CPI

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
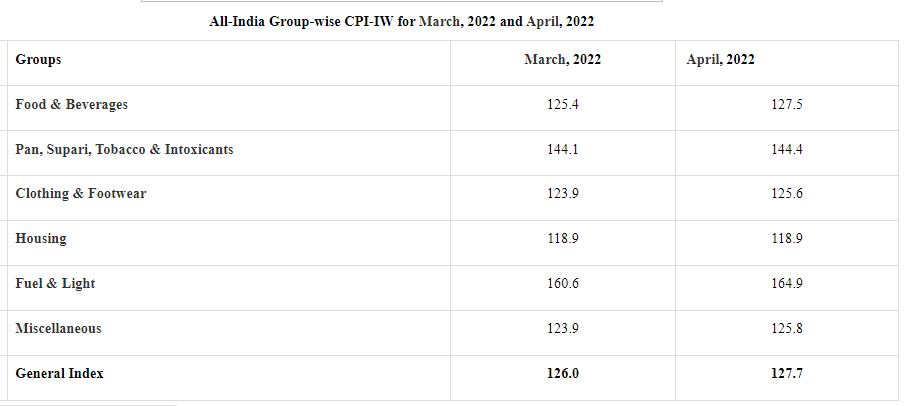
- The All-India CPI-IW for April, 2022 increased by 1.7 points and stood at 127.7 (one hundred twenty seven point seven).
- On 1-month percentage change, it increased by 1.35 per cent with respect to previous month compared to an increase of 0.42 per cent recorded between corresponding months a year ago.
BACKGROUND
What is Inflation?
- Inflation refers to a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
- It is the rise in the prices of most goods and services of daily or common use, such as food, clothing, housing, recreation, transport, consumer staples, etc.
- Inflation measures the average price change in a basket of commodities and services over time.
- The opposite and rare fall in the price index of this basket of items is called ‘deflation’.
- Inflation is indicative of the decrease in the purchasing power of a unit of a country’s currency. This is measured in percentage.
|
Purchasing power is the value of a currency expressed in terms of the number of goods or services that one unit of money can buy. All else being equal, inflation decreases the number of goods or services we would be able to purchase.
For example, if one had taken one unit of currency to a store in the 1950s, it would have been possible to buy a greater number of items than would be the case today, indicating that the currency had a greater purchasing power in the 1950s.
If one's monetary income stays the same, but the price level increases, the purchasing power of that income falls.
Note: Inflation does not always imply falling purchasing power of one's money income since income may rise faster than the price level. A higher real income means a higher purchasing power since real income refers to the income adjusted for inflation. |
Measures of Inflation in India
- In India, the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation measures inflation.
- There are two main set of inflation indices for measuring price level changes in India – the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and the Consumer Price Index (CPI). GDP deflator is also used to measure inflation.
Consumer Price Index
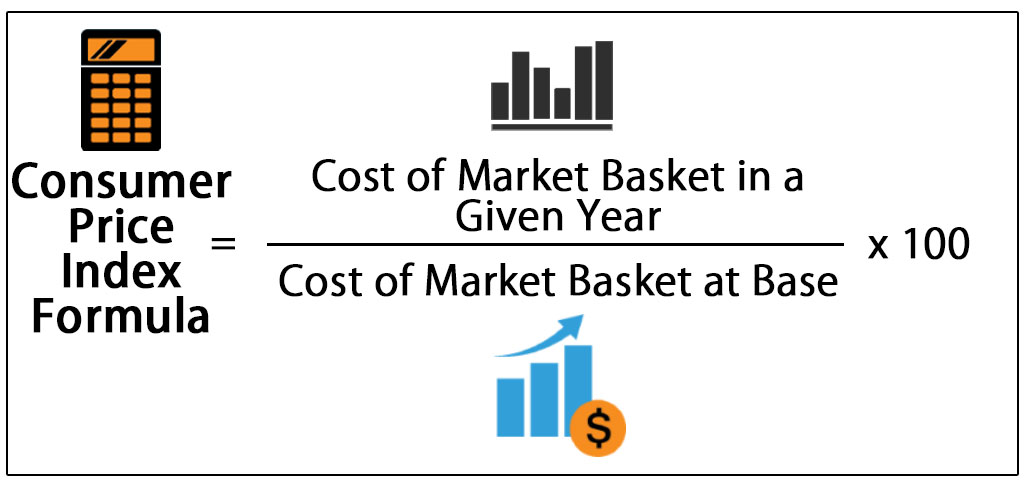
- Consumer Price Index or CPI is an index measuring retail inflation in the economy by collecting the change in prices of most common goods and services used by consumers.
- CPI is calculated for a fixed list of items including food, housing, apparel, transportation, electronics, medical care, education, etc. The price data is collected periodically, and thus, the CPI is used to calculate the inflation levels in an economy.
Who maintains Consumer Price Index in India?
- In India, there are four consumer price index numbers, which are calculated, and these are as follows:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW)
- CPI for Agricultural Labourers (AL)
- CPI for Rural Labourers (RL) and
- CPI for Urban Non-Manual Employees (UNME).
- While the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation collects CPI (UNME) data and compiles it, the remaining three are collected by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour.
WPI
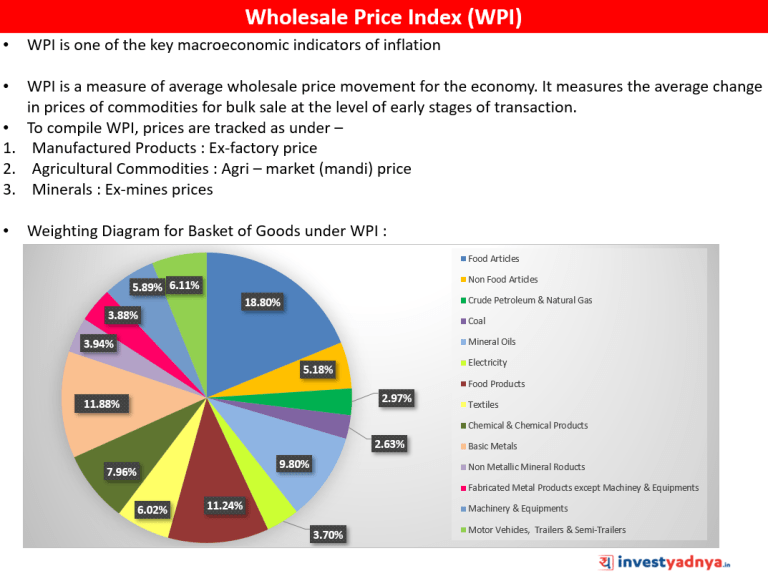
- Wholesale Price Index, or WPI, measures the changes in the prices of goods sold and traded in bulk by wholesale businesses to other businesses.
Who publishes WPI in India and what does it show?
- The numbers are released by the Economic Advisor in the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- An upward surge in the WPI indicates inflationary pressure in the economy and vice versa.
- The quantum of rise in the WPI month-after-month is used to measure the level of wholesale inflation in the economy. Base year: 2011-12. (In the calculation of an index the base year is the year with which the values from other years are compared).
Must Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/inflation-29



1.png)
