DAILY NEWS ANALYSIS 04 DECEMBER
SECURITY
DRDO to develop naval fighter jet
The Defence Research Development Organisation (DRDO) has offered to develop a new twin-engine deck-based fighter aircraft for the Navy based on the experience of the naval light combat aircraft (LCA).
The Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) programme, began in the 1980s to replace India's ageing MiG-21 fighters. In 2003, the LCA was officially named "Tejas".
Tejas:
- It is an Indian single-engine, delta wing, multirole light fighter designed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force and Indian Navy.
- It is an indigenous light-weight, multi role supersonic aircraft developed in both fighter and trainer versions. Advanced materials like composites are used in the manufacture of the Tejas to reduce weight and increase the component life.
- It is designed to carry a veritable plethora of air-to-air, air-to- surface, precision guided and standoff weaponry.
ECONOMY
GST revenues not enough for States’ compensation: Centre
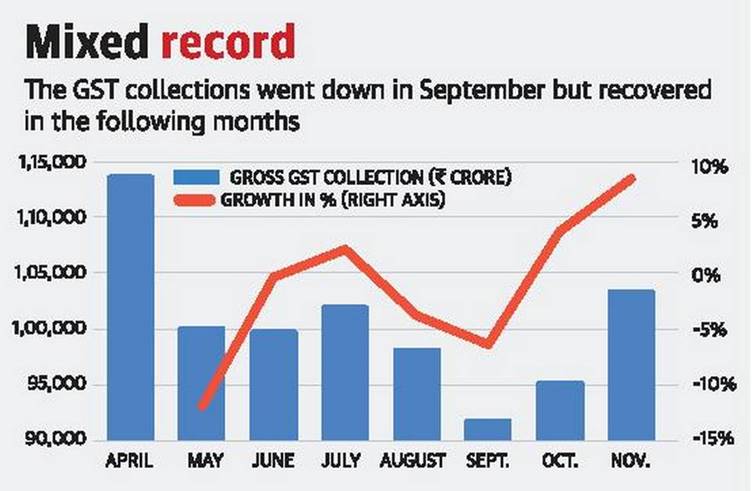
The Centre has written to all States voicing concern that due to the lower Goods and Services Tax (GST) collections, the compensation cess might not be enough to pay for losses arising out of the tax system.
Reasons behind decline of GST:
- Continuous rationalization of taxes.
- Non-incorporation of invoice matching while filing of GST. It has allowed higher return.
- GST non-compliance is on rise. People not filling their GST returns are increasing.
- Businesses are generating fake invoices to claim higher input tax credits than they should be receiving.
- Business slowdown is causing decline in GST receipt.
- Overall slowdown in economy has further affected the GST revenue.
About GST:
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax (or consumption tax) imposed in India on the supply of goods and services. It is a comprehensive multistage, destination-based tax; comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all the indirect taxes. Goods and services are divided into five different tax slabs for collection of tax - 0%, 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%.
Taxes Subsumed under it:
- Central excise duty
- Services tax
- Additional customs duty
- Surcharges
- State-level value added tax
- Octroi
Petroleum products, alcoholic drinks, and electricity are not taxed under GST and instead are taxed separately by the individual state governments.
POLITY
51 left India, defrauding over Rs. 17,900 crore
The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has informed the Finance Ministry that 51 absconders and proclaimed offenders in 66 cases, who face allegations of fraud involving over Rs. 17,900 crore, have left for other countries.
Actions by Government:
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) had filed applications in court against 10 individuals under the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act.
- The CBIC sent two extradition requests to the External Affairs Ministry.
- The Interpol had issued Red Notices for the extradition of eight individuals.
- Government has advised Public Sector Banks to obtain certified copy of the passport of promoters/directors and other authorised signatories of companies availing of loan facilities of more than Rs.50 crore.
Sena may push 80% job quota Bill as early as winter session
The Shiv Sena wants to push a law to reserve 80% of jobs in the State for local residents in the winter session of the Assembly.
Other states to bring such law:
- Andhra Pradesh became the first State to pass a legislation for a 75% quota for locals in private, industrial jobs.
- Madhya Pradesh government is mulling for a law for 70% reservation in jobs for local youth in private and government sectors.
Effects:
- It will create job opportunities for local talents.
- It will develop industry linkages with the Skill India mission thus enabling more skilled manpower.
- It will create a healthy competition between states for industrialisation and lead to an inclusive growth.
- Providing jobs in lieu of the land is the most basic a company can do.
- It will ensure that wages of unorganized sectors do not go down because of the migration of labour from other states.
Negatives:
- It will increase the cost of compliance for a company. Bigger corporates may shy away from investment in such state.
- One Nation, One market was the theme of GST. Such reservations may distort the theme by creating artificial barriers.
- It may be unconstitutional in nature. Constitution provides for equality in employment and state can provide reservation for SC, ST, women and social & educationally backward caste. Local residential conditions are prescribed by Parliament only.
- It is populist in nature and will create unhealthy competition among states. Such competition will only create artificial barriers for migration eventually curtailing the cultural mixing.
- Definition of locals has not been specified.
- In the era of Ease of doing business, such legislations are unnecessary intervention by the government in economy.
Way Forward:
- Maharashtra must focus on skilling of its youth by imparting them knowledge of new technologies.
- It should focus on reducing cost of doing business thus attracting the businesses to invest in Maharashtra. More investment will lead to better employment opportunities for the locals.
- It should call high net worth individuals hailing from the state to invest in the state.
Lok Sabha passes Bill to merge 2 Union Territories
A Bill to merge the Union Territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu into one UT has been passed by the Parliament.
Needs and Benefits:
- Both the Union Territories have separate budgets and different secretariats even though they are just 35 km apart.
- The merger of the two UTs, located along the western coast near Gujarat, will be done for better administration and check duplications of various works.
- The country currently has nine Union Territories after the creation of the UTs of Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh. After the merger, number of UT (Union territories) will come down to 8.
ENVIRONMENT
India tests Swedish technology to reduce stubble burning
Pollution from stubble burning in winter is the key contributor to the sharp decline in air quality in Delhi. However, stubble burning continues unabated.
Technological intervention:
- India is testing a Swedish technology “torrefaction” that can convert rice stubble into ‘bio-coal’.
- The Office of the Principal Scientific Advisor (PSA) to Government of India has funded a pilot project in Punjab to evaluate the feasibility of the technology.
Working of Torrefaction:
- Torrefaction is a thermal process to convert biomass into a coal-like material, which has better fuel characteristics than the original biomass.
- The technology involves heating up straw, grass; sawmill residue and wood biomass to 250 degrees Celsius – 350 degrees Celsius.
- This changes the elements of the biomass into ‘coal-like’ pellets. These pellets can be used for combustion along with coal for industrial applications like steel and cement production.
SOCIETY
Setting the clock back on intersex human rights
The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2019, has led to a few protests across the country for failing to address the concerns of the LGBTQ community.
Provisions of the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2019:
- The Bill prohibits the discrimination against a transgender person, including denial of service or unfair treatment in relation to education, employment, healthcare, access to, or enjoyment of goods, facilities, opportunities available to the public, right to movement, right to reside, rent, or otherwise occupy property, opportunity to hold public or private office, and access to a government or private establishment.
- The Bill also seeks to provide rights of health facilities to transgender persons including separate HIV surveillance centres, and sex reassignment surgeries.
- Provision of certificate of identity for a transgender person by making application to the District Magistrate for a certificate of identity, indicating the gender as ‘transgender’.
- It also calls for establishing a National Council for Transgender persons (NCT).
- Offences against transgender persons will attract imprisonment between six months and two years, in addition to a fine.
Concern with the bill:
- The Transgender Persons Bill does not distinguish between transgender and intersex persons.
- Transgender have a different gender identity than what was assigned to them at birth, while intersex indicates the diversity of gender-based on biological characteristics at birth.
- The title of the Bill itself is exclusionary, as it does not accommodate all persons whose legal protection it seeks to recognize.
- As per court-based jurisprudence, medical procedures are not a necessity for self-identification. There should be the right to self-identification without the need for medical intervention.
- The Bill does not make provision for affirmative action in employment or education despite the Supreme Court’s mandate in NALSA v. UOI case.
- The Bill sets out lighter sentences for several criminal offences, such as “sexual abuse" and “physical abuse".
- It also fails to address the lack of an effective mechanism to enforce the legal prohibition against discrimination on the ground of gender identity.



1.png)
