DAILY NEWS ANALYSIS 11 APRIL
HEALTH
1. Coronavirus lockdown: PM Modi holds meeting with CMs; lockdown extension focus of discussion
-A countrywide shortage of medicines and medical devices is likely in the coming weeks, the Department of Pharmaceuticals has warned the Home Ministry, urging it to take immediate steps to help drug makers resume production under the current lockdown.
-Underlining that half of India’s output of pharmaceuticals is exported as global markets offer better prices, the Department of Pharmaceuticals stressed that this could lead to disproportionate shortages in the domestic market, calling for suitable measures to be taken “in the right earnest” to prevent this “avoidable” situation.
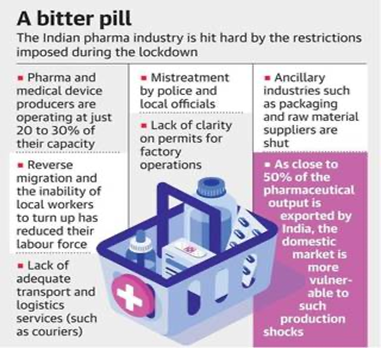
-Production units engaged in making essential commodities, including medicines, vaccines, masks and their ancillaries had been exempted from the restrictions imposed as per the three-week national lockdown announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on March 24.
-Apart from directives from the Home Ministry and the Pharma Department to State governments on the issue, the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) had also written to all State Chief Secretaries on March 26 after it learnt problems that pharma firms are facing.
About National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA): It is a government regulatory agency that controls the prices of pharmaceutical drugs in India. It was constituted vide Government of India Resolution dated 29th August, 1997 as an attached office of the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers as an independent Regulator for pricing of drugs and to ensure availability and accessibility of medicines at affordable prices.
Functions of NPPA:
-To implement and enforce the provisions of the Drugs (Prices Control) Order in accordance with the powers delegated to it.
-To deal with all legal matters arising out of the decisions of the Authority.
-To monitor the availability of drugs, identify shortages, if any, and to take remedial steps.
-To collect/ maintain data on production, exports and imports, market share of individual companies, profitability of companies etc, for bulk drugs and formulations.
-To undertake and/ or sponsor relevant studies in respect of pricing of drugs/ pharmaceuticals.
-To recruit/ appoint the officers and other staff members of the Authority, as per rules and procedures laid down by the Government.
-To render advice to the Central Government on changes/ revisions in the drug policy.
-To render assistance to the Central Government in the parliamentary matters relating to the drug pricing.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/coronavirus-lockdown-scarcity-of-drugs-devices-imminent-government-warned/article31313501.ece
2. Red army keeps virus at bay in northeast
-A ‘red army’ of wise old men and women are helping villages across some hill States in the northeast keep the novel coronavirus away.
-Though a majority of those felled by the COVID-19 pandemic are aged 60 years or more, this hasn’t stopped the gaon buras (male villager elder) and gaon buris (female village elder) — usually referred to as GBs — from following their predecessors in forming a shield between the villages and the enemy — in this case, the virus.
-The village elders across the States are distinguished by their red coats provided by the government, which also pays them a stipend of ₹1,500 per month.
-The Assam Frontier (Administration of Justice) Regulation of 1945, under which GBs are appointed, prescribes the 35-60 age slab.
-However, majority of Arunachal Pradesh’s estimated 9,500 GBs are 60 or more.
-A head gaon bura, who supervises five GBs, is usually older.
-Assisting the GBs in Nagaland are the dobashi, the custodians of Naga customary laws who also wear red coats.
-They have been salaried government employees since 1842 when the British appointed the first dobashis for interpreting Naga dialects into Assamese or Hindi.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/coronavirus-red-army-keeps-virus-at-bay-in-northeast/article31313582.ece
3. Virus halts J&K’s ‘Durbar move’ for the first time in 144 years
-For the first time in 144 years, the J&K administration has decided to halt the annual shifting of the capital, called ‘Durbar move’, from Jammu to Srinagar in J&K due to the ongoing COVID-19 crisis, as 23 fresh positive cases pushed the total in the Union Territory to 207.
About Durbar Move: Introduced by Dogra monarch Maharaja Gulab Singh in 1872, the ‘Durbar move’ would see shifting of the Civil Secretariat in summers from Jammu to Srinagar and in winters from Srinagar to Jammu.
—In January 1987, the then Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi had asked then Chief Minister Farooq Abdullah to stop the practice.
—However, the ‘Durbar move’ was continued to allow it to at as a bridge between two diverse cultures of the Kashmir Valley and the Jammu region.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/virus-halts-jks-durbar-move-for-the-first-time-in-144-years/article31313003.ece
4. Team India and winning the pandemic battle
-As we look to the possible end of the 21-day national lockdown, what next?
Self-reliance is the way
—India has to chart its own strategy, whether it is in planning a staged release from the lockdown or in developing domestic capacity for medical equipment.
—Globalisation lies shredded as we read of French and German officials protesting at the Americans seizing shipments of masks that they had ordered from China, in what is being called “guerre des masques” (war of the masks).
Moving forward
—House-to-house surveillance must be implemented which involves accredited village and block level volunteers partnering front line health workers to identify symptomatic persons for later visits by medical teams.
—The involvement of designated volunteers and community-based organisations can greatly enhance case detection, isolation, counselling, severity-based care and social support.
—Potentially favourable factors for India are the younger age profile and a higher rural proportion of our population compared to China, Europe, the United States or other highly affected countries whose populations are older, urban and highly mobile.
—However, this enjoins us to energetically protect the elderly and rural segments of our population.
—Restricting urban to rural movement to essential goods and essential needs, for at least six weeks after the lockdown ends, will help.
—Further we would need a greater level of testing to detect both asymptomatic and symptomatic persons who have been infected, through random population sampling in different parts of the country.
—We should quickly gear up our testing capacity to meet this mapping mandate. Hotspots should be identified, based on numbers of self-referred symptomatic cases, persons identified on home visits and population survey results.
—These should be ring fenced, with intense search for contacts and active spreaders, with further localised lockdown as needed.
Focus on health services
—We also need to make sure that our health-care system provides timely and competent care to all who need.
—Primary health-care facilities, district hospitals, public and private tertiary care institutions have to gear up with equipment and augment human resources drawn both from trainees and retirees.
—Considering the higher risk to older health-care providers, the first line of care should be formed by younger staff members who will have milder effects even if infected.
—The older staff members can provide supervisory support. This will prevent attrition of the health workforce due to exhaustion or illness.
—Temporary hospitals for treatment and isolation facilities for persons on quarantine may need to be set up at short notice.
— Industry must produce essential medical equipment and drugs to meet our needs and, if capacity permits, assist other countries.
—This has to be our game plan, with flexibility to change the field settings and bowling options as we reassess the situation periodically. Let us get going, to win this match as Team India.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/team-india-and-winning-the-pandemic-battle/article31312597.ece
5. COVID-19 | BSF told to suspend border passes for Bangladesh, Pakistan
-The Border Security Force (BSF) has been asked to suspend all passes given to farmers to tend to crops, especially along the densely populated Bangladesh border, in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
-The border guarding force is in a fix as the West Bengal government is yet to issue guidelines restricting the movement of farmers as the harvest season is on.
-The Ministry has also asked the States to maintain “appropriate vigil on social media” against the circulation of objectionable content, the communication adds.
-The topography in some areas along the border is such that the zero line passes through the houses of villagers, one part in India and the other in Bangladesh.
—There are around 60 villages in North, South 24 Parganas and Nadia districts of South Bengal located right up to the zero line.
—Only 42% of the area is fenced owing to the riverine and complex land boundary.
—India shares 4096.7 km border with Bangladesh and 3323 km border with Pakistan.
About Border Security Force (BSF): It is the border-guarding organisation of India. It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces of India, and was raised in the wake of the 1965 War on 1 December 1965, "for ensuring the security of the borders of India and for matters connected there with".
— It is a paramilitary force charged with guarding India's land border during peacetime and preventing transnational crime at the same, it has various active roles during an outbreak of war.
—It is a Union Government Agency under the administrative control of Ministry of Home Affairs.
—The BSF has its own cadre of officers but its head, designated as a Director-General (DG), since its raising has been an officer from the Indian Police Service.
—It is an Armed Force of the Union of India tasked with various assignments from time to time.
—The BSF has grown exponentially from a few battalions in 1965, to 186 battalions with a sanctioned strength of 257,363 personnel including an expanding air wing, marine wing, an artillery regiment, and commando units.
—It currently stands as the world's largest border guarding force.
—BSF has been termed as the First Line of Defence of Indian Territories.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/covid-19-bsf-told-to-suspend-border-passes-for-bangladesh-pakistan/article31312189.ece
6. Coronavirus | India has enough stock of hydroxychloroquine, says Centre
-The Union government asserted that India had “sufficient buffer” of the much in demand drug hydroxychloroquine (HCQ).
-According to senior government sources, shipments totalling 23 million tablets of HCQ to 13 countries including U.S., Germany, Canada, Brazil, Bahrain, Seychelles, Mauritius and the SAARC neighbouring countries have already been cleared for export.
-The government’s move won it many expressions of gratitude from countries that received clearances for their medical supplies, which had been held up for weeks after the Directorate General of Foreign Trade banned them for export.
-Exports of HCQ and paracetamol were banned last week but the government overturned the ban on April 6, allowing the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) and the Department of Pharmaceuticals to assess requests from various countries and clear their supply. Twenty-four other drugs that were put on a restricted list in March have been cleared for export as well.
-Cargo flights taking HCQ or Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) like chloroquine phosphate, paracetamol and some of the 24 other drugs cleared had been running regularly since April 8, said sources.
About South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC): It is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia.
—Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
—SAARC comprises 3% of the world's area, 21% of the world's population and 4.21% (US$3.67 trillion) of the global economy, as of 2019.
—SAARC was founded in Dhaka on 8 December 1985.
— Its secretariat is based in Kathmandu, Nepal.
—The organization promotes development of economic and regional integration. It launched the South Asian Free Trade Area in 2006.
About Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT): It is the agency of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of the Government of India responsible for administering laws regarding foreign trade and foreign investment in India.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/coronavirus-centre-defends-decision-to-export-hydroxychloroquine/article31311932.ece
7. Covid-19: Ayushman Bharat roped in, private hospitals put on alert
-The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has roped in the National Health Authority (NHA), which manages the largest government-run health insurance programme — Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) or Ayushman Bharat — to identify capacities to admit patients from among 19,840 empanelled hospitals under the scheme.
-The Ministry is also holding consultations with private sector and non-profit hospitals across the country to ramp up facilities.
-The NHA is also charting out the rates to include Covid-19 packages in PMJAY.
-The Ministry has also roped in the NITI Aayog and the Indian Council of Medical Research to study hospital level preparedness in case India shifts to Stage 3 of community transmission where the virus could spread unfettered.
About Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY): It is a flagship scheme of the Indian government's National Health Policy, which aims to provide free health coverage at the secondary and tertiary level to its bottom 40% poor and vulnerable population.
—PM-JAY is the world's largest and fully state sponsored health assurance scheme.
—It was launched in September 2018, under the aegis of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in India.
Key Features
-PM-JAY is a health assurance scheme that covers 10.74 crores households across India or approx 50 crores Indians.
-It provides a cover of 5 lakh per family per year for medical treatment in empanelled hospitals, both public and private.
-It provides cashless and paperless service to its beneficiaries at the point of service, i.e the hospital.
-E-cards are provided to the eligible beneficiaries based on the deprivation and occupational criteria of Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011 (SECC 2011).
-There is no restriction on family size, age or gender.
-All previous medical conditions are covered under the scheme.
-It covers 3 days of hospitalisation and 15 days of post hospitalisation, including diagnostic care and expenses on medicines.
-The scheme is portable and a beneficiary can avail medical treatment at any PM-JAY empanelled hospital outside their state and anywhere in the country.
About National Health Authority or the NHA: It is the apex body responsible for implementing India’s flagship public health insurance/assurance scheme ‘Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana’ (AB-PMJAY).
—NHA has been set-up to implement the PM-JAY at the national level. In the States, SHAs or State Health Agencies in the form of a society/trust have been set up with full operational autonomy over the implementation of this scheme including extending the coverage to non-SECC beneficiaries.
About NITI Aayog: It is a policy think tank of the Government of India, established with the aim to achieve sustainable development goals with cooperative federalism by fostering the involvement of State Governments of India in the economic policy-making process using a bottom-up approach.
—It was established in 2015, by the NDA government, to replace the Planning Commission which followed a top-down model.
—The NITI Aayog council comprises all the state Chief Ministers, along with the Chief Ministers of Delhi and Puducherry, the Lieutenant Governor of Andaman and Nicobar, and a vice-chairman nominated by the Prime Minister.
Reference: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/ayushman-bharat-roped-in-private-hospitals-put-on-alert/article31100732.ece
8. NCW launches domestic violence helpline
-The National Commission for Women (NCW) launched a helpline number — 0721-7735372 to enable those facing domestic violence to send a WhatsApp message to access help.
-In the first week after the lockdown, the NCW recorded more than a two-fold increase in domestic violence and sexual assaults as well as as a three- fold rise in police apathy towards crimes against women.
-It was explained that after a woman sends a message on the number seeking help, the NCW’s complaints and legal cell will contact her and seek specific details about the intervention she wants and her address.
-Following this she will be linked with the local police team or a counsellor from a local NGO or a medical facility or relocated to a One Stop Centre temporarily.
-The messaging facility will also help those women who aren't comfortable making a call because of a live threat to them.
-The NCW has compiled a State-wise list of One Stop Centres as well as nodal police officers who can be contacted immediately.
-It is also working on building a network of counsellors and has sought UN Women’s help for this.
About National Commission for Women (NCW): It is the statutory body of the Government of India, generally concerned with advising the government on all policy matters affecting women.
—It was established in 31 January 1992 under the provisions of the Indian Constitution, as defined in the 1990 National Commission for Women Act.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/ncw-launches-domestic-violence-helpline/article31312219.ece
9. NHRC asks govt. about measures for mentally ill
-The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) asked the Union Ministry of Home Affairs to address the concerns of the mentally ill people on the streets during the lockdown to check the spread of the novel coronavirus.
-The NHRC took cognizance of a complaint about the alleged violation of the human rights of such people and asked the Ministry to inform it, within two weeks, of the arrangements made for them.
About National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India : It is a Statutory public body constituted on 12 October 1993 under the Protection of Human Rights Ordinance of 28 September 1993.It was given a statutory basis by the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993 (PHRA).
—The NHRC is the National Human Rights Commission of India, responsible for the protection and promotion of human rights Composition.
The NHRC consists of:
-A Chairperson, who has been a Chief Justice of India or a Judge of the Supreme Court
-One member who is, or has been, a Judge of the Supreme Court of India
-One member who is, or has been, the Chief Justice of a High Court
-Three Members, out of which at least one shall be a woman to be appointed from amongst persons having knowledge of, or practical experience in, matters relating to human rights
-In addition, the Chairpersons of National Commissions viz., National Commission for Scheduled Castes, National Commission for Scheduled Tribes, National Commission for Women, National Commission for Minorities, National Commission for Backward Classes, National Commission for Protection of Child Rights; and the Chief Commissioner for Persons with Disabilities serve as ex officio members.
-The sitting Judge of the Supreme Court or sitting Chief Justice of any High Court can be appointed only after the consultation with the Chief Justice of Supreme Court.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/nhrc-asks-govt-about-measures-for-mentally-ill/article31312152.ece
10. Revoke order that can weaken law banning sex determination test: AIDWA
-A women’s rights group has written a memorandum to Union Health Minister Harsh Vardhan asking the government to withdraw an order that could weaken the implementation of the law that bans pre-natal sex determination.
-It was referring to a gazette notification issued by the Health Ministry on April 4, which suspended Rule 8, Rule 9(8) and Rule 18A(6) of the Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques (PCPNDT) Act, 1994. This clause deals with the process for renewal of registration of genetic and ultrasound clinic, responsibilities of labs in maintaining and preserving records of all tests, techniques and procedures as well as the duties of district authorities in sharing a quarterly progress report.
-The suspension of these rules throughout the country would mean that clinics and genetic labs can carry on functioning without any scrutiny. This is the only scrutiny that these labs are subjected to, in order to assess their adherence to the basic rules and to ensure that sex selection is not being carried out by them,” the All India Democratic Women’s Association said in a statement.
-About Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques (PCPNDT) Act, 1994 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted to stop female foeticides and arrest the declining sex ratio in India.
The act banned prenatal sex determination. Every genetic counselling centre, genetic laboratory or genetic clinic engaged in counselling or conducting pre-natal diagnostics techniques, like in vitro fertilisation (IVF) with the potential of sex selection (Preimplantation genetic diagnosis) before and after conception comes under preview of the PCPNDT Act and are banned.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/revoke-order-that-can-weaken-law-banning-sex-determination-test-aidwa/article31312186.ece
ECONOMY
1. BCAS extends validity of cortication
-The Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) has extended the validity of refresher training certifications that are mandatory for assigning flight/ground duties to pilots, crew, ground staff and others.
-The validity of the certification is mandatory for assigning flight duties to pilots, crew, aircraft maintenance engineers, ground handling staff etc. The refresher courses update them on the latest technology developments, amendments in International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) norms and latest guidelines issued by the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
-The BCAS conducts at least eight types of refresher courses to the personnel involved in flight operations at the national and regional Aviation Security Training Centres/institutes
-The aviation industry has stringent regulations with regard to flying hours, training and refresher courses to ensure safety and security of passengers, the official said.
-The extension of the validity or eligibility period of the certificate holders would help in uninterrupted services in case the COVID-19 lockdown is lifted and flight operations are allowed, the official said.
About Bureau of Civil Aviation Security: It is an attached office of the Ministry of Civil Aviation (India). It is the regulatory authority for civil aviation security in India.
— It is headed by an officer of the rank of Director general of police and is designated as Director general of Security (Civil Aviation).
—Director General of security (DG BCAS) is the appropriate authority for implementation of Annexure 17(Security: Safeguarding International Civil Aviation Against Acts of Unlawful Interference) to Chicago convention of International Civil Aviation Organization.
—Director General of security (CA) is responsible for the development, implementation and maintenance of the National Civil Aviation Security Programme.
About International Civil Aviation Organization: It is a specialized agency of the United Nations.
It changes the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth.
—Its headquarters is located in the Quartier International of Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
—The ICAO Council adopts standards and recommended practices concerning air navigation, its infrastructure, flight inspection, prevention of unlawful interference, and facilitation of border-crossing procedures for international civil aviation.
— ICAO defines the protocols for air accident investigation that are followed by transport safety authorities in countries signatory to the Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/tamil-nadu/bcas-extends-validity-of-certifications/article31312257.ece
2. Moratorium on repayment puts NBFCs in a spot
-Non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) may face a tough time following the Reserve Bank of India’s recent directive on providing a moratorium on repayment.
-This is because though these entities are providing moratorium to their customers, they still have to continue repaying banks and other borrowers. NBFCs are highly dependent on banks for funding.
-According to Crisil, liquidity pressure will increase for almost 25% of the Crisil-rated NBFCs if collections do not pick up by June 2020.
About NBFC: The most important difference between non-banking financial companies and banks is that NBFCs don't take demand deposits.
— A non-banking financial institution (NBFI) or non-bank financial company (NBFC) is a financial institution that does not have a full banking license or is not supervised by a national or international banking regulatory agency.
— NBFC facilitate bank-related financial services, such as investment, risk pooling, contractual savings, and market brokering.
—Examples of these include insurance firms, pawn shops, cashier's check issuers, check cashing locations, payday lending, currency exchanges, and microloan organizations.
—Operations of non-bank financial institutions are often still covered under a country's banking regulations.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/business/moratorium-on-repayment-puts-nbfcs-in-a-spot/article31312312.ece
3. Removal of tariff ceiling may revive investment in renewables
-The Centre’s decision to remove the tariff ceiling from renewable energy tenders will give the beleaguered industry a much-needed leg-up. Capacity addition in renewables dropped to 9 GW in fiscal 2019, compared with 11-12 GW over the 2017 and 2018 fiscals, and remained subdued through fiscal 2020 as well.
-Crisil Research, however, expected solar weighted average tariff to remain in the current ₹2.50-2.60 per unit range as lower module cost, larger scale of projects, and continued tendering activity in the segment continue to spur competition among players.
-As for wind energy tenders, though tariffs have remained sticky at the ₹2.8 per unit mark, viability remains a concern as the sector grapples with execution challenges on the ground.
Reference:https://www.thehindu.com/business/removal-of-tariff-ceiling-may-revive-investment-in-renewables/article31312243.ece
4. Merged banks get time on bancassurance agreements
-Insurance regulator IRDAI has allowed the four banks, emerging from the recent mega bank merger exercise, to continue for a year with existing bancassurance agreements of the lenders that amalgamated with them.
-“The acquiring bank may continue arrangement with more than three entities in each of the life, general and health categories of insurers for a period of 12 months from the date of merger by transfer of the existing insurance arrangements of the acquired banks to their name,” the regulator said.
-This exemption allows only for transfer of existing insurance arrangements of acquired banks to the acquiring banks and should not be construed as permission by the Authority to enter into new arrangements with other insurers.
As per bancassurance regulations, a bank can only market three life, general and health insurance companies’ products. The banks that have been merged with them also had bancassurance business.
-The IRDAI eventually wants the acquiring bank to retain the existing certificate of registration (COR) to act as a corporate agent and surrender, COR(s) held by acquired banks by submitting written request to the Authority.
-The surrender shall be allowed subject to an undertaking from the acquiring bank regarding servicing of existing policyholders of acquired banks.
About Bancassurance: It is a relationship between a bank and an insurance company that is aimed at offering insurance products or insurance benefits to the bank's customers. In this partnership, bank staff and tellers become the point of sale and point of contact for the customer. Bank staff are advised and supported by the insurance company through wholesale product information, marketing campaigns and sales training. The bank and the insurance company share the commission. Insurance policies are processed and administered by the insurance company.
About Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI): It is an autonomous, statutory body tasked with regulating and promoting the insurance and re-insurance industries in India. It was constituted by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999, an Act of Parliament passed by the Government of India. The agency's headquarters are in Hyderabad, Telangana, where it moved from Delhi in 2001.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/business/merged-banks-get-time-on-bancassurance-agreements/article31312325.ece
INTERNATIONAL
1. Saudi, Russia want oil cuts finalised at G20 talks
-Top oil nations were finalising a deal at G20 talks for big output cuts to lift prices slammed by the COVID-19 crisis with Russia and Saudi Arabia taking a lion’s share and signs the United States might take unprecedented moves to help.
-Riyadh, Moscow and its allies, which make up the informal OPEC+ group, had forged a pact to curb crude production by the equivalent of 10% of global supplies in marathon talks on Thursday and said they wanted others to cut a further 5%.
-But efforts to conclude the OPEC+ deal hit the buffers when Mexico refused to sign up in full.
-However, the Mexican President said Donald Trump had told him he might make cuts on Mexico’s behalf, even though the U.S. President has given no public indication Washington would join in the cuts and has instead threatened Saudi Arabia with tariffs and other measures if it did not resolve the oil market crisis.
-Major oil markets were closed on Friday as the G20 energy minister held a video conference, hosted by Saudi Arabia, but prices failed to rally after Thursday’s cuts.
About Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC): It is an intergovernmental organization of 14 nations, founded on 14 September 1960 in Baghdad by the first five members (Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela), and headquartered since 1965 in Vienna, Austria. As of September 2018, the 14 member countries accounted for an estimated 44 percent of global oil production and 81.5 percent of the world's "proven" oil reserves, giving OPEC a major influence on global oil prices that were previously determined by the so-called "Seven Sisters" grouping of multinational oil companies.
—A larger group called OPEC+ is formed in late 2016 to have more control on global crude oil market.
About G20 (or Group of Twenty): It is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability, the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers and foreign ministers, have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one organization.
— Membership of the G20 consists of 19 individual countries plus the European Union. The EU is represented by the European Commission and by the European Central Bank.
— Collectively, the G20 economies account for around 90% of the gross world product (GWP), 80% of world trade (or, if excluding EU intra-trade, 75%), two-thirds of the world population, and approximately half of the world land area.
-The heads of the G20 nations held summits twice in 2009 and twice in 2010. Since the November 2011 Cannes summit, G20 summits have been held annually.
Reference:https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/saudi-russia-want-oil-cuts-finalised-at-g20-talks/article31312661.ece



1.png)
