DAILY NEWS ANALYSIS 22 FEBRUARY
ECONOMY
Treating medical devices on par with drugs will raise costs: ICRA
ICRA comment:
- The Centre’s decision to notify all medical devices as drugs and bringing them under purview of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, from April is bound to push up the cost.
- Companies will now have to obtain approval to manufacture, import and sell medical devices in the country thus increasing the cost of compliance, leading to longer lead time and higher expenses in launching new products.
- It is believed that much of the price hike will be passed on to the patients, cushioning the impact on the profitability margin of hospitals.
About the notification:
- The notification covers all devices used for diagnosis, life support, treatment of any ailment and the ones used to disinfect other medical devices.
- It also covers the software used in medical instruments.
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation will be regulating the medical devices.
- The order will come into effect on April 1, 2020.
- The consumables/devices will be brought under regulation in a phased manner up till April 1, 2021.
- The rules will be voluntary for the first 18 months and will become mandatory after that.
- Syringes, heart valves, I.V. cannules, surgical dressing, and cardiac stents will come under the regulation on the effective date, while ultrasound equipment will come under the regulation on November 1, 2020.
About Central Drugs Standard Control:
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is the Central Drug Authority for discharging functions assigned to the Central Government under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act.
- Within the CDSCO, the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) regulates pharmaceutical and medical devices, under the gamut of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The DCGI is advised by the Drug Technical Advisory Board (DTAB) and the Drug Consultative Committee (DCC).
- Its major functions are regulatory control over the import of drugs, approval of new drugs and clinical trials.
Scientists oppose study into ‘qualities’ of indigenous cows
At least 400 scientists have petitioned the Department of Science & Technology (DST) to withdraw a proposal that solicits research into indigenous cows.
Scientist concerns:
- Research programme appeared to endorse the belief that indigenous cows had “special” and “unique” qualities .
- This has opened the possibility of money being “wasted to investigate imaginary qualities derived from religious scriptures”.
- The programme did not encourage fair comparison with other breeds of cows around the world or other bovine species within India.
- The proposal was “drafted unscientifically from start to finish”.
- The scientific funding for several research programmes is stalled and researchers are not getting their fellowships on time, it was “infuriating” that the DST was ready to fund such a “dubious” scheme.
Government arguments:
- All research proposals by scientists under the programme would be vetted by qualified scientists and each one of them accepted — or rejected — on merit.
- Concerns on apparent bias or widening the ambit to include more bovines could be passed on to the scientist committee evaluating the proposals.
- This is a programme that could unearth new information and new ideas and was certainly worth pursuing.
About SUTRA PIC (Scientific Utilisation Through Research Augmentation-Prime Products from Indigenous Cows):
- It has the Department of Biotechnology, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the Ministry for AYUSH (Ayurveda, Unani, Siddha, Homoeopathy) among others and the Indian Council of Medical Research as partners.
Five Themes:
- Uniqueness of Indigenous Cows,
- Prime-products from Indigenous Cows for Medicine and Health,
- Prime-products from Indigenous Cows for Agricultural Applications,
- Prime-products from Indigenous Cows for Food and Nutrition,
- Prime-products from indigenous cows-based utility items.
Purpose of the scheme:
- Perform scientific research on complete characterisation of milk and milk products derived from Indian indigenous cows;
- Scientific research on nutritional and therapeutic properties of curd and ghee prepared from indigenous breeds of cows by traditional methods;
- Development of standards for traditionally processed dairy products of Indian-origin cow.
Forex reserves rise to record $476 billion
The country’s foreign exchange reserves swelled by $3.091 billion to a lifetime high of $476.092 billion in the week to February 14.
Foreign exchange reserves include foreign banknotes, foreign bank deposits, foreign treasury bills, and short & long-term foreign government securities, as well as gold reserves, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) and International Monetary Fund (IMF) reserve positions.
Importance of foreign reserve:
- At $476 billion, the country’s import cover is now over 11 months.
- Import Cover measures the number of months of imports that can be covered with foreign exchange reserves available with the central bank of the country.
- Will give the central bank the firepower to act against any sharp depreciation of the rupee.
- RBI intervenes in the foreign exchange market to curb volatility and does not target a particular level of exchange rate.
‘Adopt pragmatic approach on cigarette tax’
The Federation of All India Farmer Associations (FAIFA), a tobacco farmers body, has urged the Centre government to adopt a pragmatic approach on cigarette taxation.
Argument of organisation:
- Increase in National Calamity Contingent Duty (NCCD) on cigarettes, proposed in the Union Budget 2020-21, will have an adverse impact on the livelihood of Indian Flue Cured Virginia (FCV) tobacco farmers as the tax increase will provide a further boost to the smuggled cigarette trade.
- Indiscriminate increase in excise duty on cigarettes will result in reduction in legal cigarette production .
- It will reduce the tobacco purchases of domestic manufacturers, impacting market prices for farmers and putting more pressure on farmer’s earnings and causing further stress.
- Appealed to the government to include Tobacco in Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Product (RoDTEP) scheme and encourage exports through aggressive promotion schemes.
- Urged the government to take strict action against illegal market and totally curb the illicit trade in the country.
POLITY
Amit Shah-led Group of Ministers meets on Juvenile Justice Act
Meeting was called to discuss the amendments in Juvenile Justice act.
The 2015 Act addressed two key issues:
- “Apprehension, detention, prosecution, penalty or imprisonment, rehabilitation and social re-integration of children in conflict with law”
- “Procedures and decisions or orders relating to rehabilitation, adoption, re-integration and restoration of children in need of care and protection”.
About Juvenile Justice act:
- Change in nomenclature from ‘juvenile’ to ‘child’ or ‘child in conflict with law’, across the act to remove the negative connotation associated with the word “juvenile”;
- Inclusion of several new definitions such as orphaned, abandoned and surrendered children;
- Petty, serious and heinous offences committed by children;
- Clarity in powers, function and responsibilities of Juvenile Justice Board (JJB) and Child Welfare Committee (CWC);
- Clear timelines for inquiry by Juvenile Justice Board (JJB);
- Special provisions for heinous offences committed by children above the age of sixteen year;
- Separate new chapter on Adoption to streamline adoption of orphan, abandoned and surrendered children;
- Inclusion of new offences committed against children;
- Mandatory registration of Child Care Institutions.
Broad Provisions:
- The Juvenile Justice Board is given the option to transfer cases of heinous offences by such children to a Children’s Court (Court of Session) after conducting preliminary assessment.
- To streamline adoption procedures for orphan, abandoned and surrendered children, the existing Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) is given the status of a statutory body to enable it to perform its function more effectively.
- Processes have been streamlined with timelines for both in-country and inter-country adoption including declaring a child legally free for adoption.
- Under the institutional care, children are provided with various services including education, health, nutrition, de-addiction, treatment of diseases, vocational training, skill development, life skill education, counselling etc. to help them assume a constructive role in the society.
- Several new offences committed against children are included in the Act. These include: sale and procurement of children for any purpose including illegal adoption, corporal punishment in child care institutions, use of child by militant groups, offences against disabled children and, kidnapping and abduction of children.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/gom-meets-on-juvenile-justice-act/article30883312.ece
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
FATF places Iran on black list
Reasons behind Iran on being black list:
- It failed to comply with international anti-terrorism financing norms.
- Iran’s failed to enact the Palermo and Terrorist Financing Conventions in line with the FATF Standards.
Impact of black list:
- More scrutiny of transactions with Iran,
- Tougher external auditing of financing firms operating in the country
- Extra pressure on the few foreign banks and businesses still dealing with Iran.
- The consequence of (Iran’s) inaction is higher costs of borrowing and isolation from the financial system.
Other than Iran, only North Korea is in black list.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/fatf-places-iran-on-black-list/article30883377.ece
Pakistan retained on grey list of FATF

FATF comment on Pakistan:
- Asked to complete the 27-point action plan it has been given by June 2020 or face being put on the “black list”.
- Expressed concern on Pakistan’s failure to complete its action plan in line with the agreed timelines and in light of the Terror Financing risks emanating from the jurisdiction.
- Pakistan needs to continue to work on eight specific areas:
- Demonstrating it is “identifying and investigating” all terror financing activity in the country,
- Freezing the funds of all designated terrorists
- Its prosecutions result in “effective, proportionate and dissuasive sanctions” against all terror entities in Pakistan.
Pakistan is one of the 12 countries on the “grey list” or “other monitored jurisdictions” that are being reviewed for actions to stop terror financing and money laundering.
Impact of Grey list:
- If Pakistan continues on the Grey List or is put in Dark Grey List, it will be very difficult for the country to get financial aid from the IMF, the World Bank and the European Union, making its financial condition more precarious.
- Such action could include calling upon global financial institutions to give special attention to business relations and transactions with Pakistan.
About FATF:
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an inter-governmental body established in 1989 by the Ministers of its Member jurisdictions.
- The objectives of the FATF are to set standards and promote effective implementation of legal, regulatory and operational measures for combating money laundering, terrorist financing and other related threats to the integrity of the international financial system.
- The FATF has developed a series of recommendations that are recognised as the international standard for combating of money laundering and the financing of terrorism and proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
- FATF maintains the current list of nations: FATF blacklist (formally called the “Call for action”) and the “FATF grey list” (formally called the ‘”Other monitored jurisdictions”).
- FATF Blacklist carried with it no formal sanction, in reality, a jurisdiction placed on the FATF Blacklist often found itself under intense financial pressure.
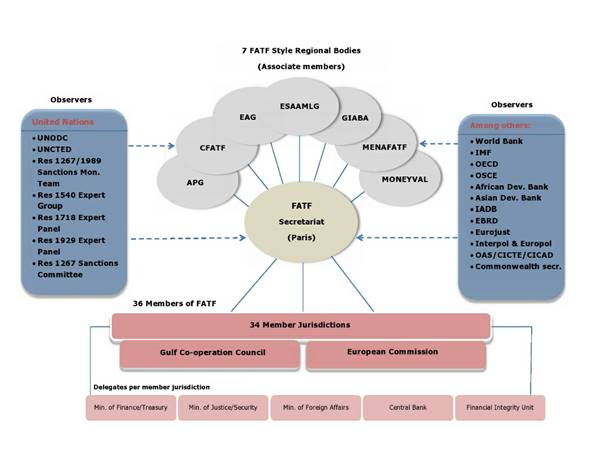
The 36 countries include mostly developed Western nations, but also China, Hong Kong (China), Malaysia and Turkey.
- Moving out of grey list requires at least 15 out of 36 votes.
- Resisting to black list requires three votes minimum.
India is a voting member of the FATF and APG, and co-chair of the Joint Group where it is represented by the Director General of India’s Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU).
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/fatf-places-iran-on-black-list/article30883377.ece
India, Maldives agree to take on terrorism, radicalisation
Joint Statement by India and Maldives:
- Focus on expansion of bilateral cooperation between India and Maldives in diverse fields, including policing and law enforcement, counter-terrorism, counter-radicalisation, organised crime, drug trafficking and capacity building.
- Focus on bilateral cooperation in the fields of counter-terrorism and counter-radicalisation.



1.png)
