Antarctic iceberg A68a
Context: The giant iceberg A68, the biggest block of free-floating ice from Antarctica with an area of about 5,800 sq. km, has been drifting in the Atlantic Ocean since 2017.
- This year, due to an ocean current, the iceberg was propelled into the South Atlantic Ocean and since then it has been drifting towards the remote sub-Antarctic island of South Georgia, prompting fears about the impact the iceberg could have on the island’s abundant wildlife.
- Icebergs travel with ocean currents and either get caught up in shallow waters or ground themselves.
What is A68a and where is it headed?
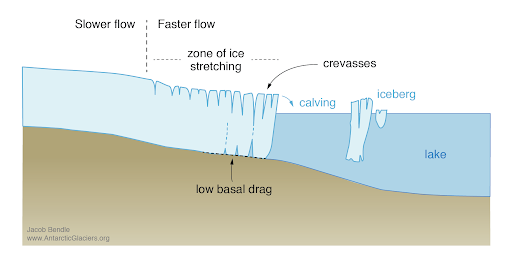
- A68a, an iceberg roughly the size of the state of Delaware, split off from Antarctica’s Larsen C ice shelf in July 2017.
- US National Ice Center (USNIC) confirmed that two new icebergs calved from A68a and were large enough to be named and tracked.
- They are called A68E and A68F.
Why did the iceberg calve?
- The iceberg’s calving is thought to be a natural event and not a result of climate change.
- However, some models predict that a warming Antarctica in the future could mean more calving events as ice shelves and glaciers retreat.



1.png)
