Fluidized Bed Gasification Technology

Disclaimer: No Copyright infringement intended.
Context
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) has developed the fluidized bed gasification technology suitable for high ash Indian coals to produce syngas and then convert syngas to methanol with 99% purity.
- This technology will help the country move towards the adoption of clean technology and promote the use of methanol as a transportation fuel (blending with petrol), thus reducing crude oil imports.
Gasification
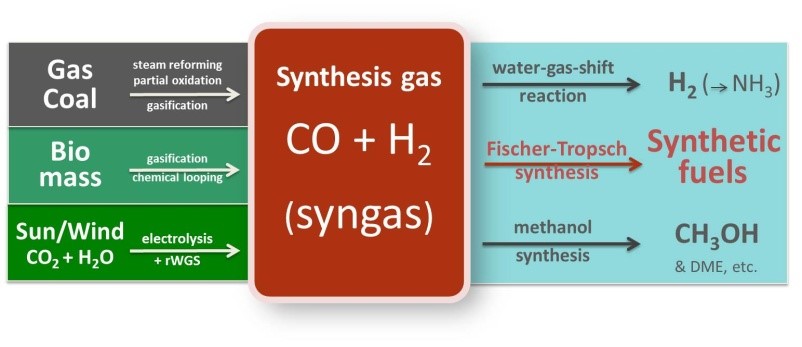
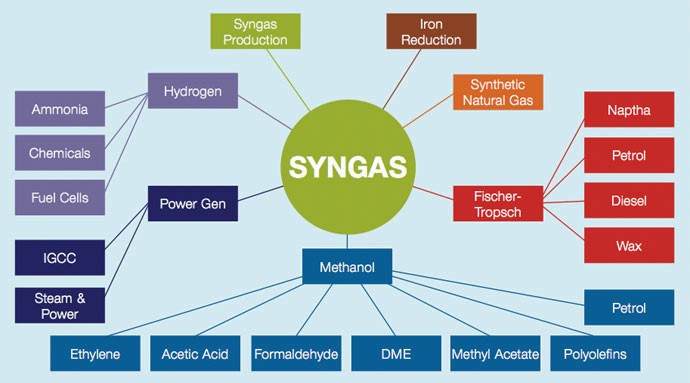
- Gasification is a technological process that can convert any carbonaceous (carbon-based) raw material such as coal into fuel gas, also known as synthesis gas (syngas for short).
- The broad process of converting coal into methanol consists of conversion of coal to synthesis (syngas) gas, syngas cleaning and conditioning, syngas to methanol conversion, and methanol purification.
- Coal to methanol plants in most countries are operated with low ash coals.
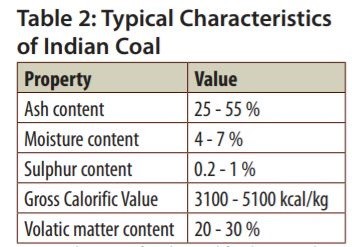
- Handling of high ash and heat required to melt this high amount of ash is a challenge in the case of Indian coal, which generally has high ask content.
- In order to overcome this challenge, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) has developed the fluidized bed gasification technology suitable for high ash Indian coals to produce syngas and then convert syngas to methanol with 99% purity.
What is fluidized bed gasification?
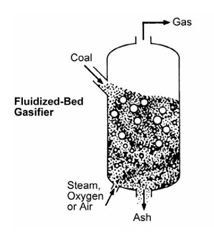
- Fluidized-bed gasifiers suspend feedstock particles/coal in an oxygen-rich gas so the resulting bed within the gasifier acts as a fluid.
- These gasifiers employ back-mixing, and efficiently mix feed coal particles with coal particles already undergoing gasification.
- To sustain fluidization, or suspension of coal particles within the gasifier, coal of small particles sizes (<6 mm) is normally used.
|
- The gasifiers normally operate at moderately high temperature to achieve an acceptable carbon conversion rate (e.g., 90-95%).
- However, the operating temperatures are usually less than the ash fusion temperature so as to avoid clinker formation and the possibility of de-fluidization of the bed.
- This, in turn means that fluidized-bed gasifiers are best suited to relatively reactive coals, low rank coals, and other fuels such as biomass.
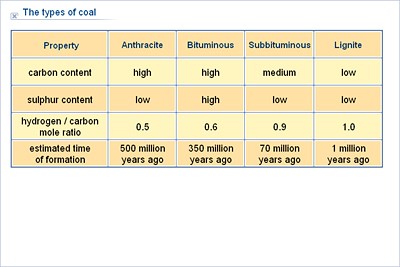
Types of Coal
Coal in India: Key Pointers
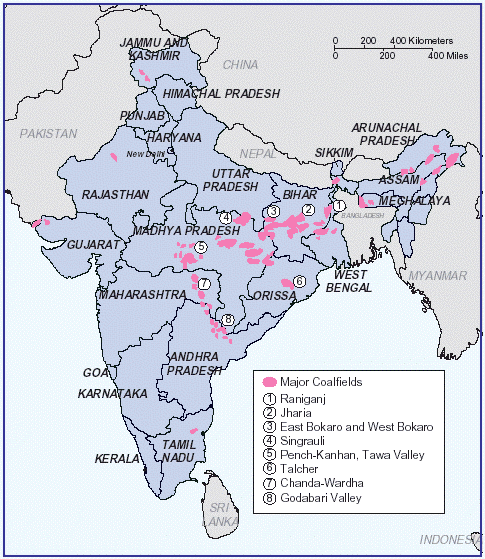
- Jharkhand top the list of India's coal reserves — at more than 26% — and production.
- The state's main coal-mining centres are Jharia, Bokaro, Auranga, Giridh, Dhanbad, Ramgarh, Karanpur and Hutar.
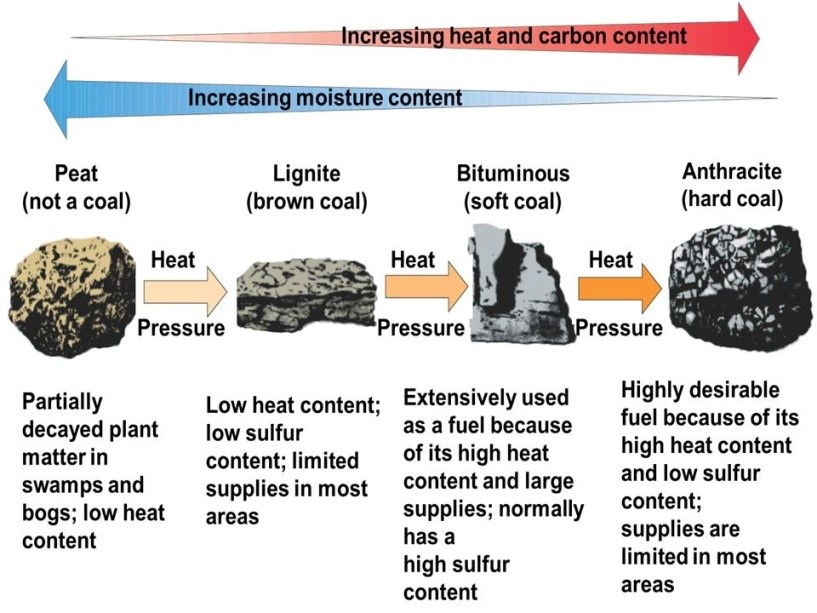
- Anthracite (more than 80% carbon content) is the best quality of coal. In India, it is found only in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Bituminous (60 to 80 % Carbon Content) is the second best quality of coal.
- It is the most commonly used type of coal for electricity generation in India.
- Most of bituminous coal is found in Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh.



1.png)
