DAILY NEWS ANALYSIS 02 MARCH
ENVIRONMENT
Eurasian otter found in Chilika Lake
Researchers conducting a study in Odisha’s Chilika Lake have found the presence of a viable, breeding population of a fishing cat in the brackish water lagoon.
About Otter:
- Otters are members of the mammalian family called Mustelidae.
- They are shy and have elusive habits, adapting to a variety of habitats ranging from marine to freshwater environments.
- Otters are found the world over, except in Australia, New Zealand, Madagascar, and other oceanic islands.
- India is home to 3 of the 13 species of otters found worldwide. These are - Eurasian Otter (Lutralutra); Smooth-coated Otter (Lutraperspicillata) and Small-clawed otter (Aonyxcinereus).
- Smooth coated otter (Lutrogaleperspicillata) has been moved from CITES Appendix II to CITES Appendix I.
- Eurasian otter and Smooth coated otter are endangered species.
Threats to Otter:
- Degradation and persecution associated with conflict with people (and fisheries).
- Habitat loss
- Poaching
- Illegal trade for use as pets and for the animals’ fur
- Use in traditional medicine.
Chilka Lake:
- Chilika Lake is the largest internal saltwater lake in Asia, it is a paradise on earth for bird watchers and nature lovers.
- The pear shaped lake is dotted with a few small islands and has fisheries and salt pans around its shore.
- Located at the mouth of the Daya River, Chilika Lake is the largest coastal lagoon in India and also the second largest saltwater lagoon in the world.
- It is the largest wintering ground for migratory birds on the Indian sub continent.
- Birds from the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea and other remote parts of Russia, Kirghiz steppes of Mongolia, Central and Southeast Asia, Ladakh and Himalayas come here.
India is host to 457 migratory fauna, shows latest CMS list
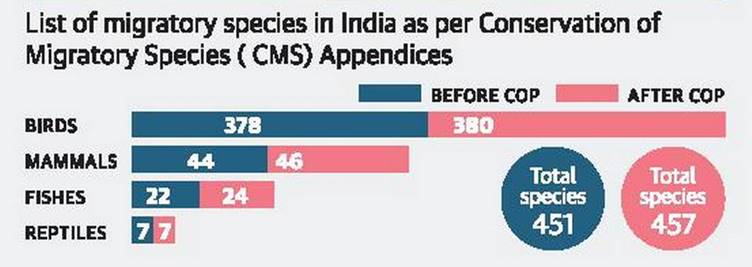
Migratory bird list under CMS:
- The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) had for the first time compiled the list of migratory species of India under the CMS.
- Six species: the Asian elephant, great Indian bustard, Bengal florican, oceanic white-tip shark, urial and smooth hammerhead shark are added to already existing 451.
- Globally, more than 650 species are listed under the CMS appendices.
- Birds make up the bulk of migratory species.
- The next highest group of migratory birds is raptors or birds of prey, such as eagles, owls, vultures and kites which are from the family Accipitridae.
- Country has three flyways (flight paths used by birds): the Central Asian flyway, East Asian flyway and East Asian–Australasian flyway.
- Dolphins are the second highest group of mammals with nine migratory species of dolphins listed.
- Seven reptiles, which include five species of turtles and the Indian gharial and salt water crocodile, are among the CMS species found in India.
Convention on Migratory Species (CMS):
- The CMS is an environmental treaty of the UN that provides a global platform for the conservation and sustainable use of migratory animals and their habitats.
- It is the only global convention specialising in the conservation of migratory species, their habitats and migration routes.
- The pact was signed in 1979 in Germany and also known as the Bonn Convention.
- CMS brings together the States through which migratory animals pass, the Range States, and lays the legal foundation for internationally coordinated conservation measures throughout a migratory range.
About Zoological survey of India:
- The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) was established on 1st July, 1916.
- The survey has its genesis in the establishment of the Zoological Section of the Indian Museum at Calcutta in 1875.
- It comes under Government of India Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- The history of ZSI begins from the days of the Asiatic Society of Bengal founded by Sir William Jones on 15 January 1784.
- The Asiatic Society of Bengal was the mother institution not only to the Indian Museum (1875) but also to the institutions like the Zoological Survey of India and the Geological Survey of India.
Shelve proposed road through tiger reserve: Maharashtra MLA writes to Arunachal CM
A Maharashtra legislator has appealed to the Arunachal Pradesh government not to pursue a proposed highway through Pakke tiger reserve.
About Pakke Tiger Reserve:
- Pakke Tiger Reserve, also known as Pakhui Tiger Reserve, is a Project Tiger reserve in the East Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India.
- The 862-sq km Pakke Reserve is home for many rare and endangered wildlife species, such as leopard, wild dog, Himalayan black bear and elephant.
- Contiguous with the Nameri Tiger Reserve of Assam, it is also an important habitat for the big cat’s big cats, one of the most endangered species in the world.
- Pakke is also the only Hornbill sanctuary in India.
- The forest around this reserve harbours four hornbills species - great hornbills, wreathed, oriental pied and the rufous-necked.
- The Pakke River lies to the east and the Bhareli River to the west and the north.
Water crisis looms large in Himalayan regions, finds study
Finding of the report:
- Eight towns in the Himalayan region of Bangladesh, Nepal, India and Pakistan were nearly 20%-70% deficient in their water supply.
- Unplanned urbanisation and climate change are the key factors responsible for the state of affairs.
- Communities were coping through short-term strategies such as groundwater extraction, which is unsustainable.
- Over 50% of the population will be living in cities by 2050, placing “tremendous stress” on water availability.
Causes behind deficiency in water supply:
- The encroachment and degradation of natural water bodies (springs, ponds, lakes, canals, and rivers)
- The growing disappearance of traditional water systems (stone spouts, wells, and local water tanks)
- Rural areas have typically garnered much of the attention in terms of development and issues surrounding urban environments have been “sidelined”
Way Forward:
- A holistic water management approach that includes spring shed management and planned adaptation is therefore paramount.
A lioness takes care of a leopard cub in Gir national park
A lioness in Gujarat’s Gir National Park mothered a leopard cub for more than a month.
About Gir National park:
- Outside of Africa, it is the only place with wild lions.
- It lies in state of Gujarat.
- The local Maldhari community has lived here for generations and coexists magnificently with the wilderness.
- The Government notified the large geographical extent of Sasan Gir as wildlife sanctuary on 18th September, 1965 in order to conserve the Asiatic Lion.
SOCIETY
‘No online supply of food from FBOs without hygiene rating’
The Punjab government’s Food and Drug Administration has prohibited online supply of food from Food Business Operators (FBOs) not possessing hygiene rating.
Government argument:
- Although, it is the moral responsibility of FBOs and OFSAs to ensure quality and hygiene of food delivered.
- The duty is also cast upon the State authorities to ensure safe food to public under the Section 18(1) (a) of food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- FSSAI has empanelled various agencies to conduct the hygiene rating of the FBOs.
FSSAI:
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is an autonomous body established under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India.
- The FSSAI has been established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006; which is a consolidating statute related to food safety and regulation in India.
- FSSAI is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the regulation and supervision of food safety.
- The main aim of FSSAI is:
- To lay down science-based standards for articles of food
- To regulate manufacture, storage, distribution, import and sale of food
- To facilitate safety of food
About Food Safety and Standards act, 2006:
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India is a statutory body under Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- The Food Safety and Standards Act (FSS), 2006 is the primary law for regulation of food products.
- This act also sets up the formulation and enforcement of food safety standards in India. The FSSAI appoints food safety authorities on the state level.
POLITY
List of monuments under ASI likely to be reviewed
Government reply:
- The number of monuments under the Centre’s protection could increase as the government is planning a review of those under the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and the ones protected by the State governments.
- At present, 3,691 monuments nationwide are protected by the ASI, with the highest number, 745 in Uttar Pradesh.
- The list of the centrally protected monuments had not seen a substantial increase in many years and important sites under the State governments could be added to the list.
- There were some sites that could be moved from the Central list allowing development works in their vicinity.
- ASI protects site under Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958.
About ASI:
- The Archaeological Survey of India is an Indian government agency attached to the Ministry of Culture that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural monuments in the country.
- It was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham who also became its first Director-General.
Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act (or AMASR Act):
- The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act (or AMASR Act) is an act of parliament of the government of India that provides for the preservation of ancient and historical monuments and archaeological sites and remains of national importance.
- It provides for the regulation of archaeological excavations and for the protection of sculptures, carvings and other like objects.
- The rules stipulate that area in the vicinity of the monument, within 100 metres is prohibited area.
- The area within 200 meters of the monument is regulated category. Any repair or modifications of buildings in this area requires prior permission.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
Explained: Reading US-Taliban pact
The US and Taliban signed an agreement for “Bringing Peace to Afghanistan”, which will enable the US and NATO to withdraw troops in the next 14 months.

Key elements of the Pact:
TROOPS WITHDRAWAL:
- The US will draw down to 8,600 troops in 135 days and the NATO or coalition troop numbers will also be brought down, proportionately and simultaneously.
- All troops will be out within 14 months.
TALIBAN COMMITMENT:
- Taliban will not allow any of its members, other individuals or groups, including al-Qaeda, to use the soil of Afghanistan to threaten the security of the United States and its allies.
- The pact is silent on other terrorist groups — such as anti-India groups Lashkar-e-Toiba or Jaish-e-Mohammed.
SANCTIONS REMOVAL:
- UN sanctions on Taliban leaders to be removed by three months (by May 29) and US sanctions by August 27.
PRISONER RELEASE:
- The joint declaration says the US will facilitate “discussion with Taliban representatives on confidence building measures, to include determining the feasibility of releasing significant numbers of prisoners on both sides”.
- The US-Taliban pact says up to 5,000 imprisoned Taliban and up to 1,000 prisoners from “the other side” held by Taliban “will be released” by March 10.
CEASEFIRE:
- The agreement states ceasefire will be simply “an item on the agenda” when intra-Afghan talks start.
Challenges:
- The Afghan government has been completely sidelined during the talks between the US and Taliban.
- The future for the people of Afghanistan is uncertain, and will depend on how Taliban honours its commitments and whether it goes back to the mediaeval practices of its 1996-2001 regime.
- Much will depend on whether the US and the Taliban are able to keep their ends of the bargain, and every step forward will be negotiated.
- Taliban cannot deliver on the assurances it has given, and yet the U.S. has handed over Afghanistan to them. There is no reference to the Constitution, rule of law, democracy and elections.
- It is unclear whether India, which is not a U.S. ally, is included in definition of protection of allies, and whether Pakistan-backed groups that threaten India, would still operate in Afghanistan.
- The U.S. has committed to taking Taliban leaders off the UN Security Council’s sanctions list by May 29, 2020, which could considerably bring down the number of terrorists Pakistan is accused of harbouring, according to the FATF grey list conditions.
- The Ghani government, which India has recognised as winner of the 2019 election, may only serve for an interim period.
India and Taliban:
- Mullah Baradar did not name India among the countries that supported the peace process, but specially thanked Pakistan for the “support, work and assistance” provided.
- India nurses bitter memories from the IC-814 hijack in 1999, when it had to release terrorists — including Maulana Masood Azhar who founded Jaish-e-Mohammed that went on to carry out terror attacks on Parliament (2001), in Pathankot (2016) and in Pulwama (2019).
- India never gave diplomatic and official recognition to the Taliban when it was in power during 1996-2001.
- India’s foreign policy establishment has shied away from engaging with the Taliban directly.
- Many Indian diplomats say although there has not been formal contact with top Taliban leaders, the Indian mission has a fair amount of access to the Pashtun community throughout Afghanistan through community development projects of about $3 billion.



1.png)
