COMPREHENSIVE AND PROGRESSIVE AGREEMENT FOR TRANS-PACIFIC PARTNERSHIP
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
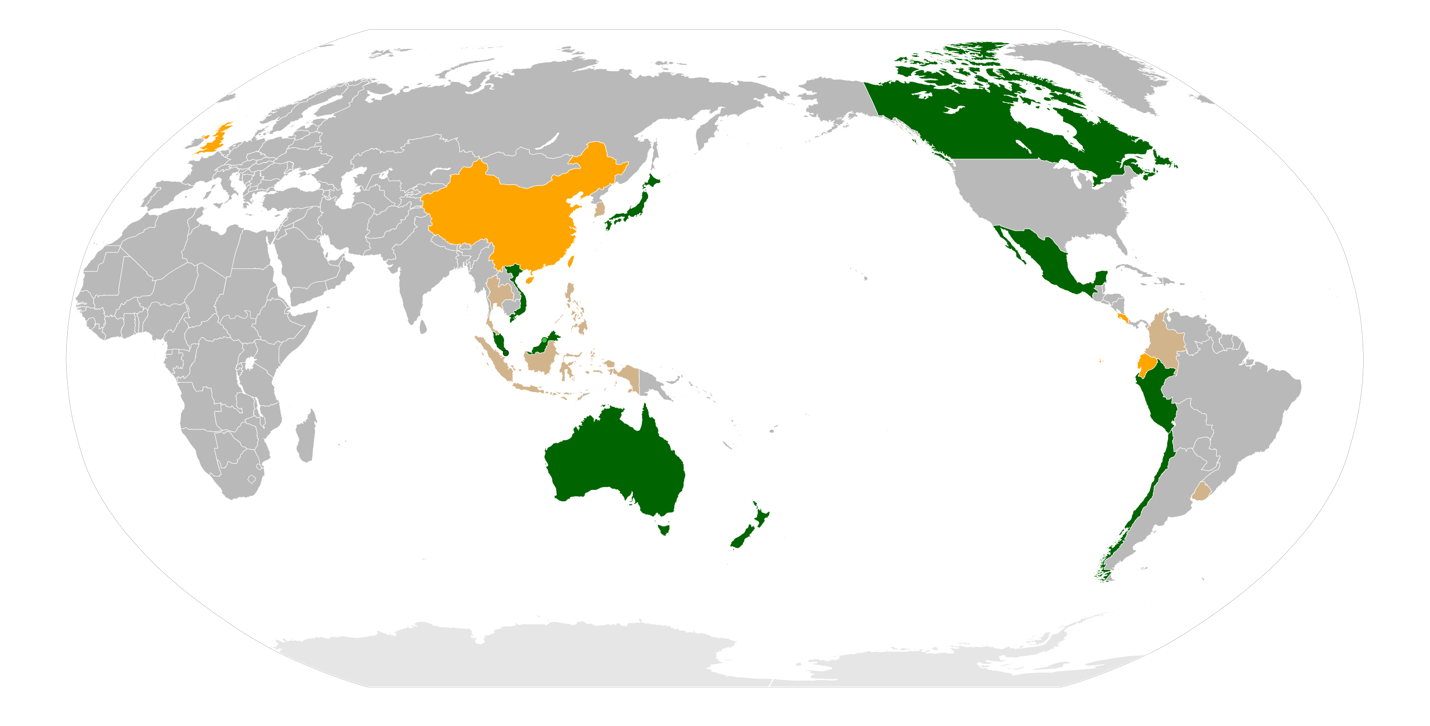
Context
- The K. acceded to the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), with Prime Minister Rishi Sunak describing the outcome as an example of “post-Brexit freedoms”.
- The agreement will now need to be ratified by Westminster and each of the CPTPP countries.
- The country will become the first new member, and the first in Europe, to join the agreement since it came into force in 2018.
Highlights of the deal
- The deal would mean that more than 99% of British exports — including for key markets such as cheese, cars, chocolate, machinery, gin and whisky — would have zero tariffs.
- The deal also aims to cut red tape for British businesses, which will no longer be required to set up local offices or be residents of the pact’s member countries to provide services there.
- It would add $2.2 billion annually to the U.K. economy in the long run.
- This, however, translates to a modest boost of 0.08% to GDP .
- The deal is a “gateway” to the Indo-Pacific region which would account for a majority (54%) of global economic growth in the future.
- It will also, as a CPTPP member, get a veto on whether China joins the treaty.
Criticism
- Joining the CPTPP is unlikely to be transformational for the UK economy. Britain already has trade deals in place with nine of the 11 current members.
- This deal translates to a modest boost of 0.08% to GDP .
- The agreement also won’t make up for the knock to GDP from leaving the European Union.
- The UK Office for Budget Responsibility expects Brexit to reduce Britain’s output by 4% over 15 years compared with remaining in the bloc.
About CPTPP
- The CPTPP, also known as TPP-11, is a free trade agreement with 11 members: Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, Peru, New Zealand, Singapore and Vietnam.
- The eleven signatories have combined economies representing 13.4 percent of global gross domestic product, at approximately US$13.5 trillion, making the CPTPP one of the world's largest free-trade areas by GDP, along with the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement, the European Single Market, and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
- It succeeded the Trans-Pacific Partnership after the United States withdrew under former President Donald Trump in 2017.
- The bloc is home to more 500 million people and will be worth 15% of global GDP once the United Kingdom joins.
- Beijing had applied to become a member of the bloc in September 2021.
- The CPTPP commission in 2023 is chaired by New Zealand.
Types Of Trade Agreements
- Trade agreements is an accord between two or more countries for a specific terms of trade, commerce, transit or investment.
- They mostly involve mutually beneficial concessions.
Preferential Trade Agreement
- In this type of agreement, two or more partners give preferential right of entry to certain products. This is done by reducing duties on an agreed number of tariff lines.
- Here a positive list is maintained i.e. the list of the products on which the two partners have agreed to provide preferential access.
- Tariff may even be reduced to zero for some products even in a PTA.
- India signed a PTA with Afghanistan.
Free Trade Agreement
- A free trade agreement is an agreement in which two or more countries agree to provide preferential trade terms, tariff concession etc. to the partner country.
- Here a negative list of products and services is maintained by the negotiating countries on which the terms of FTA are not applicable hence it is more comprehensive than preferential trade agreement.
- India has negotiated FTA with many countries e.g. Sri Lanka and various trading blocs as well e.g. ASEAN.
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement
- Partnership agreement or cooperation agreement are more comprehensive than an FTA.
- CECA/CEPA also looks into the regulatory aspect of trade and encompasses and agreement covering the regulatory issues. CECA has the widest coverage.
- CEPA covers negotiation on the trade in services and investment, and other areas of economic partnership. It may even consider negotiation on areas such as trade facilitation and customs cooperation, competition, and IPR.
- India has signed CEPAs with South Korea and Japan.
Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement
- CECA generally covers negotiation on trade tariff and TQR rates only.
- It is not as comprehensive as CEPA.
- India has signed CECA with Malaysia.
Framework agreement
- Framework agreement primarily defines the scope and provisions of orientation of the potential agreement between the trading partners.
- It provides for some new area of discussions and set the period for future liberalisation. India has previously signed framework agreements with the ASEAN, Japan etc.
Early Harvest Scheme
- An Early Harvest Scheme (EHS) is a precursor to an FTA/CECA/CEPA between two trading partners. For example early harvest scheme of RCEP has been rolled out.
- At this stage, the negotiating countries identify certain products for tariff liberalization pending the conclusion of actual FTA negotiations.
- An Early Harvest Scheme is thus a step towards enhanced engagement and confidence building.
Customs Union
- Member countries of a customs union remove trade barriers among themselves and adopt common external trade barriers.
Common Market
- A common market is a type of trading agreement wherein members remove internal trade barriers, adopt common policies when it comes to dealing with non-members, and allow members to move resources among themselves freely.
Economic Union
- An economic union is a trading agreement wherein members eliminate trade barriers among themselves, adopt common external barriers, allow free import and export of resources, adopt a set of economic policies, and use one currency.
Full Integration
- The full integration of member countries is the final level of trading agreements.
Must Read Articles:
Free Trade Agreement: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/free-trade-agreement-fta-36
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q) Joining the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership is unlikely to be transformational for the UK economy. Analyse. (250 words) |
https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/30794/OPS/G5OB2CNFU.1+GC9B2D5JQ.1.html







1.png)
