perform their roles and functions efficiently and effectively. This will help to improve the quality and delivery of services and ensure transparency and accountability in the mission operations.
Leveraging technology
- Leveraging technology and innovation for improving the quality, quantity and reliability of water supply systems, and ensuring real-time monitoring and feedback. This will help to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the water supply systems and enable timely detection and resolution of issues and problems.
Establishing a robust data system
- Establishing a robust data and information system for capturing and analyzing water-related indicators and parameters in different regions. This will help to provide evidence-based decision-making, planning and evaluation for the mission activities, and ensure data-driven governance.
Regulating the norms and standards
- Enforcing and regulating the norms and standards of water quality and quantity, and taking punitive actions against the violators. This will help to ensure compliance with the legal and regulatory framework, protect public health and the environment, and prevent misuse or overuse of water resources.

Conclusion
- The Jal Jeevan Mission is a transformative initiative that aims to provide 'Har Ghar Jal' (water for every home) by 2024. It is not only a matter of convenience or comfort for the rural people but also a matter of dignity and empowerment. By ensuring access to safe and adequate water at their homes, the mission will improve their health outcomes, enhance their productivity and income levels, reduce their drudgery and time poverty, enable their education and skill development opportunities
https://sansadtv.nic.in/episode/arthniti-%e0%a4%85%e0%a4%b0%e0%a5%8d%e0%a4%a5%e0%a4%a8%e0%a5%80%e0%a4%a4%e0%a4%bf-%e0%a5%a4-%e0%a4%b9%e0%a4%b0-%e0%a4%98%e0%a4%b0-%e0%a4%9c%e0%a4%b2-%e0%a4%9c%e0%a4%b2-%e0%a4%9c%e0%a5%80%e0%a4%b5





