Description
Copyright infringement is not intended
Context:
- The Union Cabinet chaired by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi has approved a Memorandum of Association (MoA) by India for establishment of Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) Technology Transfer Facility (TTF) was signed by the BIMSTEC member countries at the 5thBIMSTEC Summit held at Colombo, Sri Lanka.
- The main objectives of the BIMSTEC TTF are to coordinate, facilitate and strengthen cooperation in technology transfer among the BIMSTEC Member States by promoting the transfer of technologies, sharing of experiences and capacity building.
- The TTF shall facilitate transfer of technologies among the BIMSTEC Member States, amongst other things, in the following priority areas Biotechnology, Nanotechnology, Information and Communication Technology, Space technology applications, Agricultural technology, Food processing technology, Pharmaceutical technology automation, New and renewable energy technology automation, New and Renewable energy technology, Oceanography, Nuclear Technology Applications, E-waste and solid waste management technology, Health Technologies, Technologies pertinent to Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change Adaptation.
- The TTF shall have a Governing Board and the overall control of activities of the TTF shall be vested in the Governing Board. The Governing Board shall consist of one nominee from each Member State.
- The expected outcomes of the BIMSTEC TTF are:
- Databank of technologies available in BIMSTEC Countries,
- Repository of information on good practices in the areas of technology transfer management, standards, accreditation, metrology, testing and calibration facilities,
- Capacity building, sharing of experiences and good practices in development, and
- Transfer and use of technologies among BIMSTEC countries.
- The fifth summit of the the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC), held virtually in Colombo.
Colombo package
Grouping’s charter:
- It presents BIMSTEC as “an inter-governmental organization” with “legal personality.”
- It defines BIMSTEC’s purposes and lists 11 items in the first article. Which includes
- acceleration of “the economic growth and social progress in the Bay of Bengal region”, and
- promotion of “multidimensional connectivity”.
Re-constitution:
- The second element is the decision to re-constitute and reduce the number of sectors of cooperation from the unwieldy 14 to a more manageable seven.
- Each member-state will serve as a lead for a sector:
- trade, investment and development (Bangladesh);
- environment and climate change (Bhutan);
- security, including energy (India); agriculture and
- food security (Myanmar);
- people-to-people contacts (Nepal);
- science, technology and innovation (Sri Lanka), and
- connectivity (Thailand).
Master Plan for Transport Connectivity
- Summit participants adopted the Master Plan for Transport Connectivity applicable for 2018-2028.
- It was devised and backed by the Asian Development Bank (ADB).
- It lists 264 projects entailing a total investment of $126 billion. Projects worth $55 billion are under implementation.
- BIMSTEC needs to generate additional funding and push for timely implementation of the projects.
Agreements
- The package also includes three new agreements, relating to mutual legal assistance in criminal matters, cooperation between diplomatic academies, and the establishment of a technology transfer facility in Colombo.
What need to be done to strengthen BIMSTEC?
- Trade pillar needs support: The pillar of trade, economic and investment cooperation needs greater strengthening and at a faster pace.
- Bridging the bay in quest of a stronger BIMSTEC: Despite signing a framework agreement for a comprehensive Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in 2004, BIMSTEC stands far away from this goal. Of the seven constituent agreements needed for the FTA, only two are in place as of now.
- Need to finalise legal instruments for coastal shipping, road transport and intra-regional energy grid connection.
- India was the only country to offer additional funding to the Secretariat and also to support the Secretary General’s proposal to establish an Eminent Persons Group (EPG) for producing a vision document. Other countries need to emulate this sincere matching of words with action.
- BIMSTEC should focus more in the future on new areas such as the blue economy, the digital economy, and promotion of exchanges and links among start-ups and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- The personal touch: personal engagement of the political leadership should be stepped up. The decision taken in Colombo to host a summit every two years is welcome if implemented. But in the medium term, an annual summit should be the goal.
- BIMSTEC needs greater visibility. India’s turn to host the G20 leaders’ summit in 2023 presents a golden opportunity.
- Simplify the grouping’s name: The present name running into 12 words should be changed to four words only — the Bay of Bengal Community (BOBC). It will help the institution immensely.
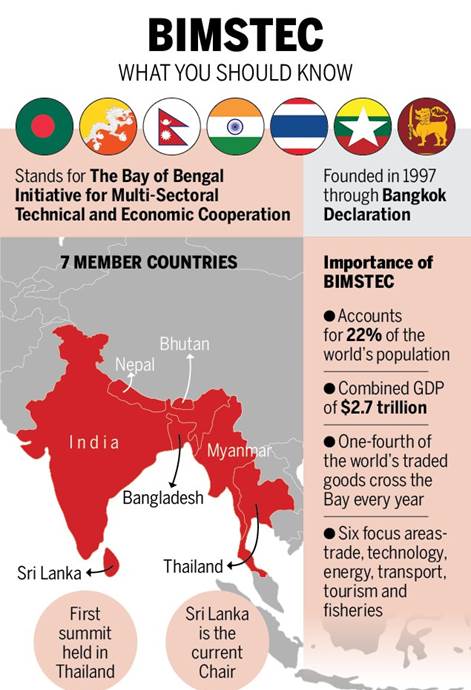
About BIMSTEC:
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is an international organisation of seven South Asian and Southeast Asian nations.
- The BIMSTEC provides a unique link between South and South-East Asia with 5 countries - Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal and Sri Lanka from South Asia and two countries - Myanmar and Thailandfrom South-East Asia coming together on one platform for cooperation in 14 key economic and social sectors of the economy.
- The BIMSTEC was founded in 1997with an ambition to pursue mutual trade, connectivity and cultural, technical and economic development in the region.
- It will celebrate its 25th anniversary this year.
- Initially, six sectors- trade, technology, energy, transport, tourism and fisheries were included for sectoral cooperation which was later expanded to 14 areas of cooperation.
- Agriculture is one of the 14 sectors.
- 22 per cent of the global population live in BIMSTEC countries, agriculture & allied activities are central to the economic and social development of the region.
- A BIMSTEC free trade agreement is under negotiation, also referred to as the mini SAARC.
- The BIMSTEC Free Trade Area Framework Agreement (BFTAFA) has been signed by all member nations to stimulate trade and investment in the parties, and attract outsiders to trade with and invest in the BIMSTEC countries at a higher level.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1833814
1.png)












