DAILY NEWS ANALYSIS 18 DECEMBER
HEALTH
Packaged foods breach safe limits of salt, fat: CSE study
An array of packaged snacks and fast foods breach safe limits of salt and fat content, says a laboratory analysis by the Centre for Science and Environment. The CSE found that per 100 g, one packet of packaged nuts, soup or noodles had salt and fat well over the limit.

Details:
- The agency tested salt, fat, trans-fat and carbohydrates in 33 popular “junk foods”, which consisted of 14 samples of chips, salted snacks, instant noodles and instant soup, and 19 samples of burgers, fries, fried chicken, pizzas, sandwiches and wraps.
- The organisation relied on the concept of the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) — a daily ceiling on the amount of salt, fat, carbohydrates and trans fats.
- The CSE relied on the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) — the daily ceiling for salt, fat, carbohydrates and trans-fat. The RDA is based on scientific consensus and has been agreed upon by the World Health Organisation and the National Institute of Nutrition in India.
Limits of RDA:
- Ideally, no more than 5 gm of salt, 60 gm of fat, 300 gm carbohydrate and 2.2 gm of trans fat should be consumed by an adult every day.
- The RDA from each breakfast, lunch and dinner should be no more than 25% and that from snacks no more than 10%.
Legal Provisions:
- As per proposed draft of Food Safety and Standards (Labelling and Display) Regulations, packaged food companies will need to declare nutritional information such as calories (energy), saturated fat, trans-fat, added sugar and sodium per serve on the front of the pack.
- The food labels are also required to declare, per serve percentage contribution to RDA on the front of the pack.
Way Forward:
- All of the popular snacks and fast foods ought to be displaying a ‘Red Octagon’, a warning symbol employed in packaged foods in Chile and Peru.
- The Red Octagon, which should be printed on the front of the pack has a number and name of the food component within that indicates how widely off the RDA a particular ingredient is. Thus a Red “3.1, Salt” on a pack of Lay’s India’s Magic Masala by PepsiCo indicates that the salt it contains is 3.1 times the RDA for snacks.
Advisory on Gujarat model of delivery kicks up row
At a time, when obstetricians are fighting to bring down the incidence of post-partum haemorrhage (PPH), the leading cause of maternal mortality in India, a recent advisory issued by the Union Health Ministry to States to adopt the Gujarat model of “non-interventional approach during the final stages of labour” as the best obstetric practice has kicked up a storm.
Challenges to advisory:
- Advisory runs contrary to WHO recommendations and the best of proven international advisories and this can undo all their efforts to reduce PPH and prevent mothers bleeding to death.
- The new advisory, however, advocates the physiological management or the “hands-off” approach during the third stage of labour.
- The major concern is about the delayed administration of oxytocin. According to experts, uterine atony (failure of uterus to contract), followed by massive haemorrhage, occurs in the third and fourth stage. Immediate administration of oxytocin as soon as foetus is delivered contracts the uterus and helps the expulsion of placenta without blood loss.
- The WHO-recommended protocol of delaying cord clamping after birth is enough to allow the foetus more blood from placenta.
- The Ministry says its advisory is meant to make childbirth a “natural and positive experience” for women.
Kerala Model:
- Kerala managed to bring down the PPH numbers drastically, when in 2013 it developed and implemented the Quality Standards in Obstetric Care, in association with the NICE International. One of the key principles adopted is the WHO-recommended strategy of “active management of third stage of labour” (AMTSL).
The Indian Medical Association (IMA) leadership demands that the Centre leave clinical decision-making to doctors and that the advisory be withdrawn as it sends out contradictory messages to nurses and birthing assistants.
SECURITY
Limit deputation of IPS officers in paramilitary at 25%: RS panel
A Rajya Sabha committee has objected to the overuse of the Central Armed Police Force (CAPF) for rigorous internal security and election-related duties to the extent that even the reserved battalions are deployed not giving them enough time for rest and recuperation.
Committee recommendations:
- The defence forces personnel are being paid Military Service Pay in view of the risk to life , social and family isolation and argued that the CAPF also deserves similar incentive in the form of Paramilitary Service Pay as they face similar risks and isolation.
- 7th Pay Commission and Committee on Allowance did not agree to such special pay, the committee insisted on doing the needful.
- The reserved battalions, which are to be used judiciously and provided rest for being in a state of preparedness are engaged in duties such as internal security and counter-insurgency, which are quite rigorous.
- Urged the MHA to draw a line to allow much required rest and recuperation to the personnel and adhere to the laid down policy on “rest and recuperation”.
- Urged the Ministry to put in place an institutional mechanism to deal with issue of suicides in CAPF.
- To boost the morale of the CAPFs, the committee insisted on limiting the deputation of officers from the IPS and the armed forces to CAPFs at 25% and the CAPFs cadres should be given the opportunity to become the Director-General of respective forces.
Central Armed Police Force (CAPF):
The Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) refer to the uniform nomenclature of security forces in India under the authority of the Ministry of Home Affairs. The seven security forces under CAPF are as follows:
- Assam Rifles
- Border Security Force (BSF)
- Central Industrial Security Force (CISF)
- Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF)
- Indo Tibetan Border Police (ITBP)
- National Security Guard (NSG)
- Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB)
ECONOMY
Market rally may get additional $2.5 billion fuel
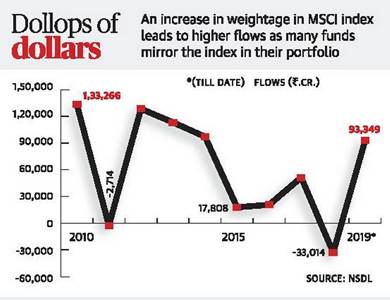
The coming months could see incremental foreign flows amounting to around $2.5 billion in Indian equities as the country’s weightage increases in the MSCI Emerging Markets (EM) index on account of the increase in foreign investment limit in listed entities.
The government has confirmed its move to implement its Budget announcement relating to increasing the statutory limit for foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) in a company from 24% to the sectoral foreign investment limit with effect from April 1, 2020.
MSCI Index:
- The MSCI Emerging Markets Index stands for Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) and is an index used to measure equity market performance in global emerging markets.
- The MSCI Emerging Markets Index consists of 26 developing economies including Argentina, Brazil, Chile, China, Colombia, Czech Republic, Egypt, Greece, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, Pakistan, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Qatar, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates.
SOCIETY
No State-wise minority classification, says Supreme Court
Religion has no borders, Chief Justice of India Sharad A. Bobde said, as the Supreme Court dismissed a petition to recognise Hindus as minorities in the States, where they are low in population.
Petitioner’s arguments:
- Frame guidelines to “identify and define” religious minorities in every State, especially where Hindus are in a minority to protect their culture and interests.
- The Hindus were not declared a minority community in several States and they were deprived of the benefits of the status.
- For the purposes of Articles 29 (protection of the interests of minorities) and 30 (the right of minorities to administer educational institutions) of the Constitution, it was necessary that the religious and linguistic minorities be determined State-wise on the basis of the numeric proportions of various communities in each State.
Court observation:
- Religion is beyond all borders, especially political borders. It has to be taken on a pan-India basis. Cultures intersect across religious barriers in India.
Telling Numbers: India 112th out of 153 countries in gender parity index
India has ranked 112th among 153 countries in the annual Global Gender Gap Index for 2020, published by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
Reports Parameters:
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Educational Attainment
- Health and Survival
- Political Empowerment
Methodology:
- Integrates the latest statistics from international organizations and a survey of executives.
Objectives of Report:
- As a compass to track progress on relative gaps between women and men on health, education, economy and politics.
- Annually, stakeholders within each country are able to set priorities relevant in each specific economic, political and cultural context.
Results:
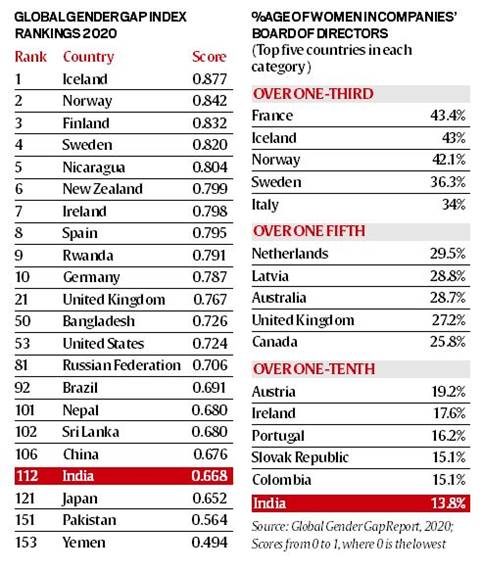
Key Findings:
- Globally, the average (population-weighted) distance completed to gender parity is at 68.6%, which is an improvement since last edition.
- The largest gender disparity is in political empowerment. Only 25% of the 35,127 seats in parliaments around the world are occupied by women and only 21% of the 3,343 ministers are women.
- Projecting current trends into the future, the overall global gender gap will close in 99.5 years, on average, across the 107 countries covered continuously since the first edition of the Report.
PIB
GEM launches National Outreach Programme - GEM Samvaad
About GEM Samvaad:
- A national outreach programme was launched by the Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce and Industry called the ‘GeM Samvaad’.
- The outreach programme will take place with stakeholders across the country and with local sellers in order to facilitate on-boarding of local sellers on the marketplace while catering to specific requirements and procurement needs of buyers.
- GeM Samvaad is essentially a dialogue between buyers and sellers. Sellers and buyers can look for new opportunities also in this outreach programme.
- The outreach programme will take place from December 2019 to February 2020 and will cover all the States and UTs of the country.
About GEM:
- It is the national public procurement portal offering end to end solutions for all procurement needs of Central and State Government Departments, PSUs, autonomous institutions and local bodies.
- Since its launch in 2016, it has transformed public procurement in the country by leveraging technology and making procurement contactless, paperless, and cashless.
- GeM has more than 15 lakh products and around 20,000 services, more than 3 lakh registered sellers and service providers and more than 40,000 government buyer organizations.
- State Departments and organisations and public sector enterprises (PSEs) have been using GeM for their buying needs. Sellers from the States are also benefiting through access to the national public procurement market using the portal.
- GeM’s vision is “to affect an evolution in public procurement promoting a transparent, efficient and inclusive marketplace.”
Shri Ravi Shankar Prasad launches National Broadband Mission
The Union Minister for Communications, Law & Justice and Electronics and Information Technology launched the National Broadband Mission.
About the National Broadband Mission (NBM):
The vision of the NBM is to fast-track growth of digital communications infrastructure, bridge the digital divide, facilitate digital empowerment and inclusion and provide affordable and universal access to broadband for all.
A key objective of the Mission is to provide broadband to all villages by 2022.
Some of the other objectives are:
- Facilitate universal and equitable access to broadband services across the country and especially in rural and remote areas.
- Laying of incremental 30 lakhs route km of Optical Fiber Cable (OFC) and increase in tower density from 0.42 to 1.0 tower per thousand of population by 2024.
- Significantly improve quality of services for mobile and internet.
- Develop innovative implementation models for Right of Way (RoW) and to work with States/UTs for having consistent policies pertaining to expansion of digital infrastructure including for RoW approvals required for laying of OFC.
- Develop a Broadband Readiness Index (BRI) to measure the availability of digital communications infrastructure and conducive policy ecosystem within a State/UT.
- Creation of a digital fiber map of the digital communications network and infrastructure, including Optical Fiber Cables and towers across the country.
- Investment from stakeholders of USD 100 billion (Rs 7 Lakh Crore) including Rs 70,000 crore from Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF).
- Address policy and regulatory changes required to accelerate the expansion and creation of digital infrastructure and services.
- Work with all stakeholders including the concerned ministries/departments/agencies and the Ministry of Finance for enabling investments for the Mission.
Telecom scene in India:
- The government has introduced this new broadband mission to meet the ever-growing needs for the internet.
- Right now, in India, an average person is consuming 9.77GB data per month, which is up by a staggering 1120% compared to 2014.
- Telecom subscribers are also growing at a rapid pace in the country.
- India had just 251.59 million internet subscribers back in 2014, however, the number saw an increase of 165% and reached 665.31 in 2019.
- Mobile subscribers were just 907.42 in 2014 and it has been increased to 1173.75 in 2019.
Successful launch of two BrahMos missiles from land and air platforms
Defence Research & Development Organisation(DRDO), Indian Air Force (IAF) and BrahMos jointly successfully conducted two BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles tests, one each from land and air platforms.
About BrahMos:
- The BrahMos is a ramjet supersonic cruise missile of a short-range developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Russian Federation’s NPO Mashinostroeyenia.
- BrahMos was named after two major rivers of India and Russia: Brahmaputra and Moskva.
- Special Features of BrahMos:
- Stealth Technology
- Advanced guidance system
- High Target Accuracy (irrespective of weather conditions)
- Constant supersonic speed
- Operates on ‘Fire and Forget’ Principle
- BrahMos can be launched from land, aircraft, ships and even submarines.
- One of the heaviest missiles, weighing up to 2.5 tonnes
Annular Eclipse of the Sun on 26th December
Details:
- From India, the annular phase will be visible in the morning after sunrise from some places within a narrow corridor of the southern part of the country (parts of Karnataka, Kerala & Tamil Nadu) and it will be seen as partial solar eclipse from the rest part of the country.
- In India, the obscuration of the Sun by the Moon at the time of the greatest phase of the annular eclipse will be nearly 93%. As one moves towards the north and south of the country from the annular path, the duration of the partial eclipse decreases.
- The next solar eclipse will be visible from India on June 21, 2020. It will be an annular solar eclipse.
Solar Eclipse:
- A solar eclipse occurs on a new moon day when the Moon comes in between the Earth and the Sun and when all the three celestial bodies are aligned.
- An annular solar eclipse will occur when the angular diameter of the Moon falls short of that of the Sun so that it cannot cover up the latter completely. As a result, a ring of the Sun’s disk remains visible around the Moon.
- The eclipsed Sun should not be viewed with the naked eye, even for a very short time. It will cause permanent damage to the eyes leading to blindness even when the moon covers most portions of the Sun.
- The safe technique to observe the solar eclipse is either by using a proper filter like aluminized Mylar, black polymer, welding glass of shade number 14 or by making a projection of Sun’s image on a whiteboard by telescope.
CSIR and the National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), France ink MoU for Promotion and Support of Scientific and Technological Research
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), India and the National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), France to establish a framework for cooperation between the two towards promotion and support of scientific and technological research.
Details:
- In view of the potentially beneficial and synergistic cooperation possibilities for translating science into technology CSIR and CNRS may explore strengthening their cooperation to foster joint innovation and transfer of technologies applicable to India or/and France and to other nations.
- This cooperation could include sharing good practices, promoting technology transfer and enhancing industry-academia cooperation.
- The broad research areas of mutual interest include biotechnology including plant and marine biotechnology; health research; environment and climate change studies; engineering science and technology; material science and technology; energy science and technology and water research.
About the CSIR:
- Set up in 1942 as an autonomous body, CSIR is now the largest publically funded multi-disciplinary industrial R&D organisation in India under the administrative supervision of the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- It conducts research in a wide spectrum of science and technology domains ranging from aerospace, instrumentation, environmental engineering, mining, minerals & materials, housing and structures to oceanography, chemicals, drugs, and biotechnology.
- CSIR provides technological intervention in many areas with regard to societal efforts including environment, health, drinking water, food, housing, energy, and farm and non-farm sectors.
- CSIR India caters to the technological needs of Indian as well as foreign industries based in India and abroad.
About the CNRS:
- Founded in 1939, CNRS is the largest fundamental research organisation in Europe.
- CNRS is an interdisciplinary public research organisation under the administrative supervision of the French Ministry of Higher Education and Research.
- CNRS ranks among the leading global research institutions for its excellent research and innovation achievements and has 22 Nobel Laureates and 12 Field medal recipients.



1.png)
