AGRICULTURAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The allocation of money to agricultural education and research has been reduced in the Union Budget 2022-23.
Emerging challenges in Agricultural Sector
Presently, agriculture faces many challenges such as:
(i) Low productivity
(ii) Decreasing profitability in farming,
(iii) Rising quality competitiveness under the pressure of globalisation,
(iv) Poor linkage of farms with the market,
(v) Low knowledge of input agriculture,
(vi) Wide gap between lab and land experiments,
(vii) Low level of mechanization and value addition
(viii) Supply Chain Management and Product Lifecycle Management,
(xi) Lack of qualified manpower to address the new and emerging challenges and deliver at grassroots level,
(x) mounting threat to sustainability arising from depleting quality of natural resources, biotic and abiotic stresses and inefficient use of agro-inputs and
(xi) poorly coordinated natural disaster management system.
To properly address these challenges a renewed thrust for agriculture education is necessary with enhanced financial support. In order to sustain, diversify and realize the potential of agriculture sectors, it is necessary to develop skilled human resources.
Importance of Agricultural Education
- Modern agriculture practices are increasingly turning out to be knowledge-based and hence gaining expertise in them is not an easy task for many of our rural farmers.
- India does require education at all levels so that India farmers are better equipped to handle the threats of globalization.
- These days with the entry of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the sector, many MNCs have forayed into the segment with dozens of agro-products.
- This has resulted as a threat to Indian farmers who lack professional expertise to better deal with the issue. Hence the need of the hour is to give agricultural education a high priority.
Importance of Agricultural Research
- New technologies, inputs, and techniques of production that increase agricultural productivity are developed through agricultural research.
- A transformed agricultural research system helps to achieve sustainable food and income security for all agricultural producers and consumers.
- Sustainable agricultural intensification itself means producing more food and agricultural products from the same overall resources (such as land, labour and water), while reducing the negative environmental impacts and at the same time increasing contributions to natural capital and the flow of environmental services.
- In a nutshell, research contributes significantly to the three aspects of food security - availability, access and affordability.
The Case of India
Concern
- India is yet to emerge as a significant trade partner in the world agriculture market.
- Presently, India holds around 1% of the global trade in agro- commodities, which is very less as compared to huge workforce engaged in this field.
- Despite many major structural transformations such as better input facilities and technology changes with regards to irrigation, High yielding seeds and changes in cropping pattern etc., the agriculture sector in India is still termed as the poor’s profession in India.
- It’s high time, Indian agricultural policy makers re-establish and re-brand its outlook to meet prevailing global threats.
Investment in Agricultural Research and Education
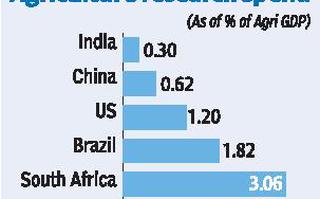
- According to the Economic Survey 2017-18, the total R&D expenditure in India as percentage of GDP has been stagnant at 0.6 to 0.7 per cent in the last two decades.
- This is much lower than the US (2.8 per cent), China (2.1 per cent), South Korea (4.3 per cent) and Israel (4.2 per cent).
- GDPs of the US and China are around seven and four times bigger than that of India.
Silver-lining
- Today, with an annual production of 308 million tonnes of food grains, India is not only in the realm of food security but is also catering to needs of other countries.
- However, the demand for foodgrain is expected to rise to 350 million tonnes with likely increase in India's population to 150 crore by 2030-32.
Final Thoughts
- Research expenditure on agriculture acquires special significance given the millions of Indians dependent on this sector.
- The demand for food will rise amid depleting natural resources and the challenge of climate change.
- In this backdrop, there is a need to rethink and adapt agricultural research and development, along with increasing investment in scientific research to achieve adequate and nutritious food along with environmental sustainability.
- To make the country self-reliant, concerted efforts need to be continued in agricultural research in areas such as genomics, digital agriculture, climate-smart technologies and methods, efficient water use equipment, development of high yielding and bio-friendly varieties, systematic production, quality and safety standards among others.
- Increasing R&D spending on agriculture is not only a vital necessity for ensuring food security, but also important from the socio-economic point of view.
- So the onus is on the government to increase financial allocation to research and create an enabling environment for private investments.
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/economy/union-budget-2022-23-allocation-for-agricultural-education-and-research-reduced-81360



1.png)
