DAILY NEWS ANALYSIS 08 JULY
320 elephants ‘leased’ by Assam have not returned
News important for: GS paper 3 I Biodiversity and issues arising out of it
Context
A concern has been raised by Assam Government and state Wildlife Crime Prevention Unit about illegal trading of elephants.

Analysis
- The Wildlife Crime Prevention Unit (WPCU) stated that corrective steps have to be taken to stop illegal trade and bring elephants back to the state.
- There is urgent requirement of Captive Elephants (Management and Maintenance) Rules to protect the species.
- This is a violation of Wildlife (Protection Act) 1972.
Conservation of Elephants
- In India there are around 30,000 elephants spread across the nation in 16 states.
- Kerala has maximum number of elephants followed by Karnataka and Assam.
- There are 28 elephants reserves notified by various state governments so far.
- Assam has maximum number of elephant reserves followed by Odisha.
- There are around 183 elephant corridors in India with maximum in Meghalaya.
|
Project Elephant-1992
The project was started with a vision to protect elephants.
It had 3 key objectives:
|
Source link:
Indo-Afghan trade chokes on U.S. curbs
News important for: GS paper 2 I International Relations
Context
Union Budget 2019-20 has cut short the finance of Cahaba port this year from 150 crore to 45 crore.
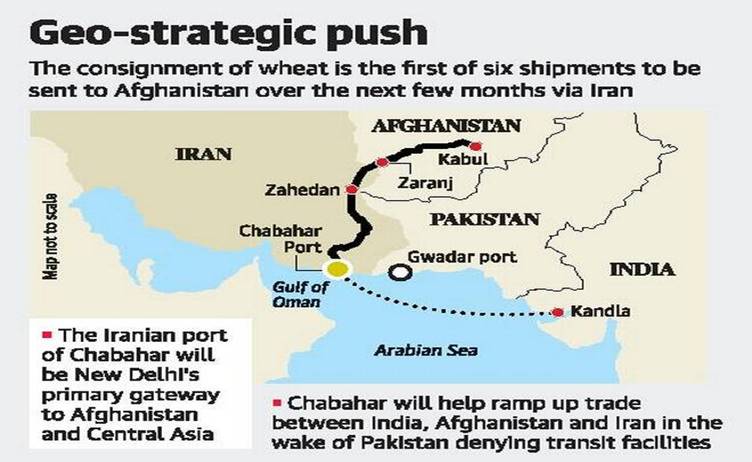
Analysis
- The step comes as another blow to Indo-Afghan trade.
- The move is ahead of U.S. sanctions on Iran and U.S. - Iran conflict.
- Chabahar had flourished for transportation of goods and commodities to Afghanistan and central Asia with the volume of loading and unloading twice as much as before.
- The air operations are already suspended to Afghanistan after Pakistan imposed its airspace curb in the wake of Balakot air strike.
- As a result of the ban, Afghan fruit and agricultural products that had made up the bulk of the cargo on flights between Kabul and Delhi are being shipped to other international markets.
- The steps may bring the trade between both the countries to a standstill.
Source link:
Defence allocation disappoints military
News important for: GS paper 3 I Defence budget
Context
The defence forces of the country are unsatisfied over the budget allocation in union budget 2019-20 to defence.
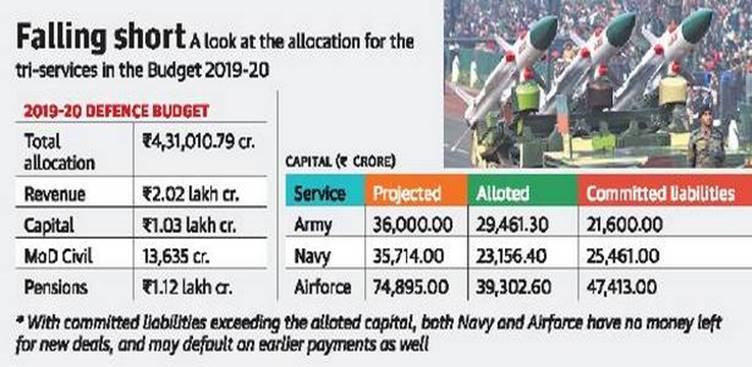
Analysis
· The navy and air force is short of money to finance new deals for technology improvement.
· The Navy has major deals lined up and they are in advanced stages.
· A deal for 24 MH-60R Multi-Role Helicopters from the U.S. valued at $2.6 billion is expected to be concluded by year-end.
· A proposal for 10 more P-8I long range maritime patrol aircraft estimated to cost over $3 billion is waiting for clearance from the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC).
· Navy and Air Force have no money left for new deals, and may default on earlier payments as well.
· The army is short of revenue as well and its major part goes to providing salaries.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/defence-allocation-disappoints-military/article28313288.ece
Researchers fault Survey finding on UID-MGNREGS link
News important for: GS paper 2 I Union and state and their responsibilities, Government schemes
Context
Researchers studying UID-MGNREGS have raised concerns over economic survey’s positive causal impact of Aadhar linked payments.
Analysis
· The economic Survey 2019-20 has used the rural jobs scheme as a case study to show the benefits of the use of technology in improving efficiency in welfare schemes for the most vulnerable groups.
· The percentage of wage payments generated within 15 days improved from 27% in 2014-15 to more than 90% by 2018-19.
· The Survey credited this to the introduction of ALP in 2015-16.
However the researchers have denied the claims and figures:
· According to the researchers the payment is done in two stages:
· One where the State verifies the work done and generates a fund transfer order
· The other where money is actually credited into the worker’s bank account.
· There has been an improvement in stage 1 and not in stage 2 of the payment.
· Another conflict is regarding the performance of MGNREGA in drought affected areas.
· Survey claims that performance was parallel before and after the introduction of Aadhar.
· Researchers claim that this has not been proven yet and survey has presented only favourable data to prove its point.
Source link:
Crimes that India’s statute books have failed to define
News important for: GS paper 1 I population and associated issues, Society
Context
Indian constitution does not hold any specific law for mass crime, genocide and crime against humanity (CAH).
Analysis
· Crime against Humanity is internationally dealt by the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court.
· They are defined as offences such as murder, extermination, enslavement, deportation, torture, imprisonment and rape committed as a part of “widespread or systematic attack directed against any civilian population, with knowledge of the attack”.
· India is not a party of Rome Statue and thus there is no obligation on it to enact a separate legislation for CAH.
· India has ratified Genocide convention, 1948 but it has not been tough into domestic legislation.
· The probable reasons India has objected on the Rome Statute are three:
· Using ‘widespread or systematic’ as one of the conditions, preferring ‘widespread and systematic’, which would require a higher threshold of proof.
· Non-distinction between international and internal armed conflicts. This was probably because its internal conflicts with naxals and other non-state actors in places like Kashmir and the Northeast could fall under the scope of CAH
· Inclusion of enforced disappearance of persons under CAH. It is pertinent here that India has signed but not yet ratified the UN International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearances as it would put the country under an obligation to criminalise it through domestic legislation.
Several patterns of mass killings has been witnessed in the country as in Mumbai in 1993, in Gujarat in 2002, in Kandhamal, Odisha in 2008, and Muzaffarnagar in Uttar Pradesh in 2013, anti sikh riot of 1984 in Delhi.
India needs to reflect upon its domestic criminal justice system to take a stand on mass killings and CAH.
Source link:
Talaq Bill in a cliff-hanger in Rajya Sabha
News important for: GS paper 2 I Union and state and their responsibilities.
Context
Triple talaq bill passed by the lok sabha is still to be cleared by the upper house.

Analysis
· Few alliance parties have concerns over the criminality clause of the bill.
· The bill does not have a majority support yet is conflicted.
Provisions of Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Marriage) Bill 2019:
· The Bill makes all declaration of talaq, including in written or electronic form, to be void (i.e. not enforceable in law) and illegal.
· The Bill makes declaration of talaq a cognizable offence, attracting up to three years’ imprisonment with a fine.
· The offence will be cognizable only if information relating to the offence is given by: (i) the married woman (against whom talaq has been declared), or (ii) any person related to her by blood or marriage.
· The Bill provides that the Magistrate may grant bail to the accused. The bail may be granted only after hearing the woman (against whom talaq has been pronounced), and if the Magistrate is satisfied that there are reasonable grounds for granting bail.
· The offence may be compounded by the Magistrate upon the request of the woman.
· A Muslim woman, against whom talaq has been declared, is entitled to seek subsistence allowance from her husband for herself and for her dependent children.
· A Muslim woman, against whom such talaq has been declared, is entitled to seek custody of her minor children.
Source link:
Analysis
· The navy and air force is short of money to finance new deals for technology improvement.
· The Navy has major deals lined up and they are in advanced stages.
· A deal for 24 MH-60R Multi-Role Helicopters from the U.S. valued at $2.6 billion is expected to be concluded by year-end.
· A proposal for 10 more P-8I long range maritime patrol aircraft estimated to cost over $3 billion is waiting for clearance from the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC).
· Navy and Air Force have no money left for new deals, and may default on earlier payments as well.
· The army is short of revenue as well and its major part goes to providing salaries.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/defence-allocation-disappoints-military/article28313288.ece
Researchers fault Survey finding on UID-MGNREGS link
News important for: GS paper 2 I Union and state and their responsibilities, Government schemes
Context
Researchers studying UID-MGNREGS have raised concerns over economic survey’s positive causal impact of Aadhar linked payments.
Analysis
· The economic Survey 2019-20 has used the rural jobs scheme as a case study to show the benefits of the use of technology in improving efficiency in welfare schemes for the most vulnerable groups.
· The percentage of wage payments generated within 15 days improved from 27% in 2014-15 to more than 90% by 2018-19.
· The Survey credited this to the introduction of ALP in 2015-16.
However the researchers have denied the claims and figures:
· According to the researchers the payment is done in two stages:
· One where the State verifies the work done and generates a fund transfer order
· The other where money is actually credited into the worker’s bank account.
· There has been an improvement in stage 1 and not in stage 2 of the payment.
· Another conflict is regarding the performance of MGNREGA in drought affected areas.
· Survey claims that performance was parallel before and after the introduction of Aadhar.
· Researchers claim that this has not been proven yet and survey has presented only favourable data to prove its point.
Source link:
Crimes that India’s statute books have failed to define
News important for: GS paper 1 I population and associated issues, Society
Context
Indian constitution does not hold any specific law for mass crime, genocide and crime against humanity (CAH).
Analysis
· Crime against Humanity is internationally dealt by the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court.
· They are defined as offences such as murder, extermination, enslavement, deportation, torture, imprisonment and rape committed as a part of “widespread or systematic attack directed against any civilian population, with knowledge of the attack”.
· India is not a party of Rome Statue and thus there is no obligation on it to enact a separate legislation for CAH.
· India has ratified Genocide convention, 1948 but it has not been tough into domestic legislation.
· The probable reasons India has objected on the Rome Statute are three:
· Using ‘widespread or systematic’ as one of the conditions, preferring ‘widespread and systematic’, which would require a higher threshold of proof.
· Non-distinction between international and internal armed conflicts. This was probably because its internal conflicts with naxals and other non-state actors in places like Kashmir and the Northeast could fall under the scope of CAH
· Inclusion of enforced disappearance of persons under CAH. It is pertinent here that India has signed but not yet ratified the UN International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearances as it would put the country under an obligation to criminalise it through domestic legislation.
Several patterns of mass killings has been witnessed in the country as in Mumbai in 1993, in Gujarat in 2002, in Kandhamal, Odisha in 2008, and Muzaffarnagar in Uttar Pradesh in 2013, anti sikh riot of 1984 in Delhi.
India needs to reflect upon its domestic criminal justice system to take a stand on mass killings and CAH.
Source link:
Talaq Bill in a cliff-hanger in Rajya Sabha
News important for: GS paper 2 I Union and state and their responsibilities.
Context
Triple talaq bill passed by the lok sabha is still to be cleared by the upper house


1.png)
